Awesome
LeanParameterOptimization
Parameter optimization for Lean Trading Algorithms
This toolset allows you to execute multiple parallel backtests using a local Lean clone. It is possible to configure several different optimization methods to fit your trading algorithm to an array of different success measures.
You must edit the config file optimization.json to define parameters and other settings. The parameter values are fed into the Lean config and can be accessed in an algorithm using the QuantConnect.Configuration.Config methods.
An example algorithm is provided here: ParameterizedAlgorithm.cs and here: ParameterizedSharedAppDomainAlgorithm.py
Quickstart
- Clone Lean from https://github.com/jameschch/Lean.
- Clone LeanParameterOptimization so that it shares the same parent folder as the Lean clone.
- Edit the optimization.json file and enter the location of your trading algorithm in "algorithmLocation".
- Now enter the class name of your algorithm in "algorithmTypeName".
- Enter the location of your trade and quote bar data in the "dataFolder" setting.
- Configure the "maxThreads" to define the number of parallel backtests (ignored for Python).
- Set "algorithmLanguage" to CSharp or Python.
- Build and run the project "Jtc.Optimization.Launcher.Legacy"
Configuration
Full documentation is provided in comments: OptimizerConfiguration
A few important options:
fitnessTypeName
Genetic
The default OptimizerFitness is a simple Sharpe Ratio tournament. There is also CompoundingAnnualReturnFitness to maximize raw returns. It is possible to optimize any Lean statistic using ConfiguredFitness.
SharpeMaximizer
Specifying the SharpeMaximizer fitness allows access to all of the optimization methods provided by the SharpLearning library. These include Random Search. Grid Search, Particle Swarm, Smac and several others.
NFoldCrossSharpeMaximizer
The simple SharpeMaximizer has been extended in NFoldCrossSharpeMaximizer so that the success score is measured over N-fold periods. This will prevent overfitting to a single in-sample period.
WalkForwardSharpeMaximizer
Also now available is an experimental release of N-fold Walk Forward optimization.
WalkForwardWeightedMetricSharpeMaximizer
An attempt to extend the single iteration walk forward optimizer has now evolved into a specialized ensemble machine learning method.
An optimization algorithm must be selected as iteration parent. This optimizer will improve a weighted metric cost function composed of the following: i) The out-sample score of each walk forward period fold, which is derived from an optimization of the in-sample fold using a separately selected optimization algorithm. ii) The standard deviation of the parameter search ranges (the genes) drawn from the best performer in each fold (the alpha).
After each parent iteration, the fold optimization range is constrained with the highest and lowest parameter values of the fold alphas. The effect of this gradual tightening of constraints is analogous to synthesized annealing, allowing convergence on a minimized range of successful parameters.
The parent optimizer will stop early for cases in which all out-sample scores return a failure. This indicates that the in-sample does not generalize and can often be resolved with a longer optimization period.
useSharedAppDomain
If it possible to run each parallel backtest in it's own context, or in a single context. The latter option can be useful for training a machine learning model and tends to execute more quickly. For Python algorithms this setting is ignored as only a single context is supported.
minimumTrades
Setting this value correctly will prevent fitting to a small number of high-success events that are unlikely to generalize. Any backtest not meeting the minimum trades will be ignored.
enableRunningDuplicateParameters
When training a non-deterministic machine learning model (such as QLearning), this will allow executing the same parameters multiple times on a single period. By default, duplicate parameters are not executed more than once.
Optimizers
The optimizers support multiple parallel executions of a Lean algorithm as standard. Currently, the following methods are available:
- Genetic Tournament
- Random Search
- Grid (exhaustive) Search
- Particle Swarm
- Bayesian
- Globalized Bounded Nelder Mead
- Smac
These methods can target several fitness and maximization goals:
- N-Fold Cross-Validated Sharpe Ratio
- N-Fold Cross-Validated Compounding Annual Return
- Walk Forward Period Sharpe Ratio
- Nested Cross-Validated Sharpe Ratio
- Maximization and minimization of most Lean algorithm statistics (Sharpe Ratio, Alpha, Win Rate, etc)
User Interfaces
Now also provided are several Blazor interfaces:
- Optimization Config Editor - https://optimizers.ml/config
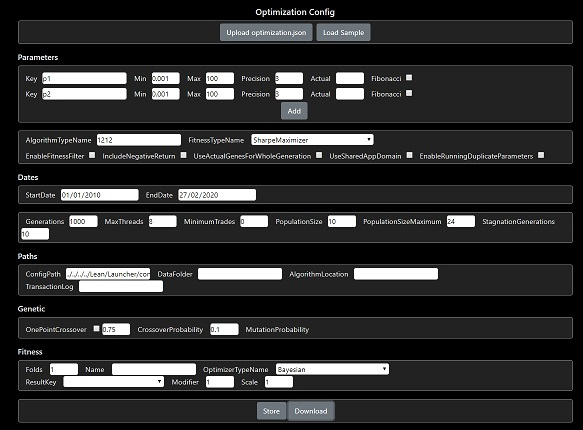
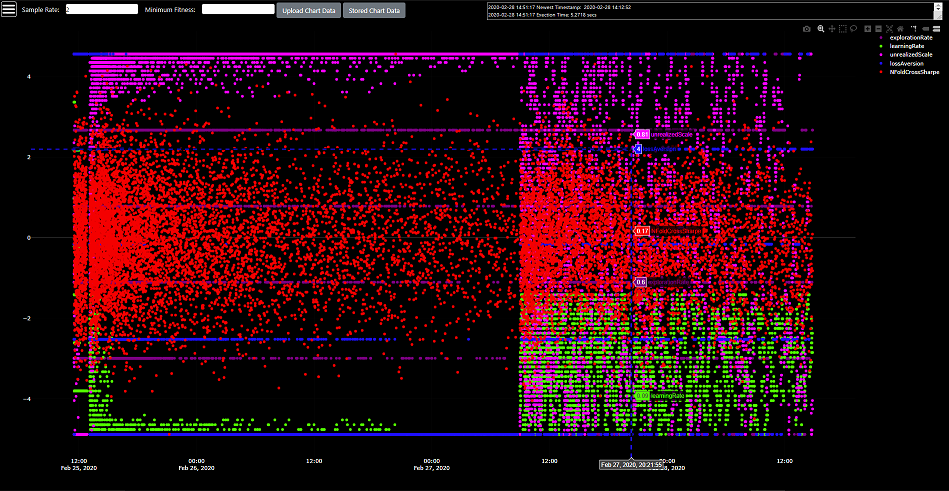
- Optimization Results Chart - https://optimizers.ml/chart
- Algorithm Code Editor and Runner (C#, Javascript) - https://optimizers.ml/codeeditor
WIP
- Python multi-threaded parallel optimization
- Python running in browser
- User supplied C# to wasm compile in browser
- Genetic optimization in browser
- Other optimization methods in browser
- Script to modify base Lean clone with required changes
Issues
- Logging to console for multiple contexts was broken during ,net5 upgrade
- Specifc changes to base Lean code are necessary. Please use this fork: https://github.com/jameschch/Lean