Awesome
ε-NFA: Epsilon-Nondeterministic finite automaton
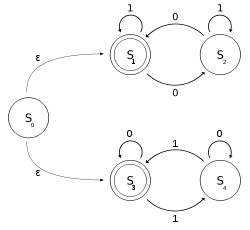
What is Epsilon-Nondeterministic finite automaton
ε-NFA: Epsilon-Nondeterministic finite automaton (so call:Nondeterministic finite automaton with ε-moves)
In the automata theory, a nondeterministic finite automaton with ε-moves (NFA-ε)(also known as NFA-λ) is an extension of nondeterministic finite automaton(NFA), which allows a transformation to a new state without consuming any input symbols. The transitions without consuming an input symbol are called ε-transitions or λ-transitions. In the state diagrams, they are usually labeled with the Greek letter ε or λ.
(sited from here)
Looking for DFA implement?
I also write a DFA implenent in Go here. https://github.com/kkdai/dfa
Looking for NFA implement?
I also write a NFA implenent in Go here. https://github.com/kkdai/nfa
Installation and Usage
Install
go get github.com/kkdai/e-nfa
Usage
Following is sample code to implement a epsilon-NFA automata diagram as follow:

package main
import (
"github.com/kkdai/enfa"
"fmt"
)
func main() {
nfa := NewENFA(0, false)
nfa.AddState(1, false)
nfa.AddState(2, false)
nfa.AddState(3, true)
nfa.AddState(4, false)
nfa.AddState(5, false)
nfa.AddTransition(0, "1", 1)
nfa.AddTransition(0, "0", 4)
nfa.AddTransition(1, "1", 2)
nfa.AddTransition(1, "", 3) //epsilon
nfa.AddTransition(2, "1", 3)
nfa.AddTransition(4, "0", 5)
nfa.AddTransition(4, "", 1, 2) //E -> epsilon B C
nfa.AddTransition(5, "0", 3)
nfa.PrintTransitionTable()
if !nfa.VerifyInputs([]string{"1"}) {
fmt.Printf("Verify inputs is failed")
}
nfa.Reset()
if !nfa.VerifyInputs([]string{"1", "1", "1"}) {
fmt.Printf("Verify inputs is failed")
}
nfa.Reset()
if !nfa.VerifyInputs([]string{"0", "1"}) {
fmt.Printf"Verify inputs is failed")
}
nfa.Reset()
if !nfa.VerifyInputs([]string{"0", "0", "0"}) {
fmt.Printf("Verify inputs is failed")
}
}
Inspired By
Project52
It is one of my project 52.
License
This package is licensed under MIT license. See LICENSE for details.
