Awesome
ssh-audit
ssh-audit is a tool for ssh server & client configuration auditing.
jtesta/ssh-audit (v2.0+) is the updated and maintained version of ssh-audit forked from arthepsy/ssh-audit (v1.x) due to inactivity.
Features
- SSH1 and SSH2 protocol server support;
- analyze SSH client configuration;
- grab banner, recognize device or software and operating system, detect compression;
- gather key-exchange, host-key, encryption and message authentication code algorithms;
- output algorithm security information (available since, removed/disabled, unsafe/weak/legacy, etc);
- output algorithm recommendations (append or remove based on recognized software version);
- analyze SSH version compatibility based on algorithm information;
- historical information from OpenSSH, Dropbear SSH and libssh;
- policy scans to ensure adherence to a hardened/standard configuration;
- runs on Linux and Windows;
- supports Python 3.8 - 3.13;
- no dependencies
Usage
usage: ssh-audit.py [-h] [-1] [-2] [-4] [-6] [-b] [-c] [-d]
[-g <min1:pref1:max1[,min2:pref2:max2,...]> / <x-y[:step]>] [-j] [-l {info,warn,fail}] [-L]
[-M custom_policy.txt] [-m] [-n] [-P "Built-In Policy Name" / custom_policy.txt] [-p N]
[-T targets.txt] [-t N] [-v] [--conn-rate-test N[:max_rate]] [--dheat N[:kex[:e_len]]]
[--lookup alg1[,alg2,...]] [--skip-rate-test] [--threads N]
[host]
positional arguments:
host target hostname or IPv4/IPv6 address
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-1, --ssh1 force ssh version 1 only
-2, --ssh2 force ssh version 2 only
-4, --ipv4 enable IPv4 (order of precedence)
-6, --ipv6 enable IPv6 (order of precedence)
-b, --batch batch output
-c, --client-audit starts a server on port 2222 to audit client software config (use -p to change port; use -t
to change timeout)
-d, --debug enable debugging output
-g <min1:pref1:max1[,min2:pref2:max2,...]> / <x-y[:step]>, --gex-test <min1:pref1:max1[,min2:pref2:max2,...]> / <x-y[:step]>
conducts a very customized Diffie-Hellman GEX modulus size test. Tests an array of minimum,
preferred, and maximum values, or a range of values with an optional incremental step amount
-j, --json enable JSON output (use -jj to enable indentation for better readability)
-l {info,warn,fail}, --level {info,warn,fail}
minimum output level (default: info)
-L, --list-policies list all the official, built-in policies. Combine with -v to view policy change logs
-M custom_policy.txt, --make-policy custom_policy.txt
creates a policy based on the target server (i.e.: the target server has the ideal
configuration that other servers should adhere to), and stores it in the file path specified
-m, --manual print the man page (Docker, PyPI, Snap, and Windows builds only)
-n, --no-colors disable colors (automatic when the NO_COLOR environment variable is set)
-P "Built-In Policy Name" / custom_policy.txt, --policy "Built-In Policy Name" / custom_policy.txt
run a policy test using the specified policy (use -L to see built-in policies, or specify
filesystem path to custom policy created by -M)
-p N, --port N the TCP port to connect to (or to listen on when -c is used)
-T targets.txt, --targets targets.txt
a file containing a list of target hosts (one per line, format HOST[:PORT]). Use -p/--port
to set the default port for all hosts. Use --threads to control concurrent scans
-t N, --timeout N timeout (in seconds) for connection and reading (default: 5)
-v, --verbose enable verbose output
--conn-rate-test N[:max_rate]
perform a connection rate test (useful for collecting metrics related to susceptibility of
the DHEat vuln). Testing is conducted with N concurrent sockets with an optional maximum
rate of connections per second
--dheat N[:kex[:e_len]]
continuously perform the DHEat DoS attack (CVE-2002-20001) against the target using N
concurrent sockets. Optionally, a specific key exchange algorithm can be specified instead
of allowing it to be automatically chosen. Additionally, a small length of the fake e value
sent to the server can be chosen for a more efficient attack (such as 4).
--lookup alg1[,alg2,...]
looks up an algorithm(s) without connecting to a server.
--skip-rate-test skip the connection rate test during standard audits (used to safely infer whether the DHEat
attack is viable)
--threads N number of threads to use when scanning multiple targets (-T/--targets) (default: 32)
- if both IPv4 and IPv6 are used, order of precedence can be set by using either
-46or-64. - batch flag
-bwill output sections without header and without empty lines (implies verbose flag). - verbose flag
-vwill prefix each line with section type and algorithm name. - an exit code of 0 is returned when all algorithms are considered secure (for a standard audit), or when a policy check passes (for a policy audit).
Basic server auditing:
ssh-audit localhost
ssh-audit 127.0.0.1
ssh-audit 127.0.0.1:222
ssh-audit ::1
ssh-audit [::1]:222
To run a standard audit against many servers (place targets into servers.txt, one on each line in the format of HOST[:PORT]):
ssh-audit -T servers.txt
To audit a client configuration (listens on port 2222 by default; connect using ssh -p 2222 anything@localhost):
ssh-audit -c
To audit a client configuration, with a listener on port 4567:
ssh-audit -c -p 4567
To list all official built-in policies (hint: use resulting policy names with -P/--policy):
ssh-audit -L
To run a policy audit against a server:
ssh-audit -P ["policy name" | path/to/server_policy.txt] targetserver
To run a policy audit against a client:
ssh-audit -c -P ["policy name" | path/to/client_policy.txt]
To run a policy audit against many servers:
ssh-audit -T servers.txt -P ["policy name" | path/to/server_policy.txt]
To create a policy based on a target server (which can be manually edited):
ssh-audit -M new_policy.txt targetserver
To run the DHEat CPU exhaustion DoS attack (CVE-2002-20001) against a target using 10 concurrent sockets:
ssh-audit --dheat=10 targetserver
To run the DHEat attack using the diffie-hellman-group-exchange-sha256 key exchange algorithm:
ssh-audit --dheat=10:diffie-hellman-group-exchange-sha256 targetserver
To run the DHEat attack using the diffie-hellman-group-exchange-sha256 key exchange algorithm along with very small but non-standard packet lengths (this may result in the same CPU exhaustion, but with many less bytes per second being sent):
ssh-audit --dheat=10:diffie-hellman-group-exchange-sha256:4 targetserver
Screenshots
Server Standard Audit Example
Below is a screen shot of the standard server-auditing output when connecting to an unhardened OpenSSH v5.3 service:

Server Policy Audit Example
Below is a screen shot of the policy auditing output when connecting to an un-hardened Ubuntu Server 20.04 machine (hint: use -L/--list-policies to see names of built-in policies to use with -P/--policy):
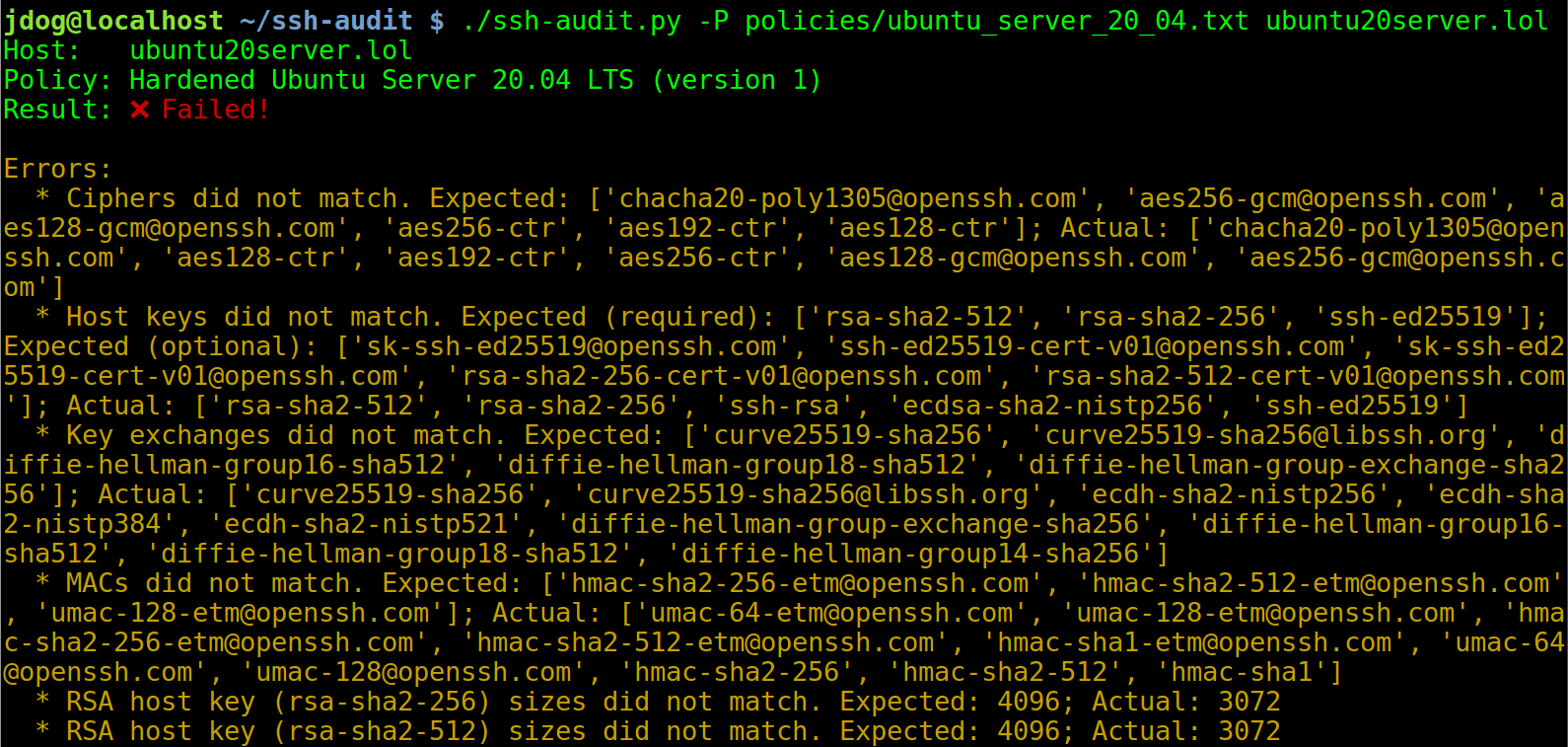
After applying the steps in the hardening guide (see below), the output changes to the following:

Client Standard Audit Example
Below is a screen shot of the client-auditing output when an unhardened OpenSSH v7.2 client connects:

Hardening Guides
Guides to harden server & client configuration can be found here: https://www.ssh-audit.com/hardening_guides.html
Pre-Built Packages
Pre-built packages are available for Windows (see the Releases page), PyPI, Snap, and Docker:
To install from PyPI:
$ pip3 install ssh-audit
To install the Snap package:
$ snap install ssh-audit
To install from Dockerhub:
$ docker pull positronsecurity/ssh-audit
(Then run with: docker run -it --rm -p 2222:2222 positronsecurity/ssh-audit 10.1.1.1)
The status of various other platform packages can be found below (via Repology):
<a href="https://repology.org/project/ssh-audit/versions"><img src="https://repology.org/badge/vertical-allrepos/ssh-audit.svg?columns=4" alt="Packaging status" align="center"></a>
Web Front-End
For convenience, a web front-end on top of the command-line tool is available at https://www.ssh-audit.com/.
ChangeLog
v3.4.0-dev
- Added warning to all key exchanges that do not include protections against quantum attacks due to the Harvest Now, Decrypt Later strategy (see https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Harvest_now,_decrypt_later).
- Migrated from deprecated
getoptmodule toargparse; partial credit oam7575. - When running against multiple hosts, now prints each target host regardless of output level.
- Batch mode (
-b) no longer automatically enables verbose mode, due to sometimes confusing results; users can still explicitly enable verbose mode using the-vflag.
v3.3.0 (2024-10-15)
- Added Python 3.13 support.
- Added built-in policies for Ubuntu 24.04 LTS server & client, OpenSSH 9.8, and OpenSSH 9.9.
- Added IPv6 support for DHEat and connection rate tests.
- Added TCP port information to JSON policy scan results; credit Fabian Malte Kopp.
- Added LANcom LCOS server recognition and Ed448 key extraction; credit Daniel Lenski.
- Now reports ECDSA and DSS fingerprints when in verbose mode; partial credit Daniel Lenski.
- Removed CVE information based on server/client version numbers, as this was wildly inaccurate (see this thread for the full discussion, as well as the results of the community vote on this matter).
- Fixed crash when running with
-Pand-Toptions simultaneously. - Fixed host key tests from only reporting a key type at most once despite multiple hosts supporting it; credit Daniel Lenski.
- Fixed DHEat connection rate testing on MacOS X and BSD platforms; credit Drew Noel and Michael Osipov.
- Fixed invalid JSON output when a socket error occurs while performing a client audit.
- Fixed
--conn-rate-testfeature on Windows. - When scanning multiple targets (using
-T/--targets), the-p/--portoption will now be used as the default port (set to 22 if-p/--portis not given). Hosts specified in the file can override this default with an explicit port number (i.e.: "host1:1234"). For example, when using-T targets.txt -p 222, all hosts intargets.txtthat do not explicitly include a port number will default to 222; when using-T targets.txt(without-p), all hosts will use a default of 22. - Updated built-in server & client policies for Amazon Linux 2023, Debian 12, Rocky Linux 9, and Ubuntu 22.04 to improve host key efficiency and cipher resistance to quantum attacks.
- Added 1 new cipher:
grasshopper-ctr128. - Added 2 new key exchanges:
mlkem768x25519-sha256,sntrup761x25519-sha512.
v3.2.0 (2024-04-22)
- Added implementation of the DHEat denial-of-service attack (see
--dheatoption; CVE-2002-20001). - Expanded filter of CBC ciphers to flag for the Terrapin vulnerability. It now includes more rarely found ciphers.
- Fixed parsing of
ecdsa-sha2-nistp*CA signatures on host keys. Additionally, they are now flagged as potentially back-doored, just as standard host keys are. - Gracefully handle rare exceptions (i.e.: crashes) while performing GEX tests.
- The built-in man page (
-m,--manual) is now available on Docker, PyPI, and Snap builds, in addition to the Windows build. - Snap builds are now architecture-independent.
- Changed Docker base image from
python:3-slimtopython:3-alpine, resulting in a 59% reduction in image size; credit Daniel Thamdrup. - Added built-in policies for Amazon Linux 2023, Debian 12, OpenSSH 9.7, and Rocky Linux 9.
- Built-in policies now include a change log (use
-L -vto view them). - Custom policies now support the
allow_algorithm_subset_and_reorderingdirective to allow targets to pass with a subset and/or re-ordered list of host keys, kex, ciphers, and MACs. This allows for the creation of a baseline policy where targets can optionally implement stricter controls; partial credit yannik1015. - Custom policies now support the
allow_larger_keysdirective to allow targets to pass with larger host keys, CA keys, and Diffie-Hellman keys. This allows for the creation of a baseline policy where targets can optionally implement stricter controls; partial credit Damian Szuberski. - Color output is disabled if the
NO_COLORenvironment variable is set (see https://no-color.org/). - Added 1 new key exchange algorithm:
gss-nistp384-sha384-*. - Added 1 new cipher:
aes128-ocb@libassh.org.
v3.1.0 (2023-12-20)
- Added test for the Terrapin message prefix truncation vulnerability (CVE-2023-48795).
- Dropped support for Python 3.7 (EOL was reached in June 2023).
- Added Python 3.12 support.
- In server policies, reduced expected DH modulus sizes from 4096 to 3072 to match the online hardening guides (note that 3072-bit moduli provide the equivalent of 128-bit symmetric security).
- In Ubuntu 22.04 client policy, moved host key types
sk-ssh-ed25519@openssh.comandssh-ed25519to the end of all certificate types. - Updated Ubuntu Server & Client policies for 20.04 and 22.04 to account for key exchange list changes due to Terrapin vulnerability patches.
- Re-organized option host key types for OpenSSH 9.2 server policy to correspond with updated Debian 12 hardening guide.
- Added built-in policies for OpenSSH 9.5 and 9.6.
- Added an
additional_notesfield to the JSON output.
v3.0.0 (2023-09-07)
- Results from concurrent scans against multiple hosts are no longer improperly combined; bug discovered by Adam Russell.
- Hostname resolution failure no longer causes scans against multiple hosts to terminate unexpectedly; credit Dani Cuesta.
- Algorithm recommendations resulting from warnings are now printed in yellow instead of red; credit Adam Russell.
- Added failure, warning, and info notes to JSON output (note that this results in a breaking change to the banner protocol, "enc", and "mac" fields); credit Bareq Al-Azzawi.
- Docker Makefile now creates multi-arch builds for amd64, arm64, and armv7; credit Sebastian Cohnen.
- Fixed crash during GEX tests.
- Refined GEX testing against OpenSSH servers: when the fallback mechanism is suspected of being triggered, perform an additional test to obtain more accurate results.
- The color of all notes will be printed in green when the related algorithm is rated good.
- Prioritized host key certificate algorithms for Ubuntu 22.04 LTS client policy.
- Marked all NIST K-, B-, and T-curves as unproven since they are so rarely used.
- Added built-in policy for OpenSSH 9.4.
- Added 12 new host keys:
ecdsa-sha2-curve25519,ecdsa-sha2-nistb233,ecdsa-sha2-nistb409,ecdsa-sha2-nistk163,ecdsa-sha2-nistk233,ecdsa-sha2-nistk283,ecdsa-sha2-nistk409,ecdsa-sha2-nistp224,ecdsa-sha2-nistp192,ecdsa-sha2-nistt571,ssh-dsa,x509v3-sign-rsa-sha256. - Added 15 new key exchanges:
curve448-sha512@libssh.org,ecdh-nistp256-kyber-512r3-sha256-d00@openquantumsafe.org,ecdh-nistp384-kyber-768r3-sha384-d00@openquantumsafe.org,ecdh-nistp521-kyber-1024r3-sha512-d00@openquantumsafe.org,ecdh-sha2-brainpoolp256r1@genua.de,ecdh-sha2-brainpoolp384r1@genua.de,ecdh-sha2-brainpoolp521r1@genua.de,kexAlgoDH14SHA1,kexAlgoDH1SHA1,kexAlgoECDH256,kexAlgoECDH384,kexAlgoECDH521,sm2kep-sha2-nistp256,x25519-kyber-512r3-sha256-d00@amazon.com,x25519-kyber512-sha512@aws.amazon.com. - Added 8 new ciphers:
aes192-gcm@openssh.com,cast128-12-cbc,cast128-12-cfb,cast128-12-ecb,cast128-12-ofb,des-cfb,des-ecb,des-ofb. - Added 14 new MACs:
cbcmac-3des,cbcmac-aes,cbcmac-blowfish,cbcmac-des,cbcmac-rijndael,cbcmac-twofish,hmac-sha256-96,md5,md5-8,ripemd160,ripemd160-8,sha1,sha1-8,umac-128.
v2.9.0 (2023-04-29)
- Dropped support for Python 3.6, as it reached EOL at the end of 2021.
- Added Ubuntu Server & Client 22.04 hardening policies.
- Removed experimental warning tag from
sntrup761x25519-sha512@openssh.com. - Updated CVE database; credit Alexandre Zanni.
- Added
-gand--gex-testfor granular GEX modulus size tests; credit Adam Russell. - Snap packages now print more user-friendly error messages when permission errors are encountered.
- JSON 'target' field now always includes port number; credit tomatohater1337.
- JSON output now includes recommendations and CVE data.
- Mixed host key/CA key types (i.e.: RSA host keys signed with ED25519 CAs, etc.) are now properly handled.
- Warnings are now printed for 2048-bit moduli; partial credit Adam Russell.
- SHA-1 algorithms now cause failures.
- CBC mode ciphers are now warnings instead of failures.
- Generic failure/warning messages replaced with more specific reasons (i.e.: 'using weak cipher' => 'using broken RC4 cipher').
- Updated built-in policies to include missing host key size information.
- Added built-in policies for OpenSSH 8.8, 8.9, 9.0, 9.1, 9.2, and 9.3.
- Added 33 new host keys:
dsa2048-sha224@libassh.org,dsa2048-sha256@libassh.org,dsa3072-sha256@libassh.org,ecdsa-sha2-1.3.132.0.10-cert-v01@openssh.com,eddsa-e382-shake256@libassh.org,eddsa-e521-shake256@libassh.org,null,pgp-sign-dss,pgp-sign-rsa,spki-sign-dss,spki-sign-rsa,ssh-dss-sha224@ssh.com,ssh-dss-sha384@ssh.com,ssh-dss-sha512@ssh.com,ssh-ed448-cert-v01@openssh.com,ssh-rsa-sha224@ssh.com,ssh-rsa-sha2-256,ssh-rsa-sha2-512,ssh-rsa-sha384@ssh.com,ssh-rsa-sha512@ssh.com,ssh-xmss-cert-v01@openssh.com,ssh-xmss@openssh.com,webauthn-sk-ecdsa-sha2-nistp256@openssh.com,x509v3-ecdsa-sha2-1.3.132.0.10,x509v3-sign-dss-sha1,x509v3-sign-dss-sha224@ssh.com,x509v3-sign-dss-sha256@ssh.com,x509v3-sign-dss-sha384@ssh.com,x509v3-sign-dss-sha512@ssh.com,x509v3-sign-rsa-sha1,x509v3-sign-rsa-sha224@ssh.com,x509v3-sign-rsa-sha384@ssh.com,x509v3-sign-rsa-sha512@ssh.com. - Added 46 new key exchanges:
diffie-hellman-group14-sha224@ssh.com,diffie-hellman_group17-sha512,diffie-hellman-group-exchange-sha224@ssh.com,diffie-hellman-group-exchange-sha384@ssh.com,ecdh-sha2-1.2.840.10045.3.1.1,ecdh-sha2-1.2.840.10045.3.1.7,ecdh-sha2-1.3.132.0.1,ecdh-sha2-1.3.132.0.16,ecdh-sha2-1.3.132.0.26,ecdh-sha2-1.3.132.0.27,ecdh-sha2-1.3.132.0.33,ecdh-sha2-1.3.132.0.34,ecdh-sha2-1.3.132.0.35,ecdh-sha2-1.3.132.0.36,ecdh-sha2-1.3.132.0.37,ecdh-sha2-1.3.132.0.38,ecdh-sha2-4MHB+NBt3AlaSRQ7MnB4cg==,ecdh-sha2-5pPrSUQtIaTjUSt5VZNBjg==,ecdh-sha2-9UzNcgwTlEnSCECZa7V1mw==,ecdh-sha2-D3FefCjYoJ/kfXgAyLddYA==,ecdh-sha2-h/SsxnLCtRBh7I9ATyeB3A==,ecdh-sha2-m/FtSAmrV4j/Wy6RVUaK7A==,ecdh-sha2-mNVwCXAoS1HGmHpLvBC94w==,ecdh-sha2-qCbG5Cn/jjsZ7nBeR7EnOA==,ecdh-sha2-qcFQaMAMGhTziMT0z+Tuzw==,ecdh-sha2-VqBg4QRPjxx1EXZdV0GdWQ==,ecdh-sha2-wiRIU8TKjMZ418sMqlqtvQ==,ecdh-sha2-zD/b3hu/71952ArpUG4OjQ==,ecmqv-sha2,gss-13.3.132.0.10-sha256-*,gss-curve25519-sha256-*,gss-curve448-sha512-*,gss-gex-sha1-*,gss-gex-sha256-*,gss-group14-sha1-*,gss-group14-sha256-*,gss-group15-sha512-*,gss-group16-sha512-*,gss-group17-sha512-*,gss-group18-sha512-*,gss-group1-sha1-*,gss-nistp256-sha256-*,gss-nistp384-sha256-*,gss-nistp521-sha512-*,m383-sha384@libassh.org,m511-sha512@libassh.org. - Added 28 new ciphers:
3des-cfb,3des-ecb,3des-ofb,blowfish-cfb,blowfish-ecb,blowfish-ofb,camellia128-cbc@openssh.org,camellia128-ctr@openssh.org,camellia192-cbc@openssh.org,camellia192-ctr@openssh.org,camellia256-cbc@openssh.org,camellia256-ctr@openssh.org,cast128-cfb,cast128-ecb,cast128-ofb,cast128-12-cbc@ssh.com,idea-cfb,idea-ecb,idea-ofb,rijndael-cbc@ssh.com,seed-ctr@ssh.com,serpent128-gcm@libassh.org,serpent256-gcm@libassh.org,twofish128-gcm@libassh.org,twofish256-gcm@libassh.org,twofish-cfb,twofish-ecb,twofish-ofb - Added 5 new MACs:
hmac-sha1-96@openssh.com,hmac-sha224@ssh.com,hmac-sha256-2@ssh.com,hmac-sha384@ssh.com,hmac-whirlpool.
v2.5.0 (2021-08-26)
- Fixed crash when running host key tests.
- Handles server connection failures more gracefully.
- Now prints JSON with indents when
-jjis used (useful for debugging). - Added MD5 fingerprints to verbose output.
- Added
-d/--debugoption for getting debugging output; credit Adam Russell. - Updated JSON output to include MD5 fingerprints. Note that this results in a breaking change in the 'fingerprints' dictionary format.
- Updated OpenSSH 8.1 (and earlier) policies to include
rsa-sha2-512andrsa-sha2-256. - Added OpenSSH v8.6 & v8.7 policies.
- Added 3 new key exchanges:
gss-gex-sha1-eipGX3TCiQSrx573bT1o1Q==,gss-group1-sha1-eipGX3TCiQSrx573bT1o1Q==, andgss-group14-sha1-eipGX3TCiQSrx573bT1o1Q==. - Added 3 new MACs:
hmac-ripemd160-96,AEAD_AES_128_GCM, andAEAD_AES_256_GCM.
v2.4.0 (2021-02-23)
- Added multi-threaded scanning support.
- Added built-in Windows manual page (see
-m/--manual); credit Adam Russell. - Added version check for OpenSSH user enumeration (CVE-2018-15473).
- Added deprecation note to host key types based on SHA-1.
- Added extra warnings for SSHv1.
- Added built-in hardened OpenSSH v8.5 policy.
- Upgraded warnings to failures for host key types based on SHA-1.
- Fixed crash when receiving unexpected response during host key test.
- Fixed hang against older Cisco devices during host key test & gex test.
- Fixed improper termination while scanning multiple targets when one target returns an error.
- Dropped support for Python 3.5 (which reached EOL in Sept. 2020).
- Added 1 new key exchange:
sntrup761x25519-sha512@openssh.com.
v2.3.1 (2020-10-28)
- Now parses public key sizes for
rsa-sha2-256-cert-v01@openssh.comandrsa-sha2-512-cert-v01@openssh.comhost key types. - Flag
ssh-rsa-cert-v01@openssh.comas a failure due to SHA-1 hash. - Fixed bug in recommendation output which suppressed some algorithms inappropriately.
- Built-in policies now include CA key requirements (if certificates are in use).
- Lookup function (
--lookup) now performs case-insensitive lookups of similar algorithms; credit Adam Russell. - Migrated pre-made policies from external files to internal database.
- Split single 3,500 line script into many files (by class).
- Added setup.py support; credit Ganden Schaffner.
- Added 1 new cipher:
des-cbc@ssh.com.
v2.3.0 (2020-09-27)
- Added new policy auditing functionality to test adherence to a hardening guide/standard configuration (see
-L/--list-policies,-M/--make-policyand-P/--policy). For an in-depth tutorial, see https://www.positronsecurity.com/blog/2020-09-27-ssh-policy-configuration-checks-with-ssh-audit/. - Created new man page (see
ssh-audit.1file). - 1024-bit moduli upgraded from warnings to failures.
- Many Python 2 code clean-ups, testing framework improvements, pylint & flake8 fixes, and mypy type comments; credit Jürgen Gmach.
- Added feature to look up algorithms in internal database (see
--lookup); credit Adam Russell. - Suppress recommendation of token host key types.
- Added check for use-after-free vulnerability in PuTTY v0.73.
- Added 11 new host key types:
ssh-rsa1,ssh-dss-sha256@ssh.com,ssh-gost2001,ssh-gost2012-256,ssh-gost2012-512,spki-sign-rsa,ssh-ed448,x509v3-ecdsa-sha2-nistp256,x509v3-ecdsa-sha2-nistp384,x509v3-ecdsa-sha2-nistp521,x509v3-rsa2048-sha256. - Added 8 new key exchanges:
diffie-hellman-group1-sha256,kexAlgoCurve25519SHA256,Curve25519SHA256,gss-group14-sha256-,gss-group15-sha512-,gss-group16-sha512-,gss-nistp256-sha256-,gss-curve25519-sha256-. - Added 5 new ciphers:
blowfish,AEAD_AES_128_GCM,AEAD_AES_256_GCM,crypticore128@ssh.com,seed-cbc@ssh.com. - Added 3 new MACs:
chacha20-poly1305@openssh.com,hmac-sha3-224,crypticore-mac@ssh.com.
v2.2.0 (2020-03-11)
- Marked host key type
ssh-rsaas weak due to practical SHA-1 collisions. - Added Windows builds.
- Added 10 new host key types:
ecdsa-sha2-1.3.132.0.10,x509v3-sign-dss,x509v3-sign-rsa,x509v3-sign-rsa-sha256@ssh.com,x509v3-ssh-dss,x509v3-ssh-rsa,sk-ecdsa-sha2-nistp256-cert-v01@openssh.com,sk-ecdsa-sha2-nistp256@openssh.com,sk-ssh-ed25519-cert-v01@openssh.com, andsk-ssh-ed25519@openssh.com. - Added 18 new key exchanges:
diffie-hellman-group14-sha256@ssh.com,diffie-hellman-group15-sha256@ssh.com,diffie-hellman-group15-sha384@ssh.com,diffie-hellman-group16-sha384@ssh.com,diffie-hellman-group16-sha512@ssh.com,diffie-hellman-group18-sha512@ssh.com,ecdh-sha2-curve25519,ecdh-sha2-nistb233,ecdh-sha2-nistb409,ecdh-sha2-nistk163,ecdh-sha2-nistk233,ecdh-sha2-nistk283,ecdh-sha2-nistk409,ecdh-sha2-nistp192,ecdh-sha2-nistp224,ecdh-sha2-nistt571,gss-gex-sha1-, andgss-group1-sha1-. - Added 9 new ciphers:
camellia128-cbc,camellia128-ctr,camellia192-cbc,camellia192-ctr,camellia256-cbc,camellia256-ctr,aes128-gcm,aes256-gcm, andchacha20-poly1305. - Added 2 new MACs:
aes128-gcmandaes256-gcm.
v2.1.1 (2019-11-26)
- Added 2 new host key types:
rsa-sha2-256-cert-v01@openssh.com,rsa-sha2-512-cert-v01@openssh.com. - Added 2 new ciphers:
des,3des. - Added 3 new PuTTY vulnerabilities.
- During client testing, client IP address is now listed in output.
v2.1.0 (2019-11-14)
- Added client software auditing functionality (see
-c/--client-auditoption). - Added JSON output option (see
-j/--jsonoption; credit Andreas Jaggi). - Fixed crash while scanning Solaris Sun_SSH.
- Added 9 new key exchanges:
gss-group1-sha1-toWM5Slw5Ew8Mqkay+al2g==,gss-gex-sha1-toWM5Slw5Ew8Mqkay+al2g==,gss-group14-sha1-,gss-group14-sha1-toWM5Slw5Ew8Mqkay+al2g==,gss-group14-sha256-toWM5Slw5Ew8Mqkay+al2g==,gss-group15-sha512-toWM5Slw5Ew8Mqkay+al2g==,diffie-hellman-group15-sha256,ecdh-sha2-1.3.132.0.10,curve448-sha512. - Added 1 new host key type:
ecdsa-sha2-1.3.132.0.10. - Added 4 new ciphers:
idea-cbc,serpent128-cbc,serpent192-cbc,serpent256-cbc. - Added 6 new MACs:
hmac-sha2-256-96-etm@openssh.com,hmac-sha2-512-96-etm@openssh.com,hmac-ripemd,hmac-sha256-96@ssh.com,umac-32@openssh.com,umac-96@openssh.com.
v2.0.0 (2019-08-29)
- Forked from https://github.com/arthepsy/ssh-audit (development was stalled, and developer went MIA).
- Added RSA host key length test.
- Added RSA certificate key length test.
- Added Diffie-Hellman modulus size test.
- Now outputs host key fingerprints for RSA and ED25519.
- Added 5 new key exchanges:
sntrup4591761x25519-sha512@tinyssh.org,diffie-hellman-group-exchange-sha256@ssh.com,diffie-hellman-group-exchange-sha512@ssh.com,diffie-hellman-group16-sha256,diffie-hellman-group17-sha512. - Added 3 new encryption algorithms:
des-cbc-ssh1,blowfish-ctr,twofish-ctr. - Added 10 new MACs:
hmac-sha2-56,hmac-sha2-224,hmac-sha2-384,hmac-sha3-256,hmac-sha3-384,hmac-sha3-512,hmac-sha256,hmac-sha256@ssh.com,hmac-sha512,hmac-512@ssh.com. - Added command line argument (
-t/--timeout) for connection & reading timeouts. - Updated CVEs for libssh & Dropbear.
v1.7.0 (2016-10-26)
- implement options to allow specify IPv4/IPv6 usage and order of precedence
- implement option to specify remote port (old behavior kept for compatibility)
- add colors support for Microsoft Windows via optional colorama dependency
- fix encoding and decoding issues, add tests, do not crash on encoding errors
- use mypy-lang for static type checking and verify all code
v1.6.0 (2016-10-14)
- implement algorithm recommendations section (based on recognized software)
- implement full libssh support (version history, algorithms, security, etc)
- fix SSH-1.99 banner recognition and version comparison functionality
- do not output empty algorithms (happens for misconfigured servers)
- make consistent output for Python 3.x versions
- add a lot more tests (conf, banner, software, SSH1/SSH2, output, etc)
- use Travis CI to test for multiple Python versions (2.6-3.5, pypy, pypy3)
v1.5.0 (2016-09-20)
- create security section for related security information
- match and output assigned CVE list and security issues for Dropbear SSH
- implement full SSH1 support with fingerprint information
- automatically fallback to SSH1 on protocol mismatch
- add new options to force SSH1 or SSH2 (both allowed by default)
- parse banner information and convert it to specific software and OS version
- do not use padding in batch mode
- several fixes (Cisco sshd, rare hangs, error handling, etc)
v1.0.20160902
- implement batch output option
- implement minimum output level option
- fix compatibility with Python 2.6
v1.0.20160812
- implement SSH version compatibility feature
- fix wrong mac algorithm warning
- fix Dropbear SSH version typo
- parse pre-banner header
- better errors handling
v1.0.20160803
- use OpenSSH 7.3 banner
- add new key-exchange algorithms
v1.0.20160207
- use OpenSSH 7.2 banner
- additional warnings for OpenSSH 7.2
- fix OpenSSH 7.0 failure messages
- add rijndael-cbc failure message from OpenSSH 6.7
v1.0.20160105
- multiple additional warnings
- support for none algorithm
- better compression handling
- ensure reading enough data (fixes few Linux SSH)
v1.0.20151230
- Dropbear SSH support
v1.0.20151223
- initial version






