Awesome

Introduction
Terrascan is a static code analyzer for Infrastructure as Code. Terrascan allows you to:
- Seamlessly scan infrastructure as code for misconfigurations.
- Monitor provisioned cloud infrastructure for configuration changes that introduce posture drift, and enables reverting to a secure posture.
- Detect security vulnerabilities and compliance violations.
- Mitigate risks before provisioning cloud native infrastructure.
- Offers flexibility to run locally or integrate with your CI\CD.
Resources
-
To try Terrascan in your browser, see the Terrascan Sandbox https://www.tenable.com/terrascan
-
To learn more about Terrascan's features and capabilities, see the documentation portal: https://runterrascan.io
Key features
- 500+ Policies for security best practices
- Scanning of Terraform (HCL2)
- Scanning of AWS CloudFormation Templates (CFT)
-
- Scanning of Azure Resource Manager (ARM)
- Scanning of Kubernetes (JSON/YAML), Helm v3, and Kustomize
- Scanning of Dockerfiles
- Support for AWS, Azure, GCP, Kubernetes, Dockerfile, and GitHub
- Integrates with docker image vulnerability scanning for AWS, Azure, GCP, Harbor container registries.
Quick Start
Step 1: Install
Terrascan supports multiple ways to install and is also available as a Docker image. See Terrascan's releases page for the latest version of builds in all supported platforms. Select the correct binary for your platform.
Install as a native executable
$ curl -L "$(curl -s https://api.github.com/repos/tenable/terrascan/releases/latest | grep -o -E "https://.+?_Darwin_x86_64.tar.gz")" > terrascan.tar.gz
$ tar -xf terrascan.tar.gz terrascan && rm terrascan.tar.gz
$ install terrascan /usr/local/bin && rm terrascan
$ terrascan
Install on ArchLinux / Manjaro via AUR
ArchLinux and Manjaro users can install by:
yay -S terrascan
Install via brew
Homebrew users can install by:
$ brew install terrascan
Docker image
Terrascan is also available as a Docker image and can be used as follows
$ docker run tenable/terrascan
Refer to documentation for information.
Step 2: Scan
To scan your code for security issues you can run the following (defaults to scanning Terraform).
$ terrascan scan
Note: Terrascan will exit with an error code if any errors or violations are found during a scan.
List of possible Exit Codes
| Scenario | Exit Code |
|---|---|
| scan summary has errors and violations | 5 |
| scan summary has errors but no violations | 4 |
| scan summary has violations but no errors | 3 |
| scan summary has no violations or errors | 0 |
| scan command errors out due to invalid inputs | 1 |
Step 3: Integrate with CI\CD
Terrascan can be integrated into CI/CD pipelines to enforce security best practices. Please refer to our documentation to integrate with your pipeline.
Terrascan Commands
You can use the terrascan command with the following options:
$ terrascan
Terrascan
Usage:
terrascan [command]
Available Commands:
help Help about any command
init Initialize Terrascan
scan Detect compliance and security violations across Infrastructure as Code.
server Run Terrascan as an API server
version Terrascan version
Flags:
-c, --config-path string config file path
-h, --help help for terrascan
-l, --log-level string log level (debug, info, warn, error, panic, fatal) (default "info")
-x, --log-type string log output type (console, json) (default "console")
-o, --output string output type (human, json, yaml, xml) (default "human")
Use "terrascan [command] --help" for more information about a command.
Policies
Terrascan policies are written using the Rego policy language. Every rego includes a JSON "rule" file which defines metadata for the policy. By default, Terrascan downloads policies from Terrascan repositories while scanning for the first time. However, if you want to download the latest policies, you need to run the Initialization process. See Usage for information about the Initialization process.
Note: The scan command will implicitly run the initialization process if there are no policies found.
Docker Image Vulnerabilities
You can use the --find-vuln flag to collect vulnerabilities as reported in its registry as part of Terrascan's output. Currently Terrascan supports Elastic Container Registry (ECR), Azure Container Registry, Google Container Registry, and Google Artifact Registry.
The --find-vuln flag can be used when scanning IaC files as follows:
$ terrascan scan -i <IaC provider> --find-vuln
For more information and explanation of how to setup your environment to authenticate with the registry's APIs see the usage documentation.
Customizing scans
By default, Terrascan scans your entire configuration against all policies. However, Terrascan supports granular configuration of policies and resources.
Read more about in-file instrumentation and the config file on our documentation site.
For now, some quick tips:
- Exclude a particular policy for a specific resource.
- Manually configure policies to be suppressed or applied globally from a scan across all resources or, for just a particular resource.
How to exclude a policy while scanning a resource
You can configure Terrascan to skip a particular policy (rule) while scanning a resource. Follow these steps depending on your platform:
Terraform
Use Terraform scripts to configure Terrascan to skip rules by inserting a comment with the phrase "ts:skip=<RULENAME><SKIP_REASON>". The comment should be included inside the resource as shown in the example below.

Kubernetes
In Kubernetes yamls, you can configure Terrascan to skip policies by adding an annotation as seen in the snippet below.

How to include or exclude specific policies or resources from being scanned
Use the Terrascan config file to manually select the policies which should be included or excluded from the entire scan. This is suitable for edge use cases. Use the "in-file" suppression option to specify resources that should be excluded from being tested against selected policies. This ensures that the policies are skipped only for particular resources, rather than all of the resources.

Sample scan output
Terrascan's default output is a list of violations present in the scanned IaC. A sample output:
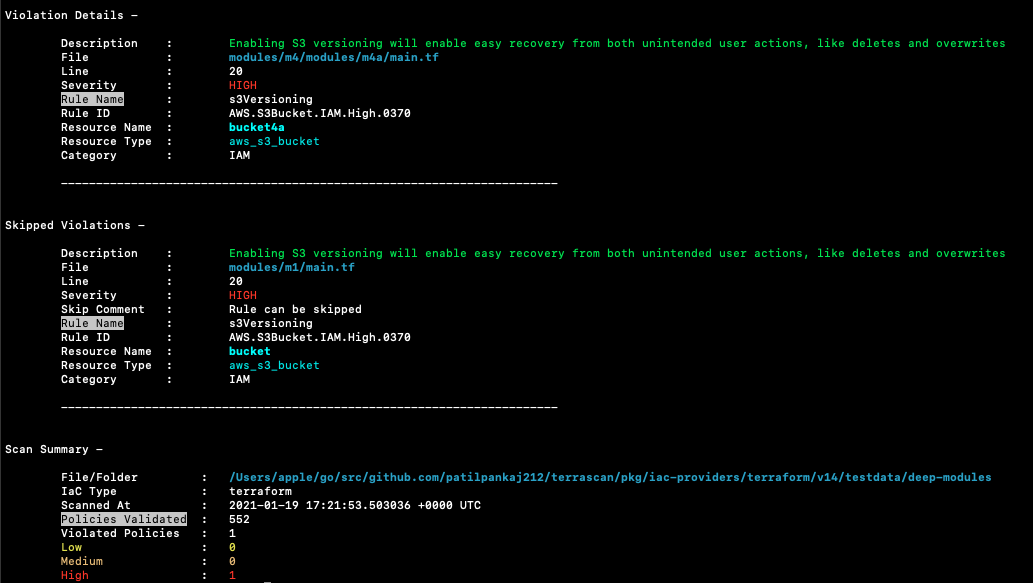
Building Terrascan
Terrascan can be built locally. This is helpful if you want to be on the latest version or when developing Terrascan. gcc and Go 1.19 or above are required.
$ git clone git@github.com:tenable/terrascan.git
$ cd terrascan
$ make build
$ ./bin/terrascan
To build your own docker, refer to this example (Alpine Linux):
FROM golang:alpine AS build-env
RUN apk add --update git
RUN git clone https://github.com/tenable/terrascan && cd terrascan \
&& CGO_ENABLED=0 GO111MODULE=on go build -o /go/bin/terrascan cmd/terrascan/main.go
Developing Terrascan
To learn more about developing and contributing to Terrascan, refer to the contributing guide.
Code of Conduct
We believe having an open and inclusive community benefits all of us. Please note that this project is released with a Contributor Code of Conduct. By participating in this project you agree to abide by its terms.
License
Terrascan is licensed under the Apache 2.0 License.




