Awesome
<img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/stefangabos/zebrajs/master/docs/images/logo.png" alt="zebrajs" align="right">Zebra Dialog 
A small, compact, mobile-friendly and highly configurable jQuery plugin for creating responsive modal dialog boxes
A modal dialog box is a focused interface element that prompts users to take action before returning to the main application. These dialogs are commonly used to capture user attention, deliver important information, confirm actions, or highlight warnings and errors. By temporarily blocking interaction with the rest of the page, modal windows ensure that users address critical tasks or notifications before proceeding, making them a fundamental part of modern web applications.
Zebra Dialog is a small (~12KB minified, 3KB gzipped), compact (one JavaScript file, no dependencies other than jQuery 1.7.0+), mobile-friendly and highly configurable jQuery plugin for creating responsive modal dialog boxes, meant to replace native JavaScript alert, confirm and prompt dialog boxes.
Can also be used as a notification widget (when configured to show no buttons and to close automatically) for updates or errors, without distracting users from their browser experience by displaying obtrusive alerts.
Features
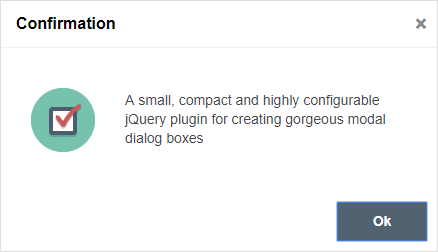
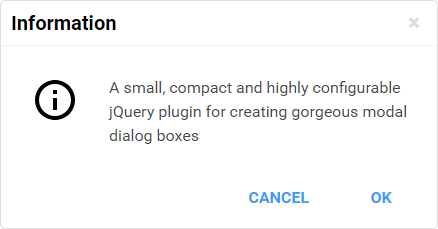
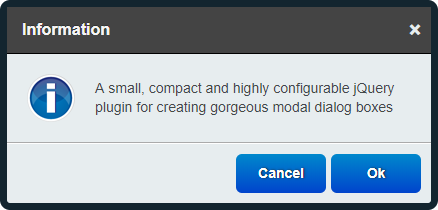
- great looking dialog boxes, out of the box, with 3 beautiful themes included
- 6 types of dialog boxes available: confirmation, error, information, prompt, question and warning
- content can also be added through AJAX calls, iFrames or from inline elements (together with attached events)
- easily customisable appearance by editing the CSS file
- create modal or non-modal dialog boxes
- easily add custom buttons
- position the dialog box wherever you want - not just in the middle of the screen
- dialog boxes are draggable
- callback functions can be used for further customisations
- use callback functions to handle users' choice
- works on mobile devices
- works in pretty much any browser (Chrome, Firefox, Safari, Edge, Opera, Internet Explorer 6+)
For the classic theme, the icons used for confirmation, information, error and question dialog boxes are made by DryIcon while the warning icon is made by Function Design & Development Studio (website is not online anymore).
For the flat theme, the icons used are made by Elegant Themes
For the materialize theme theme, the icons used are taken from Google's Material Design "design language".
🎂 Support the development of this project
Your support means a lot and it keeps me motivated to keep working on open source projects.<br> If you like this project please ⭐ it by clicking on the star button at the top of the page.<br> If you are feeling generous, you can buy me a coffee by donating through PayPal, or you can become a sponsor.<br> Either way - Thank you! 🎉
<img src="https://img.shields.io/github/stars/stefangabos/zebra_dialog?color=green&label=star%20it%20on%20GitHub" width="132" height="20" alt="Star it on GitHub"> 
Demo
See the demos
Requirements
Zebra Dialog has no dependencies other than jQuery 1.7.0+
Installation
Zebra Dialog is available as a npm package. To install it use:
# the "--save" argument adds the plugin as a dependency in packages.json
npm install zebra_dialog --save
How to use
First, load jQuery from a CDN and provide a fallback to a local source like:
<script src="https://code.jquery.com/jquery-3.7.1.min.js"></script>
<script>window.jQuery || document.write('<script src="path/to/jquery-3.7.1.js"><\/script>')</script>
Load the Zebra Dialog jQuery plugin:
<script src="path/to/zebra_dialog.min.js"></script>
Alternatively, you can load Zebra Dialog from JSDelivr CDN like this:
<!-- for the most recent version, not recommended in production -->
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/zebra_dialog@latest/dist/zebra_dialog.min.js"></script>
<!-- for a specific version -->
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/zebra_dialog@3.0.6/dist/zebra_dialog.min.js"></script>
<!-- replacing "min" with "src" will serve you the non-compressed version -->
Load the style sheet file from a local source
<link rel="stylesheet" href="path/to/theme/zebra_dialog.min.css">
...or from JSDelivr CDN
<!-- for the most recent version of the "flat" theme -->
<link
rel="stylesheet"
href="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/zebra_dialog@latest/dist/css/flat/zebra_dialog.min.css">
<!-- for the most recent version of the "default" theme -->
<link
rel="stylesheet"
href="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/zebra_dialog@latest/dist/css/default/zebra_dialog.min.css">
<!-- replacing "min" with "src" will serve you the non-compressed version -->
Now, within the DOM-ready event do
$(document).ready(function() {
// show a dialog box when clicking on an element
$('#element').on('click', function(e) {
e.preventDefault();
new $.Zebra_Dialog('The link was clicked!');
});
});
Configuration options
Properties
<table width"100%"> <thead> <tr> <th>Property</th> <th>Type</th> <th>Default</th> <th>Description</th> </tr> </thead> <tbody> <tr> <td valign="top"><code>animation_speed_hide</code></td> <td valign="top"><em>integer</em></td> <td valign="top">250</td> <td valign="top"> The speed, in milliseconds, by which the backdrop and the dialog box will be animated when closing. </td> </tr> <tr> <td valign="top"><code>animation_speed_show</code></td> <td valign="top"><em>integer</em></td> <td valign="top">0</td> <td valign="top"> The speed, in milliseconds, by which the backdrop and the dialog box will be animated when appearing. </td> </tr> <tr> <td valign="top"><code>auto_close</code></td> <td valign="top"><em>mixed</em></td> <td valign="top">false</td> <td valign="top"> The number of milliseconds after which to automatically close the dialog box or <code>false</code> to not automatically close the dialog box. </td> </tr> <tr> <td valign="top"><code>auto_focus_button</code></td> <td valign="top"><em>mixed</em></td> <td valign="top">true</td> <td valign="top"> The index (0-based) of the button (from left to right) to place the focus on when a dialog box is first shown.<br><br> Set to <code>false</code> to disable.<br><br> <blockquote>When set to <code>false</code> the focus will be placed on the dialog box's content so that when the users presses <code>TAB</code>, the focus will be set on the first button.</blockquote> Setting this to <code>true</code> is equivalent to setting it to <code>0</code>.<br><br> Default is TRUE </td> </tr> <tr> <td valign="top"><code>backdrop_close</code></td> <td valign="top"><em>boolean</em></td> <td valign="top">true</td> <td valign="top"> Should the dialog box close when the backdrop is clicked? </td> </tr> <tr> <td valign="top"><code>backdrop_opacity</code></td> <td valign="top"><em>double</em></td> <td valign="top">.9</td> <td valign="top"> The opacity of the backdrop (between <code>0</code> and <code>1</code>) </td> </tr> <tr> <td valign="top"><code>buttons</code></td> <td valign="top"><em>mixed</em></td> <td valign="top"></td> <td valign="top"> Use this for localization and for adding custom buttons.<br><br> If set to <code>true</code>, the default buttons will be used, depending on the type of the dialog box: <code>['Ok', 'Cancel']</code> for <code>prompt</code>, <code>question</code> and <code>warning</code> types, and <code>['Ok']</code> for the other types of dialog boxes.<br><br> For custom buttons, use an array containing the captions of the buttons to display: <code>['My button 1', 'My button 2']</code>.<br><br> Set to <code>false</code> if you want no buttons.<br><br> You can also add custom CSS classes, set which button's callback to be triggered when the user presses ENTER while inside the input box (for <code>prompt</code> dialog boxes and when <code>prompt_rows</code> is <code>1</code>), and/or attach callback functions to individual buttons by using objects in the form of:<br><br> <code>[{</code><br> <code> caption: 'My button 1',</code><br> <code> custom_class: 'foo',</code><br> <code> default_confirmation: true,</code><br> <code> callback: function() { // code }</code><br> <code>},{</code><br> <code> caption: 'My button 2',</code><br> <code> custom_class: 'bar',</code><br> <code> callback: function() { // code }</code><br> <code>}]</code><br><br> For <code>prompt</code> dialog box types use the <code>default_confirmation</code> property to tell the library which button's callback to trigger when the user presses <code>ENTER</code> while inside the input box. If not set, you will <strong>have</strong> to handle user input via the <code>onBeforeClose</code> event, or you will not be able to process user input for this case.<br><br> <blockquote>The above applies only if <code>prompt_rows</code> is <code>1</code> as otherwise the ENTER key inserts a line-break</blockquote><br> Callback functions receive as first argument the entire dialog box, as a jQuery object, and as second argument, the value entered in the input box - when the dialog box's type is <code>prompt</code>, or <code>undefined</code> for the other dialog types.<br><br> A callback function attache to a button is executed as soon as the button is clicked rather than <strong>after </strong> the dialog box is closed, as it is the case with the <code>onClose</code> event.<br><br> <blockquote>A callback function returning FALSE will prevent the dialog box from closing.</blockquote> </td> </tr> <tr> <td valign="top"><code>center_buttons</code></td> <td valign="top"><em>boolean</em></td> <td valign="top">false</td> <td valign="top"> Setting this property to <code>true</code> will instruct the plugin to center any available buttons instead of aligning them to the right </td> </tr> <tr> <td valign="top"><code>custom_class</code></td> <td valign="top"><em>mixed</em></td> <td valign="top">false</td> <td valign="top"> An extra class to add to the dialog box's container and to the backdrop (when present).<br><br> For example, setting this value to <code>mycustom</code> and in the CSS file having something like<br><br> <code>.mycustom .ZebraDialog_Title { background: red }</code><br><br> would set the dialog box title's background to red.<br><br> <blockquote>Take a look into a theme's style sheet file to see what can be changed.</blockquote> </td> </tr> <tr> <td valign="top"><code>default_value</code></td> <td valign="top"><em>string</em></td> <td valign="top">""<br>(empty string)</td> <td valign="top"> Default value to show in the input box when the dialog box type is <code>prompt</code>.<br><br> See also the <code>placeholder</code> property. </td> </tr> <tr> <td valign="top"><code>disable_page_scrolling</code></td> <td valign="top"><em>boolean</em></td> <td valign="top">true</td> <td valign="top"> Prevents scrolling of the page behind the dialog box, when the dialog box is open.<br><br> <blockquote>This has effect only when the <code>modal</code> property is set to <code>true</code>.</blockquote> </td> </tr> <tr> <td valign="top"><code>draggable</code></td> <td valign="top"><em>mixed</em></td> <td valign="top">true for dialog boxes that have a title</td> <td valign="top"> Whether the dialog box should be draggable or not.<br><br> Dialog boxes that have a title are draggable by default unless this property is set to <code>false</code>.<br><br> For dialog boxes not having a title, set this property to <code>force</code> for making them draggable. </td> </tr> <tr> <td valign="top"><code>height</code></td> <td valign="top"><em>mixed</em></td> <td valign="top">0<br>(automatically set)</td> <td valign="top"> By default, the height of the dialog box is automatically computed to fit the content (but not exceed viewport).<br><br> Can be specified as a numeric value (which will be interpreted as a value in pixels) or as a percentage (of the viewport).<br><br> <blockquote>If <code>max_height</code> is set to valid value greater than <code>0</code>, then this property will be ignored!</blockquote> </td> </tr> <tr> <td valign="top"><code>keyboard</code></td> <td valign="top"><em>boolean</em></td> <td valign="top">true</td> <td valign="top"> When set to <code>true</code>, pressing the <code>ESC</code> key will close the dialog box. </td> </tr> <tr> <td valign="top"><code>margin</code></td> <td valign="top"><em>mixed</em></td> <td valign="top">0</td> <td valign="top"> Margin of the dialog box relative to the viewport's limits (a single value, applied both horizontally and/or vertically)<br><br>This is used when the dialog box is stretched 100% horizontally and/or vertically and <code>width</code> and <code>max_width</code> are not set (when stretched horizontally) and <code>height</code> and <code>max_height</code> are not set (when stretched vertically).<br><br> This propery is also taken into account when using the <code>position</code> property.<br><br> Can be specified as a numeric value (which will be interpreted as a value in pixels) or as a percentage (of the viewport). </td> </tr> <tr> <td valign="top"><code>max_height</code></td> <td valign="top"><em>mixed</em></td> <td valign="top">0</td> <td valign="top"> The maximum height of the dialog box.<br><br> Can be specified as a numeric value (which will be interpreted as a value in pixels) or as a percentage (of the viewport).<br><br> <blockquote>If this property is set to valid value greater than <code>0</code>, then the <code>height</code> property will be ignored.</blockquote> </td> </tr> <tr> <td valign="top"><code>max_width</code></td> <td valign="top"><em>mixed</em></td> <td valign="top">450</td> <td valign="top"> The maximum width of the dialog box.<br><br> Can be specified as a numeric value (which will be interpreted as a value in pixels) or as a percentage (of the viewport).<br><br> <blockquote>If this property is set to valid value greater than <code>0</code>, then the <code>width</code> property will be ignored.</blockquote> </td> </tr> <tr> <td valign="top"><code>message</code></td> <td valign="top"><em>string</em></td> <td valign="top"></td> <td valign="top"> The text (or HTML) to be displayed in the dialog box.<br><br> See the <code>source</code> property on how to add content via AJAX, iFrames or from inline elements. </td> </tr> <tr> <td valign="top"><code>modal</code></td> <td valign="top"><em>boolean</em></td> <td valign="top">true</td> <td valign="top"> When set to <code>true</code> there will be a semitransparent backdrop behind the dialog box, preventing users from clicking the page's content. </td> </tr> <tr> <td valign="top"><code>placeholder</code></td> <td valign="top"><em>string</em></td> <td valign="top">""<br>(empty string)</td> <td valign="top"> When set to <code>true</code> there will be a semitransparent backdrop behind the dialog box, preventing users from clicking the page's content.<br><br> See also <code>default_value</code> property. </td> </tr> <tr> <td valign="top"><code>position</code></td> <td valign="top"><em>mixed</em></td> <td valign="top">'center'</td> <td valign="top"> Position of the dialog box.<br><br> Can be either <code>center</code> (which would center the dialog box both horizontally and vertically), or an array with 2 elements, in the form of<br><br> <code>// notice that everything is enclosed in quotes</code><br> <code>['horizontal_position +/- offset',</code><br> <code>'vertical_position +/- offset']</code><br><br> where<br> <ul> <li><em>horizontal_position</em> can be <code>left</code>, <code>right</code> or <code>center</code></li> <li><em>vertical_position</em> can be <code>top</code>, <code>bottom</code> or <code>middle</code></li> <li><em>offset</em> is optional and represents the value of pixels to add/subtract from the respective horizontal or vertical position</li> </ul> <blockquote>Positions are relative to the viewport (the area of the browser that is visible to the user) and the value of the <code>margin</code> property is taken into account!</blockquote> Examples:<br><br> <code>// position the dialog box in the top-left corner</code><br> <code>// shifted 20 pixels inside</code><br> <code>['left + 20', 'top + 20']</code><br><br> <code>// position the dialog box in the bottom-right corner</code><br> <code>// shifted 20 pixels inside</code></br> <code>['right - 20', 'bottom - 20']</code><br><br> <code>// position the dialog box in center-top</code><br> <code>// shifted 20 pixels down</code><br> <code>['center', 'top + 20']</code><br><br> <blockquote>Note that when the width of the viewport is less than 768 pixels, any arithmetics will be ignored (so, things like <code>left + 20</code> will be interpreted as just <code>left</code>)</blockquote> </td> </tr> <tr> <td valign="top"><code>prompt_rows</code></td> <td valign="top"><em>integer</em></td> <td valign="top">1</td> <td valign="top"> If the dialog box type is <code>prompt</code>, setting this property to a value higher than <code>1</code> will change the input box to a textarea input having the specified number of rows. </td> </tr> <tr> <td valign="top"><code>reposition_speed</code></td> <td valign="top"><em>integer</em></td> <td valign="top">500</td> <td valign="top"> The duration (in milliseconds) of the animation used to reposition the dialog box when the browser window is resized. </td> </tr> <tr> <td valign="top"><code>show_close_button</code></td> <td valign="top"><em>boolean</em></td> <td valign="top">true</td> <td valign="top"> When set to <code>true</code>, a <em>close</em> button (the little "x") will be shown in the upper right corner of the dialog box.<br><br> If the dialog box has a title bar then the <em>close</em> button will be shown in the title bar, vertically centered and respecting the right padding.<br><br> If the dialog box does not have a title bar then the <em>close</em> button will be shown in the upper right corner of the body of the dialog box, respecting the position related properties set in the stylesheet. </td> </tr> <tr> <td valign="top"><code>source</code></td> <td valign="top"><em>mixed</em></td> <td valign="top">false</td> <td valign="top"> Add content via AJAX, iFrames or from inline elements (together with the already applied events).<br><br> This property can be any of the following:<br><br> <ul> <li> <code>ajax: object</code> - where <em>object</em> can be an <code>object</code> with any of the properties you'd normally use to make an AJAX call in jQuery (see the description for the <em>settings</em> argument <a href="http://api.jquery.com/jQuery.ajax/">here</a>), or it can be a <code>string</code> representing a valid URL whose content to be fetched via AJAX and placed inside the dialog box.<br><br> <code>source: {ajax: 'http://myurl.com/'}</code><br><br> <code>source: {</code><br> <code> ajax: {</code><br> <code> url: 'http://myurl.com/',</code><br> <code> cache: false</code><br> <code> }</code><br> <code>}</code><br><br> <blockquote>Note that you cannot use the <code>success</code> property as it will always be overwritten by the library; use the <code>complete</code> property instead, if you have to</blockquote><br> </li> <li> <code>iframe: object</code> - where <em>object</em> can be an <code>object</code> where property names are valid attributes of the <a href="https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTML/Element/iframe">iframe</a> tag, or it can be a <code>string</code> representing a valid URL to be loaded inside an iFrame and placed inside the dialog box.<br><br> <code>source: {iframe: 'http://myurl.com/'}</code><br><br> <code>source: {</code><br> <code> // iFrame's width and height are automatically set</code><br> <code> // to fit the dialog box's width and height</code><br> <code> iframe: {</code><br> <code> src: 'http://myurl.com/'</code><br> <code> }</code><br> <code>}</code><br><br> </li> <li> <code>inline: selector</code> - where <em>element</em> is a jQuery element from the page; the element will be copied and placed inside the dialog box together with any attached events. If you just want the element's inner HTML, use <code>$('#element').html()</code><br><br> <code>source: {inline: $('#myelement')}</code> </li> </ul> </td> </tr> <tr> <td valign="top"><code>title</code></td> <td valign="top"><em>string</em></td> <td valign="top">""<br>(empty string, no title)</td> <td valign="top"> Title of the dialog box </td> </tr> <tr> <td valign="top"><code>type</code></td> <td valign="top"><em>mixed</em></td> <td valign="top">information</td> <td valign="top"> Dialog box type.<br> Can be any of the following: <ul> <li>confirmation</li> <li>error</li> <li>information</li> <li>prompt</li> <li>question</li> <li>warning</li> </ul> If you don't want an icon, set the <code>type</code> property to <code>false</code>.<br><br> By default, the <code>warning</code> and <code>question</code> types have two buttons with the captions <em>Ok</em> and <em>Cancel</em> respectively, while the other types have a single button with the caption <em>Ok</em>. </td> </tr> <tr> <td valign="top"><code>vcenter_short_message</code></td> <td valign="top"><em>boolean</em></td> <td valign="top"f/td> <td valign="top"> Should messages shorter than the dialog's height be vertically centered?<br><br> <blockquote>This property is ignored when <code>source</code> is <code>iframe</code></blockquote> </td> </tr> <tr> <td valign="top"><code>width</code></td> <td valign="top"><em>integer</em></td> <td valign="top">0<br>(uses the value defined in the theme)</td> <td valign="top"> By default, the width of the dialog box is automatically computed in order to fit the content (but not exceed viewport.<br><br> Can be specified as a numeric value (which will be interpreted as a value in pixels) or as a percentage (of the viewport).<br><br> <blockquote>If <code>max_width</code> is set to valid value greater than <code>0</code>, then this property will be ignored.</blockquote> </td> </tr> </tbody> </table>Events
<table width="100%"> <thead> <tr> <th>Event</th> <th width="100%">Description</th> </tr> </thead> <tbody> <tr> <td valign="top"><code>onOpen</code></td> <td valign="top"> Event fired <em>after</em> the dialog box is opened.<br><br> The callback function receives as unique argument the dialog box, as a jQuery element. </td> </tr> <tr> <td valign="top"><code>onBeforeClose</code></td> <td valign="top"> Event fired <em>before</em> the dialog box is closed.<br><br> <blockquote>The main difference when compared to the <code>onClose</code> event is that, with this event, by returning <code>false</code> from the callback function you can prevent the closing of the dialog box - useful for validating user input.</blockquote><br> The callback function receives as first argument the caption of the clicked button or boolean <code>FALSE</code> if the dialog box is closed by pressing the <code>ESC</code> key, by clicking the dialog box's <code>x</code> button, or by clicking the backdrop. The argument can also be boolean <code>TRUE</code> when the dialog box type is <code>prompt</code> and the <code>ENTER</code> key is pressed while inside the input box.<br><br> As second argument, the callback function receives the value entered in the input box - when the dialog box type is <code>prompt</code> and a button was clicked or the <code>ENTER</code> key was pressed while inside the input box, or <code>undefined</code> for any other case.<br><br> All this is important when expecting user input as you can say that you have user input <strong>only</strong> when the value of the first argument is boolean <code>TRUE</code>or the value it's the same as the label of the button considered as confirmation (i.e. "Ok"), and the value of the second argument is <code>!== undefined</code>.<br><br> See the <code>buttons</code> property for another way of handling user input. </td> </tr> <tr> <td valign="top"><code>onClose</code></td> <td valign="top"> Event fired <em>after</em> the dialog box is closed.<br><br> For executing functions <em>before</em> the closing of the dialog box, see the <strong>onBeforeClose</strong> event or the <strong>buttons</strong> property.<br><br> <blockquote>For properly validating user input you might want to use the <strong>onBeforeClose</strong> event or the <strong>buttons</strong> property!</blockquote><br> The callback function receives as first argument the caption of the clicked button or boolean <code>FALSE</code> if the dialog box is closed by pressing the <code>ESC</code> key, by clicking the dialog box's <code>x</code> button, or by clicking the backdrop. The argument can also be boolean <code>TRUE</code> when the dialog box type is <code>prompt</code> and the <code>ENTER</code> key is pressed while inside the input box.<br><br> As second argument, the callback function receives the value entered in the input box - when the dialog box type is <code>prompt</code> and a button was clicked or the <code>ENTER</code> key was pressed while inside the input box, or <code>undefined</code> for any other case.<br><br> All this is important when expecting user input as you can say that you have user input <strong>only</strong> when the value of the first argument is boolean <code>TRUE</code>or the value it's the same as the label of the button considered as confirmation (i.e. "Ok"), and the value of the second argument is <code>!== undefined</code>.<br><br> See the <code>buttons</code> property or the <code>onBeforeClose</code> event for other ways of handling user input. </td> </tr> </tbody> </table>Methods
close()
Call this method to manually close a dialog box.
var dialog = new $.Zebra_Dialog('This is some information');
dialog.close();
update()
Use this method to adjust the dialog box's position after content is changed dynamically, at run-time.
var dialog = new $.Zebra_Dialog('This is some information');
// change the content in the dialog box
$('.ZebraDialog_Body').html('New content');
dialog.update();
Sponsors
Cross browser/device testing is done with