Awesome
ealogger
The easy asynchronous logger provides a simple to use yet powerful logging functionality for C++ applications. You can use it to log to console, to a file or system log (syslog). It was designed to be fast (uses Threads) and flexible. The library registers a signal handler for SIGUSR1 and is compatible with logrotate (only available on linux currently). It was tested on Linux, Windows and OS X.
<!-- START doctoc generated TOC please keep comment here to allow auto update --> <!-- DON'T EDIT THIS SECTION, INSTEAD RE-RUN doctoc TO UPDATE -->- Features
- Setting up ealogger
- Usage
- API Documentation
- Performance
- Development
- Status
- Bugs, feature requests, ideas
- FAQ
- License
Features
- Write log files to different sinks like files, console, syslog
- Easy to add your own sinks/targets
- Very fast in asynchronous mode
- Simple to use and no dependencies
- Extensive API documentation using doxygen
- Cross Platform
- Unit Tests based on Catch
Setting up ealogger
ealogger source code is hosted on github.com. You may either compile the source code or use binary packages.
Dependencies
Make sure your development environment meets these requirements
- cmake >= 3.4
- gcc >= 4.9
- clang >= 3.3
- MSVC >= 14 (Visual Studio 2015)
Installation
The Library uses the CMake build system. This way you can easily build it on different platforms.
CMake Options
There are some cmake options you can customize for your requirements
- BUILD_EXAMPLES (default off) : Setting this to ON will compile all the example
applications in the
examplessub folder. - BUILD_UNIT_TEST (default off): Build the Catch based unit test application
- BUILD_SHARED_LIBS (default on): Whether or not to compile as shared library
Linux / OS X
Example for building a shared library without debug symbols. We are using an out of source build here.
# clone the sources from github
git clone https://github.com/crapp/ealogger.git ealogger
# change directory and create build directory
cd ealogger
mkdir build
cd build
# run cmake from within the build directory
cmake ../ -G "Unix Makefiles" -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=Release
make
Precompiled packages for Linux distributions
Windows
This shows how to create a Visual Studio Solution with cmake
# create build directory
mkdir build
cd build
# Please change these options so they suit your build evironment.
cmake -G"Visual Studio 14 2015 Win64" ../
Open the solution file with Visual Studio and compile the library.
You may also use different generators for other platforms.
Usage
Usage of the logger is easy. For a start have a look at the example applications and the API Documentation.
Minimum Code example
Here is a small example. First we instantiate a new Logger object, than we print some messages.
namespace eal = ealogger;
namespace con = ealogger::constants;
std::unique_ptr<eal::Logger> log = std::unique_ptr<eal::Logger>(
new eal::Logger());
log->set_min_lvl(con::LOGGER_SINK::EAL_CONSOLE, con::LOG_LEVEL::EAL_INFO);
log->eal_debug("Do you see me?");
log->eal_info("An info message")
log->eal_warn("A warning message");
log->eal_error("An error message");
log->eal_fatal("A fatal message");
This will output:
2016-03-19 15:12:49 INFO: An info message
2016-03-19 15:12:49 WARNING: A warning message
2016-03-19 15:12:49 ERROR: An error message
2016-03-19 15:12:49 FATAL: A fatal message
As you can see the DEBUG level message is not printed. This is because of the minimum severity we set when we created the object.
Colorized Logfiles using multitail
Logfiles are sometimes difficult to read. So some sort of color highlighting might be useful. If you are using a Unix system you may try multitail
Here is a screenshot how this might look like
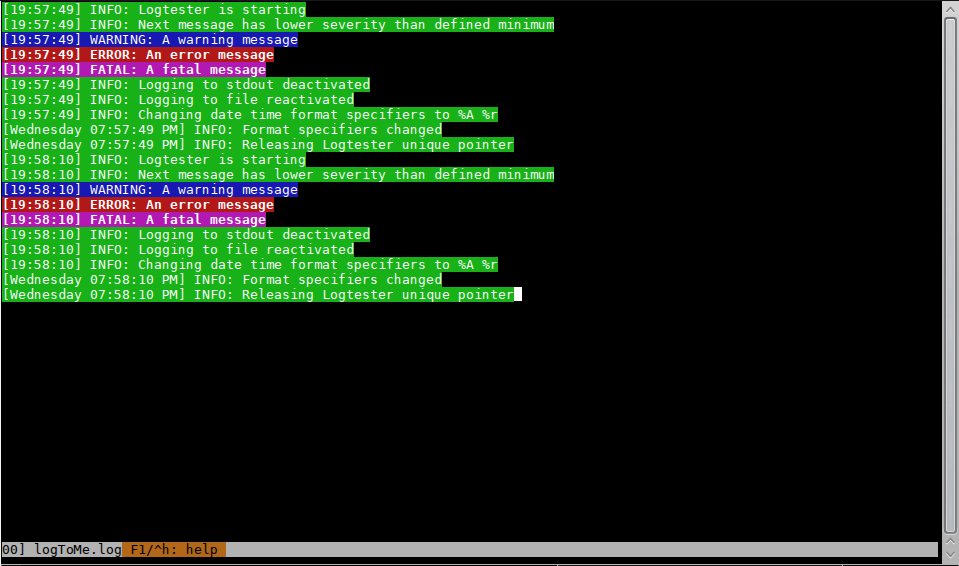
The color scheme for multitail I used to generate the colors in the screenshot looks like this
colorscheme:ealogger
cs_re:,magenta,bold:^.+FATAL.+
cs_re:,red,bold:^.+ERROR.+
cs_re:,blue:^.+WARNING.+
cs_re:,green:^.+INFO.+
Put it in ~/.multitailrc and start mutlitail
multitail -cS ealogger mylogfile.log
API Documentation
API documentation is available as doxygen generated html documentation hosted by github.io
The doxygen project file is located in the doc folder and can be used to generate a version of the documentation on your system.
Performance
ealogger is pretty fast in asynchronous mode. Here are some benchmarks for logging 100000 messages to a file.
Linux machine with GCC 6.1 and an Intel i5-3470
$ examples/ealogger_bench
Time in milliseconds to put messages on a queue: 296ms
Time untill all messages were written to the logfile: 3042ms
Development
The most important facts of the ealogger development process are explained here
Unit Tests
I am using the great Catch automated test framework. Currently only small parts of the code are covered by unit tests.
The unit tester can be run with ealogger_test. This will execute all test cases
and output the results. Have a look at the Catch framework documentation for
command line options you can use to run only specific test cases, or change the
application output.
Continuous Integration
Travis CI is used as continuous integration service. The ealogger github repository is linked to Travis CI. You can see the build history for the master branch and all release branches on the travis project page.
Besides testing compilation on different systems and compilers I also run the unit tests after the application was compiled successfully.
Branches
The github repository of ealogger has several different branches
- master: Main development branch. Everything in here is guaranteed to compile and is tested (at least a little bit :)). This is the place for new features and bugfixes. Pull requests welcome.
- dev: Test branch. Code is guaranteed to compile on the developers build environment. Nothing more nothing less.
- release-x.x: Branch for a release. Only bugfixes are allowed here. Pull requests welcome.
- gh-pages: Special branch for the static API HTML documentation that will be hosted by github.io. Content is generated with doxygen.
Coding standards
The source code is formatted with clang-format using the following configuration
Language : Cpp,
BasedOnStyle : LLVM,
AccessModifierOffset : -4,
AllowShortIfStatementsOnASingleLine : false,
AlwaysBreakTemplateDeclarations : true,
ColumnLimit : 81,
IndentCaseLabels : false,
Standard : Cpp11,
IndentWidth : 4,
TabWidth : 4,
BreakBeforeBraces : Linux,
CommentPragmas : '(^ IWYU pragma : )|(^.*\[.*\]\(.*\).*$)|(^.*@brief|@param|@return|@throw.*$)|(/\*\*<.*\*/)'
Versioning
I decided to use semantic versioning and stick to their rules.
Given a version number MAJOR.MINOR.PATCH, increment the:
MAJOR version when you make incompatible API changes,
MINOR version when you add functionality in a backwards-compatible manner, and
PATCH version when you make backwards-compatible bug fixes.
We are currently at this stage
Major version zero (0.y.z) is for initial development. Anything may change at any time. The public API should not be considered stable.
Status
This library has not reached a stable version yet. Meaning the public API and other things may be subjected to changes at any time. There have been no code reviews so far and unit tests only cover small parts of the source code. In spite of all that the library is absolutely usable and works great for what it was developed for.
Bugs, feature requests, ideas
Please use the github bugtracker to submit bugs or feature requests
FAQ
Yet another logger lib, why?
I wanted to have a flexible and easy to use logger lib without any dependencies for my C++ projects. This project started in 2013 and there wasn't any C++ library that suited my needs. I am doing lots of things with embedded hardware and other time / performance critical things so it was important for me to have a really fast logger and not one with a lot of features.
Why does it not have feature X?
Feel free to fork the project and make a pull request!
License
Copyright (C) 2013 - 2016 Christian Rapp
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
You may obtain a copy of the License at
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
limitations under the License.


