Awesome
COBOL Source editing for Visual Studio Code
This unofficial extension provides syntax highlighting for Rocket ® COBOL based COBOL languages (previously Micro Focus COBOL), as well as syntax highlighting for other related languages/file formats such JCL, PL/I and directive files and Unit Test Reports.
Some of the features this extension provides are:
- Colourisation and problem matchers for the following Rocket COBOL dialects:
- COBOL tab key support (configurable)
- COBOL source navigation support
- Shortcuts/Commands for navigation to divisions
- Fixed format margin support
- Outline view/breadcrumb support
- Text based find all references
- Peek definition
- Copybook navigation
- Intellisense support for keywords in lowercase, uppercase and camelcase
- Snippet support for various keywords
- including callable COBOL library routines
- and intrinsic functions
- Source code linter for in house/internal COBOL standards
- Compiler directive file colourisation
- Unit test report colourisation
- Drag & Drop filename into source code inserts copybook verb
- COBOL Source Utilities
- Remove column numbers
- Remove program identification area
- Remove all comments
- Text based rename paragraphs/sections and variables
- Make all keywords/fields/sections uppercased, lowercased or camelcased
- Re-sequence column numbers
- Optional xedit'ish key bindings
- Align storage items
- Text to hex literals & reverse
- Documentation for using development containers with Visual COBOL
- and more..
While also being able to use it with the official Rocket COBOL extension (for debugging for example).
Examples of features provided
Code colorization for COBOL, PL/I and JCL
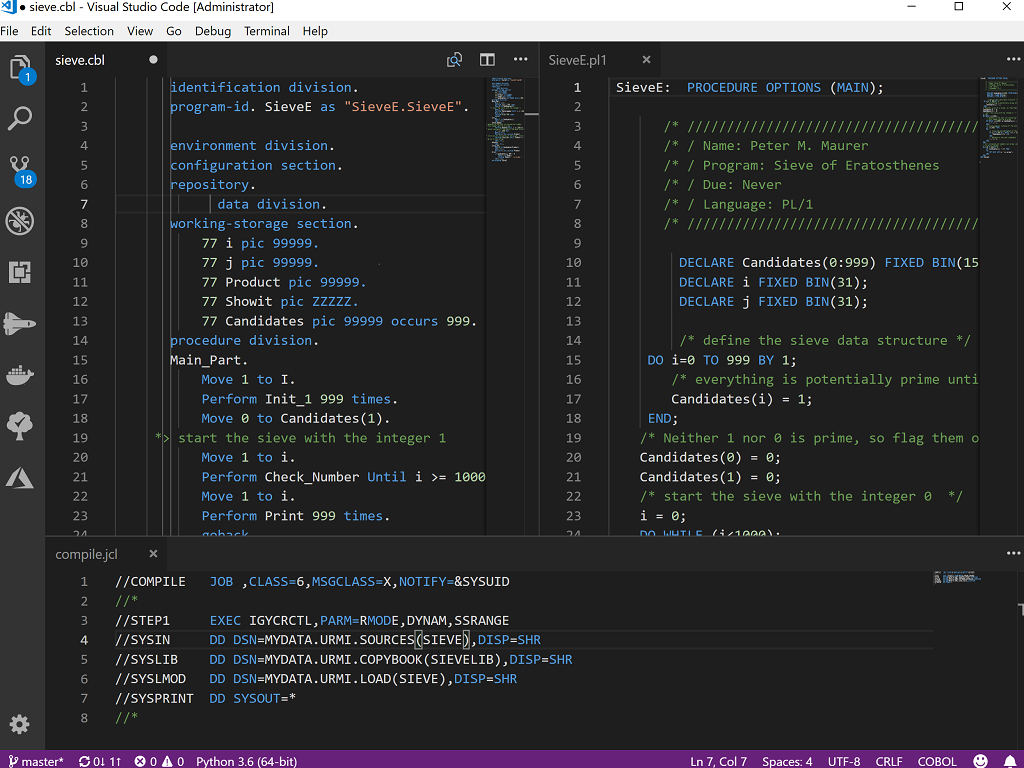
Intellisense example
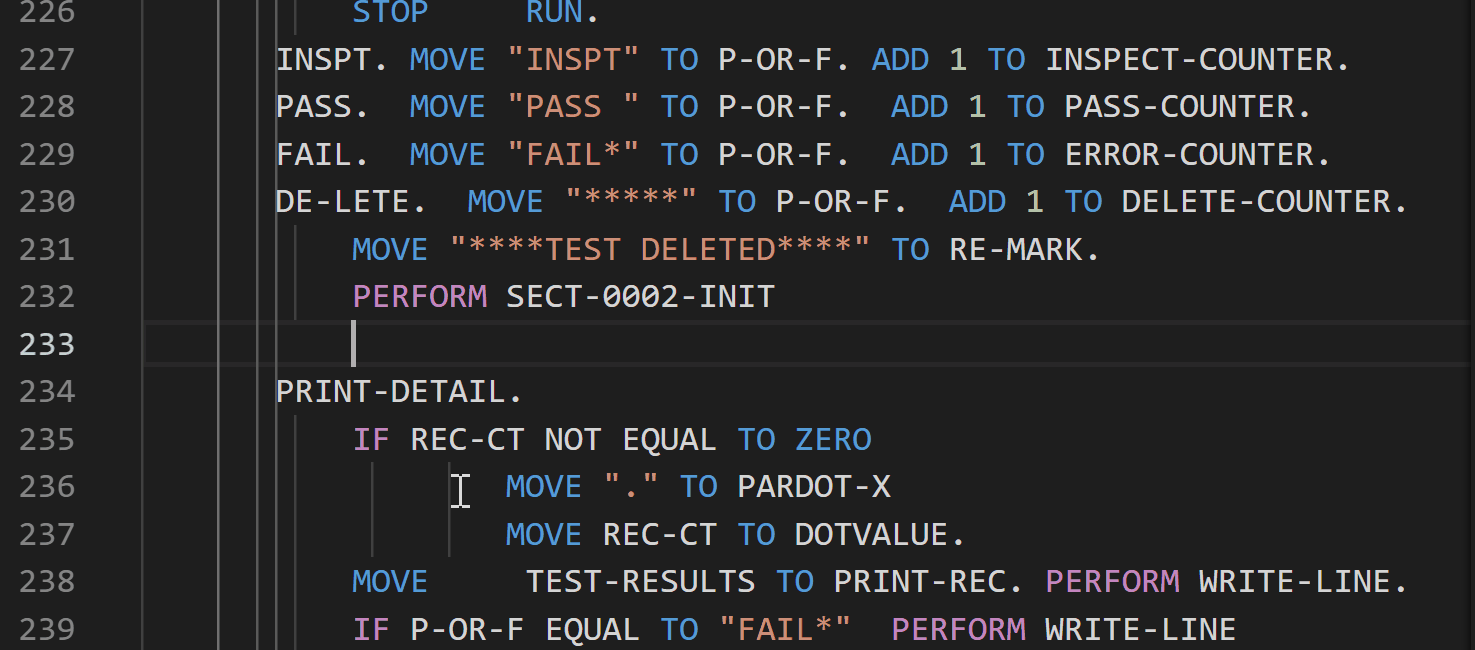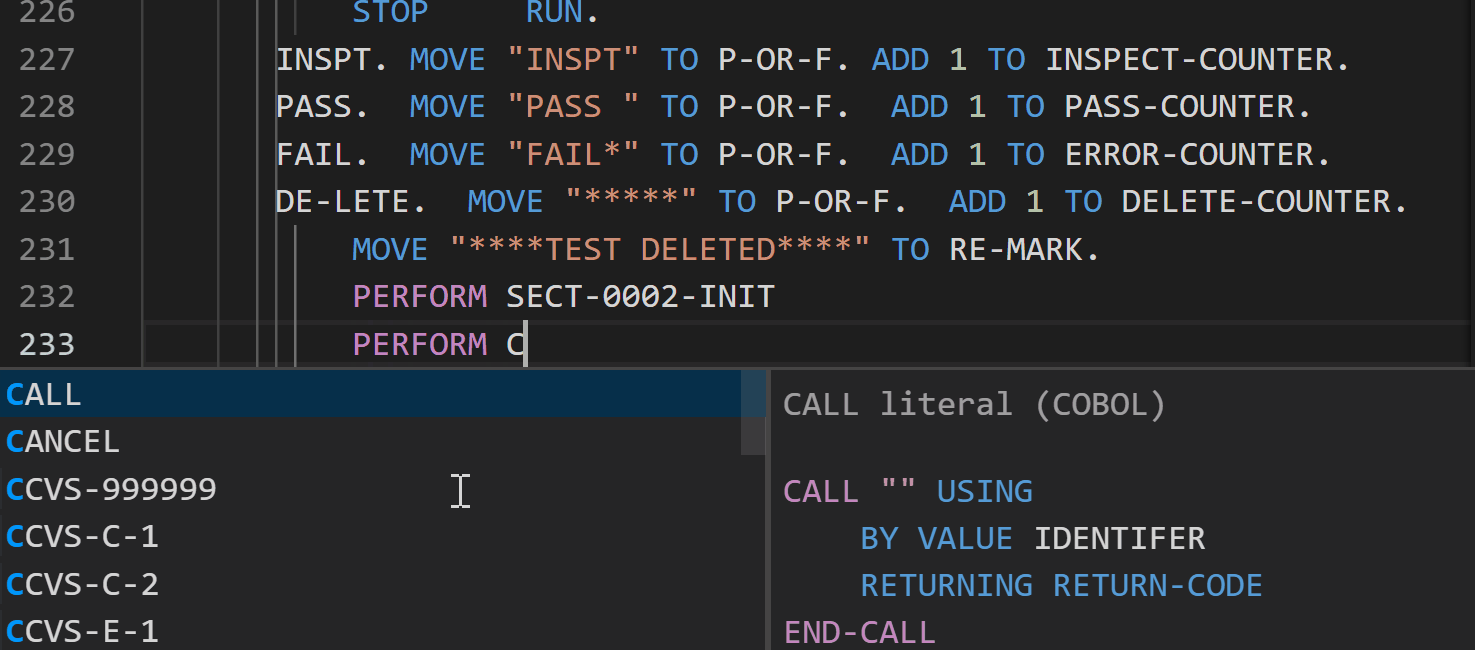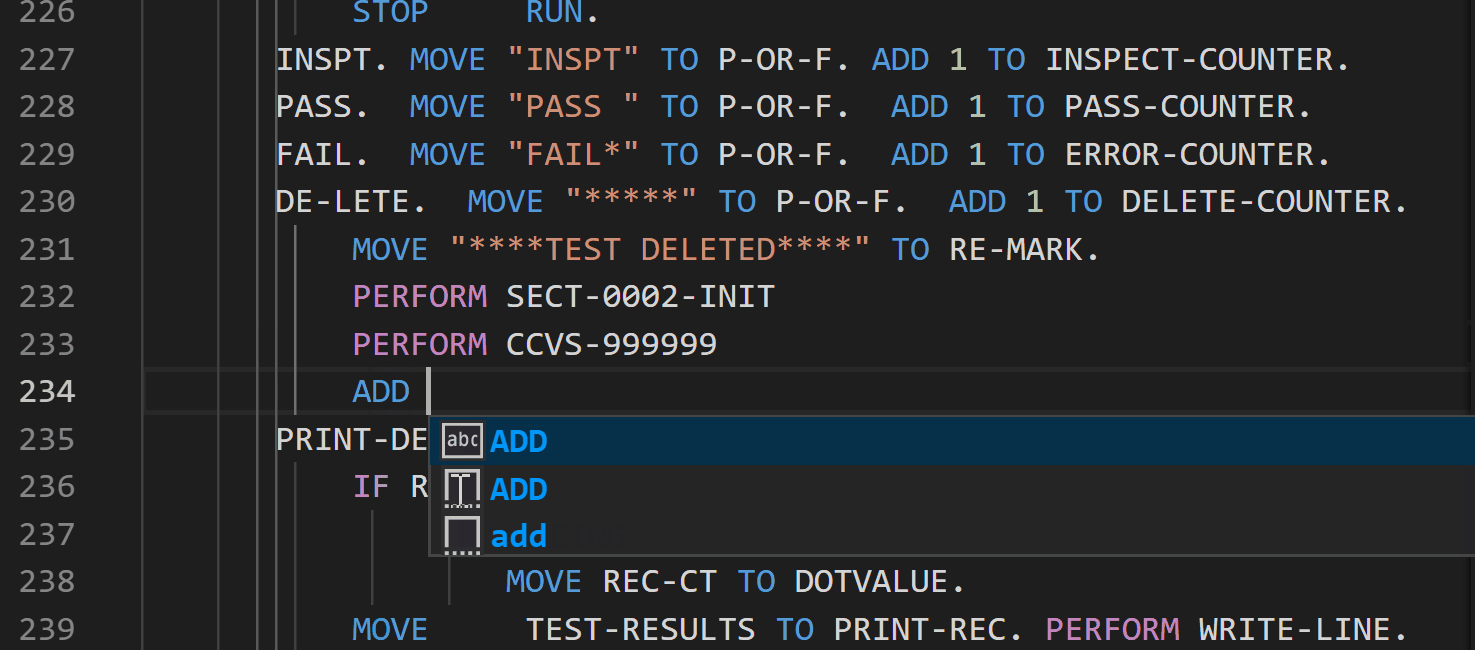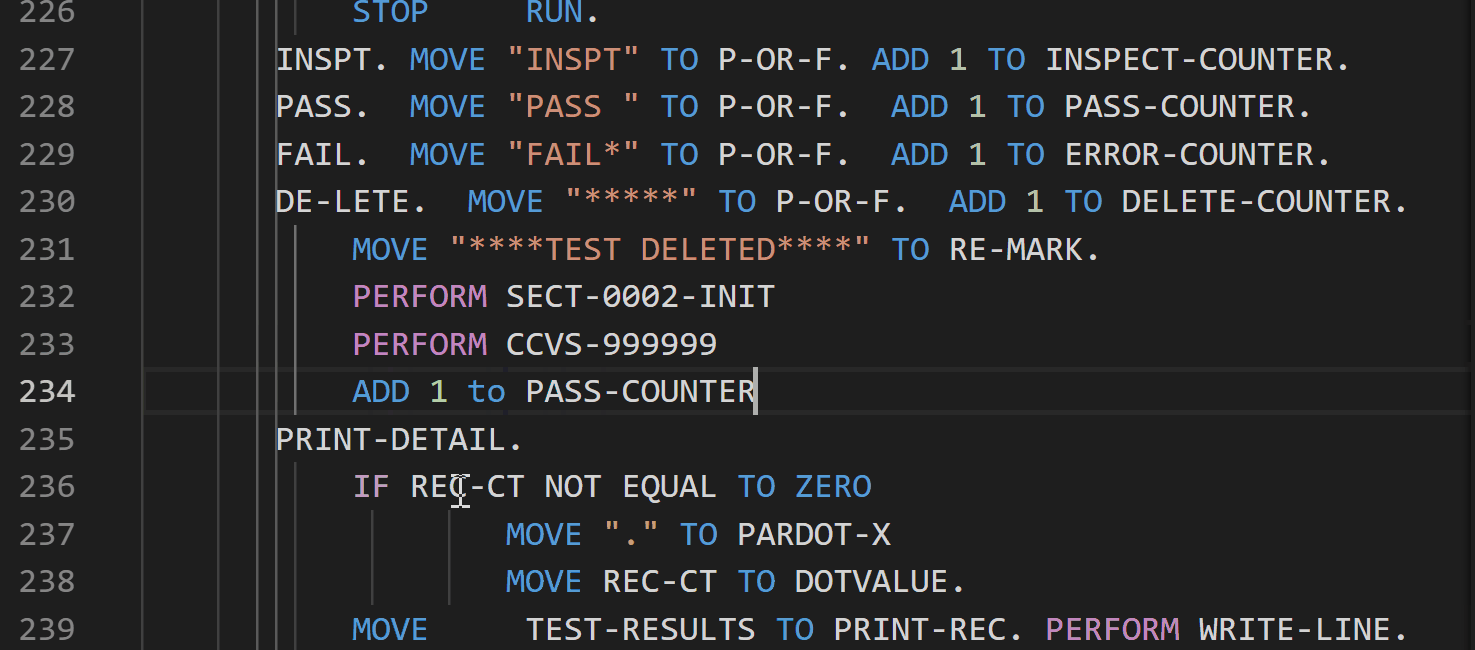
Breadcrumb support
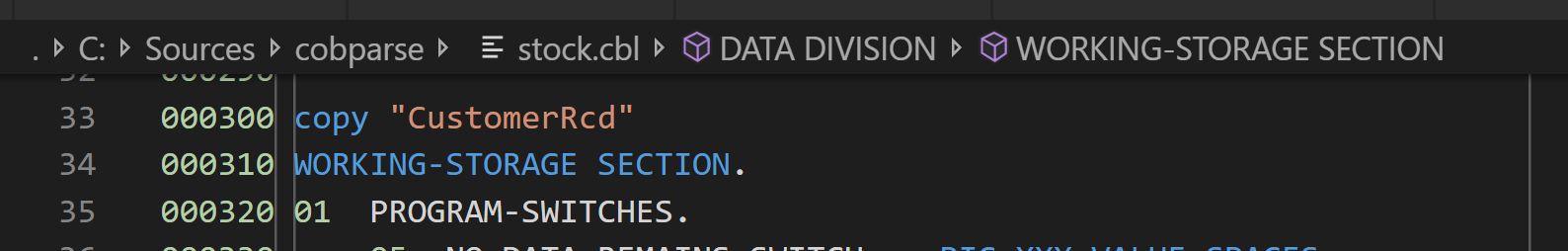
Outline support
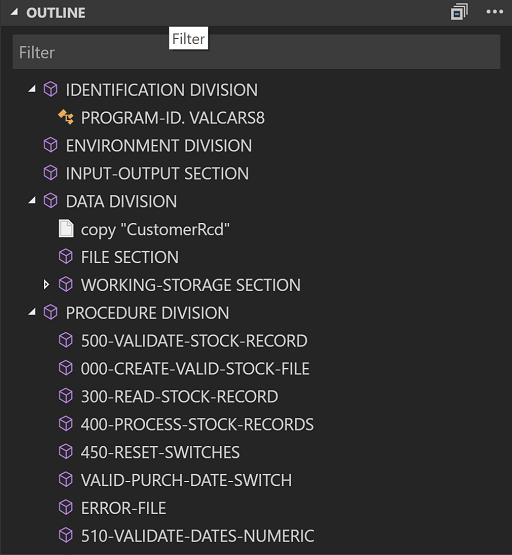
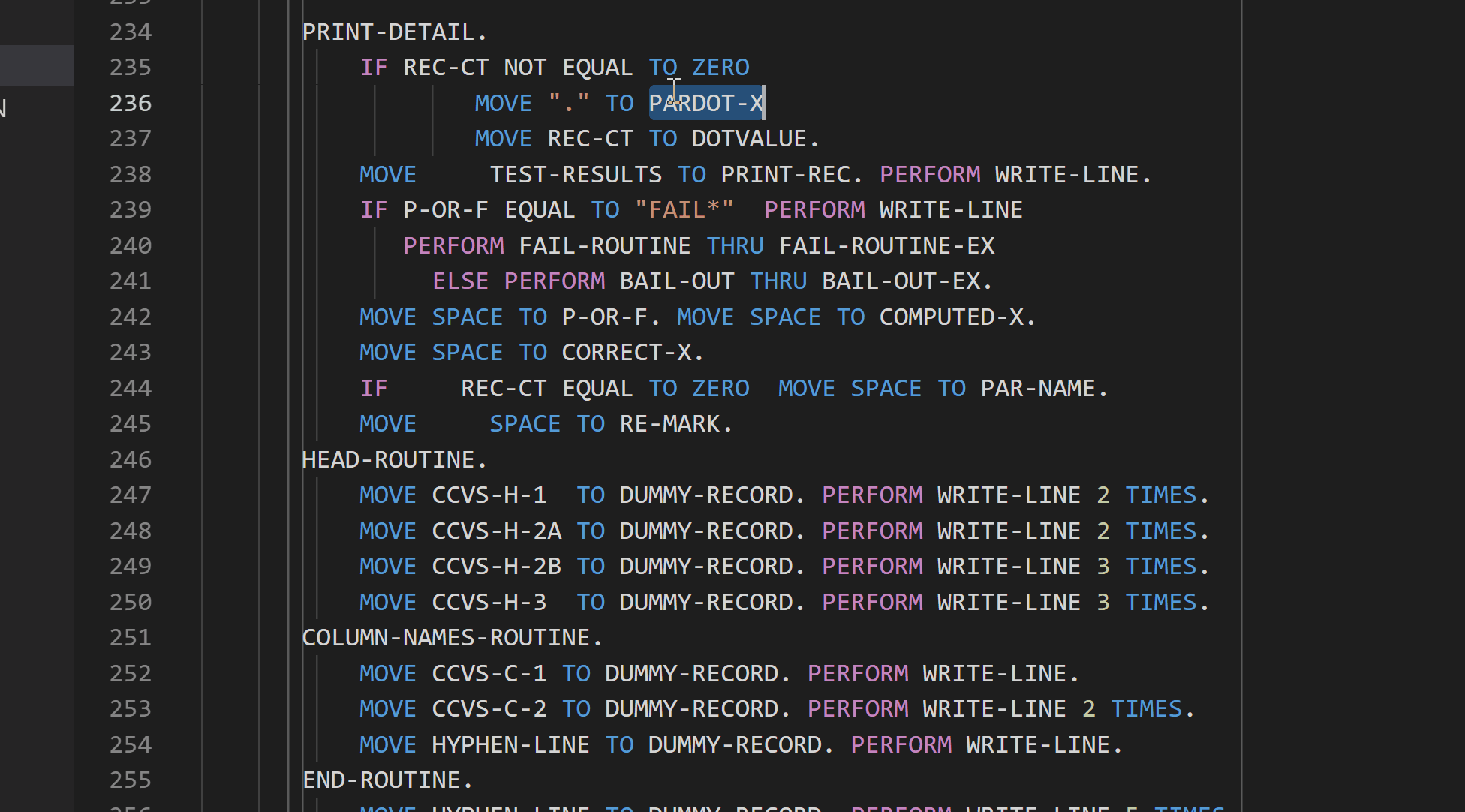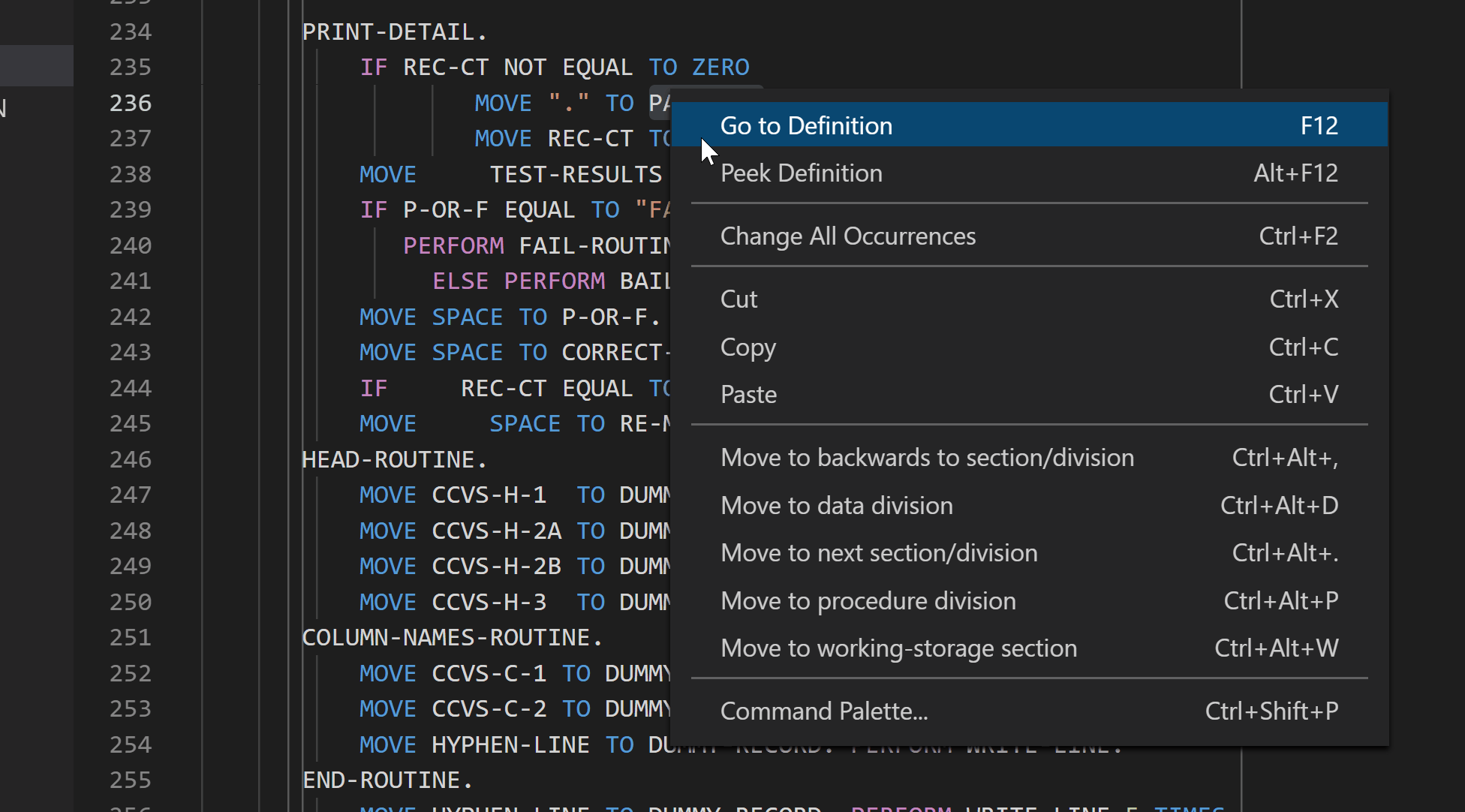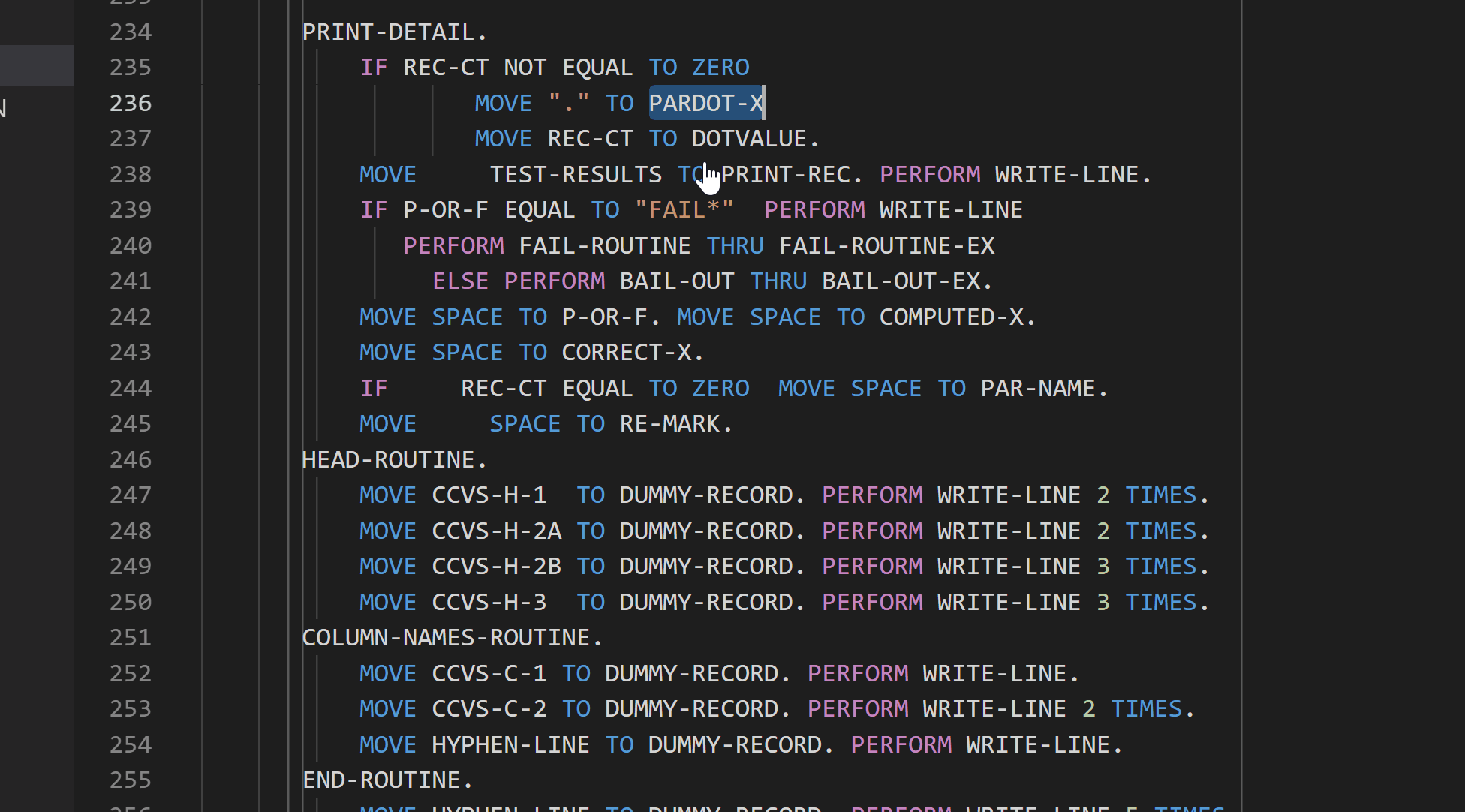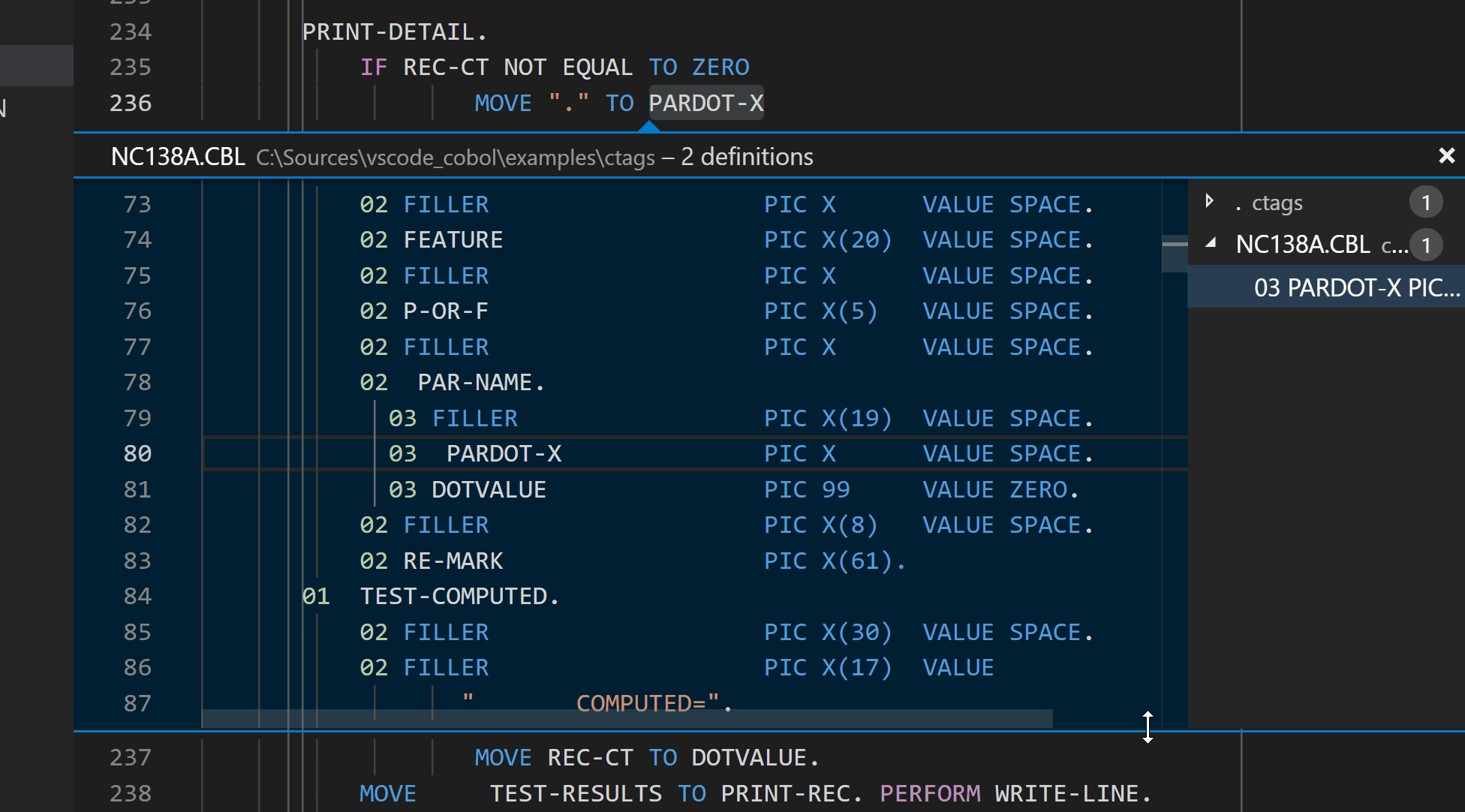
Go to definition
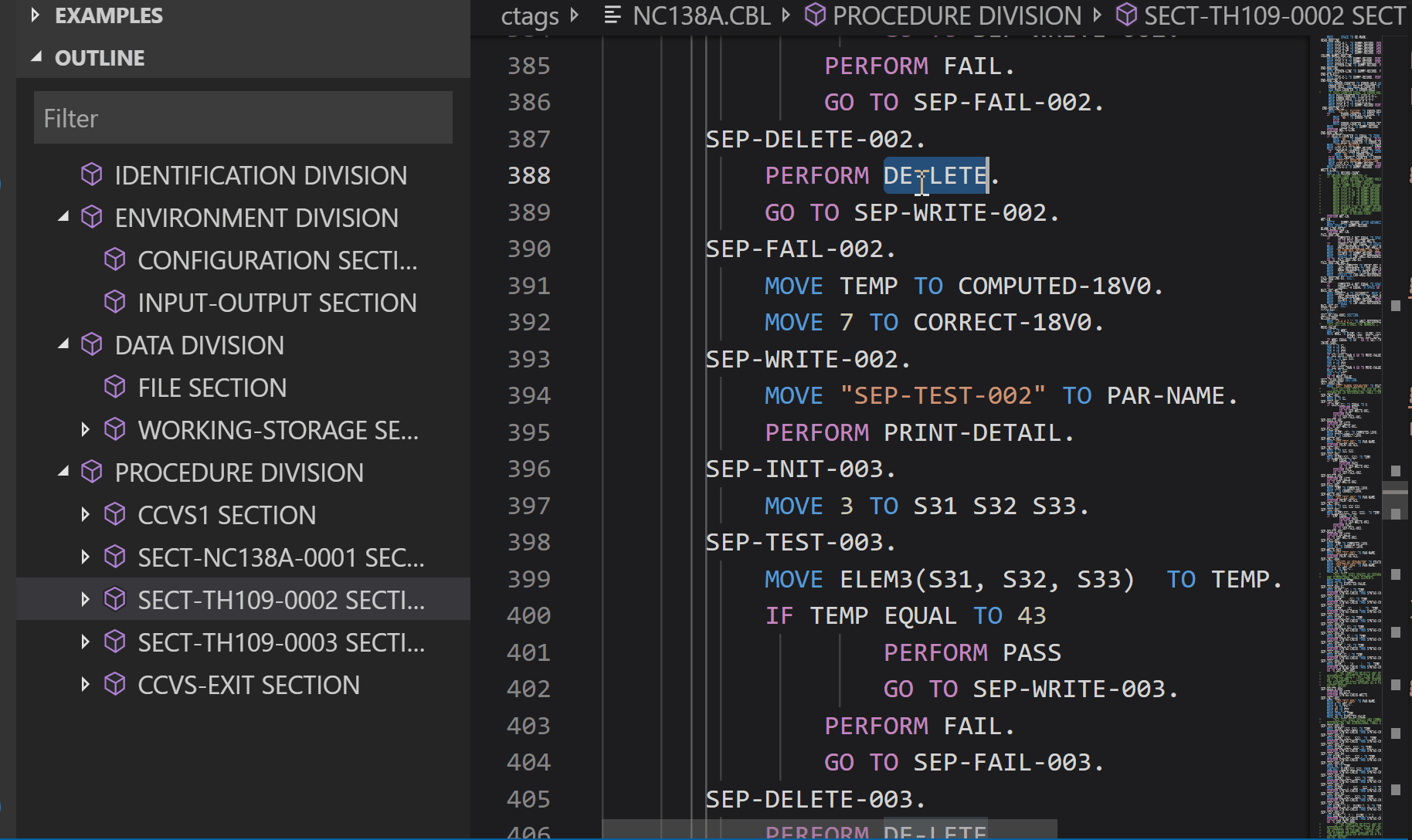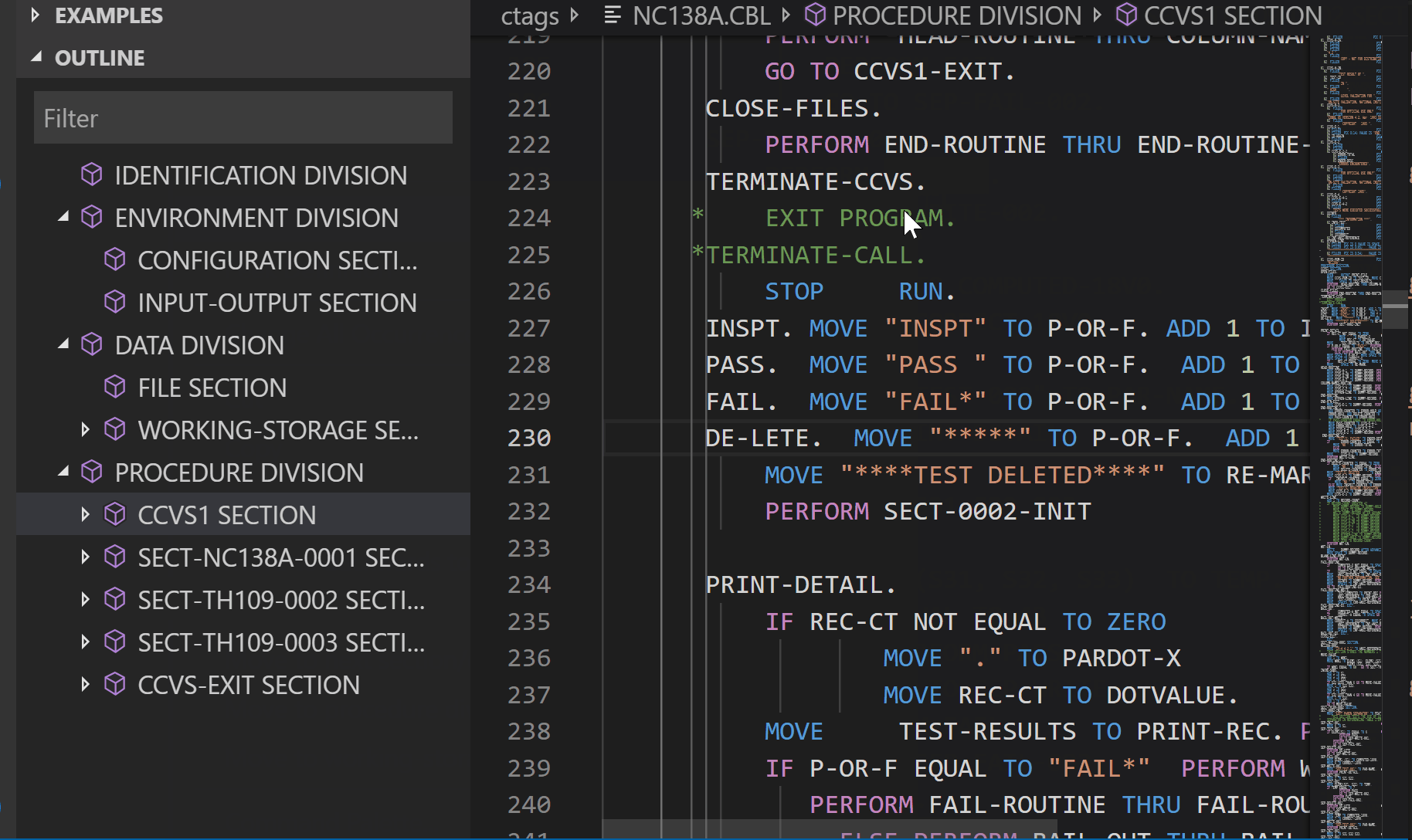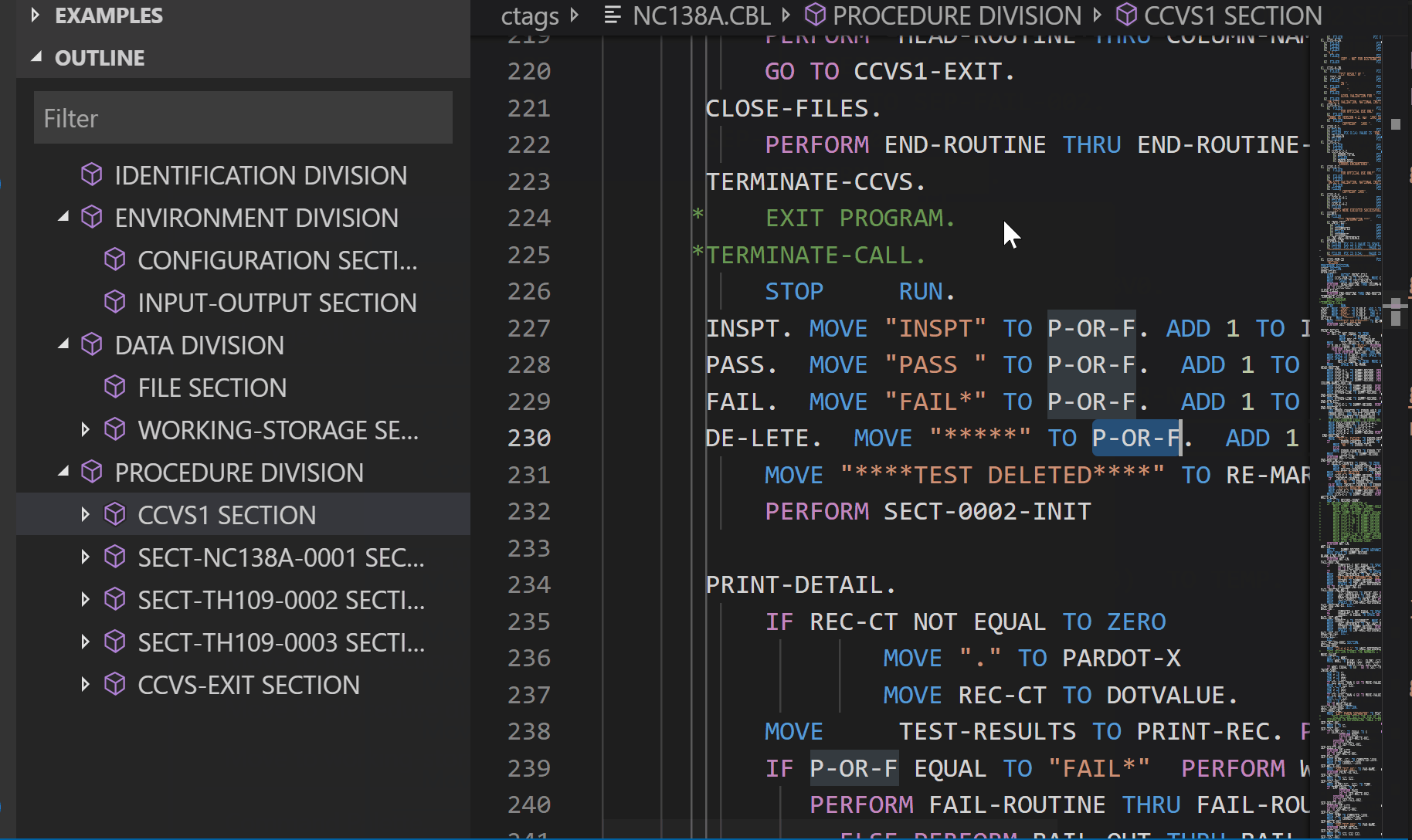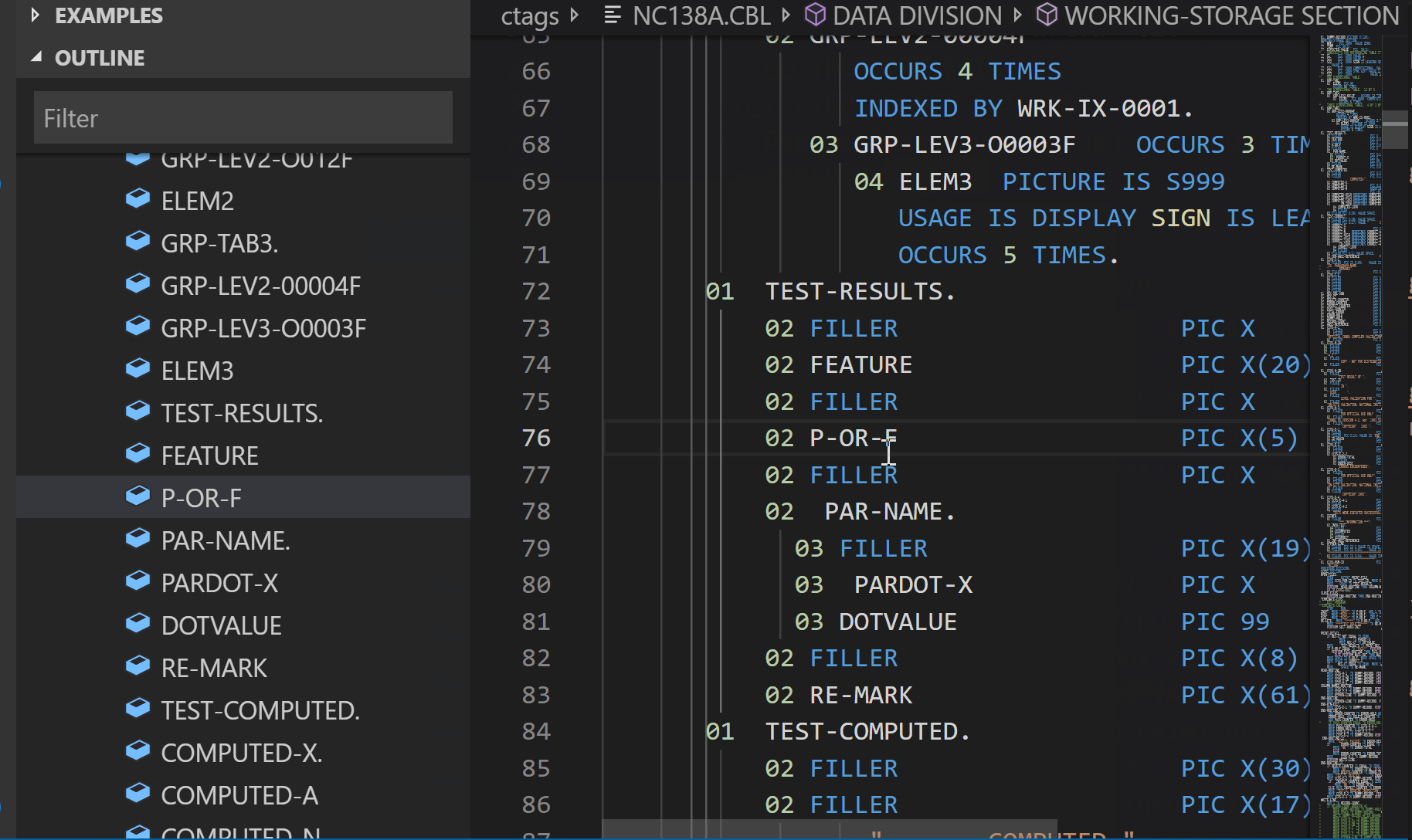
Peek definition
COBOL specific coloured comments
Keybindings
| Keys | Description |
|---|---|
| ctrl+alt+p | Go to procedure division |
| ctrl+alt+w | Go to working-storage section |
| ctrl+alt+d | Go to data division (or working-storage section if not present) |
| ctrl+alt+, | Go backwards to next section/division |
| ctrl+alt+. | Go forward to next next section/division |
| f12 or ctrl+click | Go to copybook/file |
| ctrl+hover | Peek head of copybook or symbol/field |
| right mouse/peek | Peek copybook without opening the file) |
| ctrl+alt+a | Adjust line to cursor position |
| ctrl+alt+l | Left adjust line to left margin |
| alt+right | Insert spaces to column 72 |
Keybindings - xedit'ish
Only active when coboleditor.xedit_keymap is set to true.
| Keys | Description |
|---|---|
| ctrl+a | cursor to start of line |
| ctrl+b | cursor left |
| ctrl+c | clipboard paste |
| ctrl+d | delete right character |
| ctrl+e | cursor line end |
| ctrl+f | cursor right |
| ctrl+h | delete left |
| ctrl+j | insert line after |
| ctrl+k | delete to right |
| ctrl+m | insert line before |
| ctrl+t | transpose |
| ctrl+z | scroll line up |
| alt+z | scroll line down |
Settings
- COBOL tab stops can be changed by editing the
coboleditor.tabstopssetting. - Extensions used for Go to copybook, can be changed by editing the
coboleditor.copybookextssettings. - Directories used for Go to copybook, can be changed by editing the
coboleditor.copybookdirssettings.
New File
New file creation support is provided for COBOL and ACUCOBOL programs with additional support for Micro Focus Unit Test programs.
Changing the default file associations
The command "Enforce extension via file.assocations" allows the default to be change from the "COBOL" language to "ACUCOBOL" or "COBOLIT".
Tasks
Visual Studio code can be setup to build your COBOL source code.
Task: Using MsBuild
MsBuild based projects can be consumed as build task, allowing navigation to error/warnings when they occur.
Below is an example of build task that uses mycobolproject.sln.
{
"version": "2.0.0",
"tasks": [ {
"label": "Compile: using msbuild (mycobolproject.sln)",
"type": "shell",
"command": "msbuild",
"args": [
"/property:GenerateFullPaths=true",
"/t:build",
"mycobolproject.sln"
],
"group": {
"kind": "build",
"isDefault": true
},
"presentation": {
"reveal": "always"
},
"problemMatcher": "$mfcobol-msbuild"
}
]
}
Task: Single file compile using Rocket COBOL - ERRFORMAT(3)
The example below shows you how you can create a single task to compile one program using the cobol command.
{
"label": "Compile: using cobol (single file)",
"command": "cobol",
"args": [
"${file}",
"noint",
"nognt",
"noobj",
"noquery",
"errformat(3)",
"COPYPATH($COBCPY;${workspaceFolder}\\CopyBooks;${workspaceFolder}\\CopyBooks\\Public)",
";"
],
"group": {
"kind": "build",
"isDefault": true
},
"options": {
"cwd": "${workspaceRoot}"
},
"presentation": {
"echo": true,
"reveal": "never",
"focus": true,
"panel": "dedicated"
},
"problemMatcher": "$mfcobol-errformat3"
}
Task: Single file compile using Rocket COBOL - ERRFORMAT(2)
The example below shows you how you can create a single task to compile one program using the cobol command.
{
"label": "Compile: using cobol (single file)",
"command": "cobol",
"args": [
"${file}",
"noint",
"nognt",
"noobj",
"noquery",
"errformat(2)",
"COPYPATH($COBCPY;${workspaceFolder}\\CopyBooks;${workspaceFolder}\\CopyBooks\\Public)",
";"
],
"group": {
"kind": "build",
"isDefault": true
},
"options": {
"cwd": "${workspaceRoot}"
},
"presentation": {
"echo": true,
"reveal": "never",
"focus": true,
"panel": "dedicated"
},
"problemMatcher": [ "$mfcobol-errformat2", "$mfcobol-errformat2-copybook" ]
}
Task: Single file compile using COBOL-IT
The example below shows you how you can create a single task to compile one program using the cobc command.
{
"version": "2.0.0",
"tasks": [
{
"label": "Compile: cobc (single file)",
"type": "shell",
"command": "cobc",
"args": [
"-fsyntax-only",
"-I${workspaceFolder}\\CopyBooks",
"-I${workspaceFolder}\\CopyBooks\\Public",
"${file}"
],
"problemMatcher" : "$cobolit-cobc"
}
]
}
Task: Single file compile using ACUCOBOL-GT
The example below shows you how you can create a single task to compile one program using the ccbl32 command.
{
"version": "2.0.0",
"tasks": [
{
"label": "Compile: using ccbl32 (single file)",
"type": "shell",
"command": "%ACUCOBOL%\\bin\\ccbl32",
"args": [
"-Sp", "${workspaceFolder}\\CopyBooks",
"-Sp", "${workspaceFolder}\\CopyBooks\\Public",
"${file}"
],
"windows": {
"options": {
"env": {
"ACUCOBOL" : "C:\\extend10.1.1\\AcuGT"
}
}
},
"problemMatcher" : [ "$acucobol-warning-ccbl", "$acucobol-ccbl" ]
}
]
}
Task: Breakdown of problem matchers
| Product and Version | Tools | Problem matcher(s) |
|---|---|---|
| COBOL-IT | cobc | $cobolit-cobc |
| COBOL-IT | cobc for errors/notes | $cobolit-error-cobc + $cobolit-note-cobc |
| ACUCOBOL-GT | ccbl for errors/warnings | $acucobol-ccbl + $acucobol-warning-ccbl |
| cob or cobol.exe + ERRFORMAT"3" for information | +mfcobol-errformat3-info | |
| Micro Focus Visual COBOL/Enterprise Developer | msbuild | $mfcobol-msbuild |
| cob or cobol.exe + ERRFORMAT"3" | $mfcobol-errformat3 | |
| cob or cobol.exe + ERRFORMAT"3" / filename extract with PATH | $mfcobol-errformat3-basefn | |
| cob or cobol.exe + ERRFORMAT"2" | $mfcobol-errformat2 | |
| cob or cobol.exe + ERRFORMAT"2" for errors in copybooks | $mfcobol-errformat2-copybook |
NOTE: Problem matchers can be stacked in your task definition. It is recommended that any "-copybook", "-info", "-note" and similar problem matcher are included before problem matchers without this suffix.
Remote development using dev containers
If your main development is Micro Focus Visual COBOL/Enterprise Developer you may have access to base images that provide the compiler and its tools.
If you do, all that is required is another image that contains extra tools and a devcontainer.json to configure its use.
The following Dockerfile is an example on how you can extend your existing base image with java configured, ant, git and lsb tools.
This example uses the SLES 15.1 base images using Visual COBOL 9.0.
You may need to tweak the FROM clause in the Dockerfile and if you use a different platform or product version, the zypper will also require a change too if a different platform is used (different commands eg: yum, microdnf etc..).
Dockerfile:
FROM microfocus/vcdevhub:sles15.1_9.0_x64_login
USER root
ENV JAVA_HOME=/usr/java/default
ENV PATH=${JAVA_HOME}/bin:${PATH}
ENV COBDIR=${MFPRODBASE}
ENV PATH=${COBDIR}/bin:${PATH}
ENV LD_LIBRARY_PATH=${COBDIR}/lib:${LD_LIBRARY_PATH}
ENV ANT_HOME=/opt/microfocus/VisualCOBOL/remotedev/ant/apache-ant-1.9.9
ENV PATH=${ANT_HOME}/bin:${PATH}
RUN zypper --non-interactive install --no-recommends lsb-release git
devcontainer.json:
{
// See https://aka.ms/vscode-remote/devcontainer.json for format details.
"name": "Visual COBOL",
// Update the 'dockerFile' property if you aren't using the standard 'Dockerfile' filename.
"dockerFile": "Dockerfile",
// The optional 'runArgs' property can be used to specify additional runtime arguments.
"runArgs": [
"--cap-add=SYS_PTRACE",
"--security-opt", "seccomp=unconfined"
],
// Add the IDs of any extensions you want installed in the array below.
"customizations": {
"vscode": {
"extensions": [
"bitlang.cobol"
]
}
}
}
Workspace Setup
Visual Studio Code workspaces are not "projects" but do allow you keep your source in one place.
Things to consider:
- If you have copybooks, you should change the
coboleditor.copybookdirssettings to setup where the extension can find your copybooks - If use the COPY verb with this extension, you may also need to adjust the
coboleditor.copybookextssettings (json array). - If you want the extension to understand the contents of your copybook before you access it, then turn on the
coboleditor.parse_copybooks_for_referencessettings (json array) to allow the extension to look inside the copybook references
COBOL Linter
The COBOL linter included with the extension performs two functions, the first function is to identify sections/paragraphs that are not used and the second is to apply any "house" standards.
The section/paragraph linter by default generates warning message but if you prefer the messages to be marked as information, you change the coboleditor.linter_mark_as_information boolean setting, for example:
"coboleditor.linter_mark_as_information": true
The house standards are applied to fields in various sections, each section is named and a rule defined as a regular expression to enforce.
For example to enforce all working-storage items must start with ws and local-storage ls, you can use:
"coboleditor.linter_house_standards_rules": [
"file=.*",
"thread-local=ls.*",
"working-storage=ws.*",
"object-storage=.*",
"local-storage=.*",
"linkage=.*",
"communication=.*",
"report=.*",
"screen=.*",
]
Metadata caching
By default the metadata caching is turned on and is stored in the current code workspace but it can be turned off via the coboleditor.maintain_metadata_cache setting.
Pre-Processor support for "hidden" source code
Some pre-processor reference copybooks that are inserted into the code without using standard COBOL syntax.
These source files are often difficult to edit due this extension not knowing anything about these files.
In order to help this extension, a special style of comment can be inserted into the code that allows the extension to locate these extra copybooks.
For example, if your preprocessor includes the files Shared/foo.cbl OldCopyBooks/Shared/bar.cbl, then you can use the following comment line.
*> @source-dependency Shared/foo.cbl OldCopyBooks/Shared/bar.cbl
The source-dependency names are separated by a space.
Regular expression filtering can be achieved by using a filename that starts and ends with a "/", for example to only include lines that contain adecp+ from the file proc.cbl, you can do:
*> @source-dependency /adecp+/ proc.cbl
To enable this feature enable the scan_comments_for_hints setting, for example:
"coboleditor.scan_comments_for_hints": true
The hint token can be configured by the coboleditor.scan_comment_copybook_token setting, which has the default value set to source-dependency.
It is recommended that the token name remain consistent in your source, otherwise it will make it hard for observers of your source to understand the code.
coboleditor.fileformat & coboleditor.fileformat_strategy
When coboleditor.fileformat_strategy is set to "normal", the source format will be determined heuristically but can be overriden by either embedded directives with each source file.
However, if you need to tell the extension which file(s) are which particular file format, this can be achieved with coboleditor.fileformat property.
For example, if you want all the files that match A*.cbl to be fixed and every other *.cbl is free format, you can then use:
"coboleditor.fileformat": [
{
"pattern": "**/A*.cbl",
"sourceformat": "fixed"
},
{
"pattern": "**/*.cbl",
"sourceformat": "free"
}
],
If always use fixed format you can set coboleditor.fileformat_strategy=always_fixed.
Handling code pages
The defaults embedded in the extension can be overwritten by either changing sessions at the user level in the settings json file or more efficiently, you change it just for the "COBOL" files.
For example, to ensure you use utf8 for all you files use:
{
"[COBOL]": {
"files.encoding": "utf8",
"files.autoGuessEncoding": false
}
}
Intellisense and case formatting
A overall Intellisense style can be selected via the coboleditor.intellisense_style property.
If you find a keyword or snippet includes a extra space, you can amend the coboleditor.intellisense_add_space_keywords property to include it.
Custom formatting rules can be enabled for a specific item or prefixed item via the coboleditor.custom_intellisense_rules setting.
The format is an array of strings, that are in two parts, separated by a :. The first part of item and the second is one of four characters, that denote the case style.
u = Uppercase
l = Lowercase
c = camelcase
= = unchanged
If the end items a *, a partial search is done:
For example, to ensure all items that start WS- should be uppercased.
WS-*:u
or a more specific item:
WS-COUNTER:u
The property coboleditor.format_on_return allows the intellisense rules to be applied to the previous line when the return key has been pressed.
Tips for use
-
If you find you are not getting any symbols in the outline view or the peek/goto definition functionality does not work, please check the
Output->COBOLpanel as it may give you a reason for this.For example the editor line limit has been surpassed or the file fails to be identified as a COBOL source file.
- The colors in the editor can be changed on a per theme basis, for example:
"editor.tokenColorCustomizations": {
"[Monokai]": {
"comments": "#229977"
}
}
Where comments is a token name, standard tokens can be found in the textmate documentation.
Useful tokens that are often changed are: comment.line.cobol.newpage, keyword.operator.
Usefull Source Code
Rocket COBOL ported source code
Complementary extensions
COBOL Language Dictionary - Code Spell Checker
Spell checking code is helpful but without specific support for the COBOL language it can be a painful experience, so in order to make it easier. I have produced a spell checker extension that has a the standard COBOL reserved words and keywords from various dialects such a Micro Focus COBOL and IBM Enterprise COBOL.
Spell checking can be enabled/disabled in your source code by using:
* spell-checker: disable
* spell-checker: enable
You can also ignore words in the code, for example:
* cSpell:ignoreWords TPCC, ridfld, dfhresp
Lastly, you use a regular expression, for example, to ignore words that contain a '-', you could use:
* cSpell:ignoreRegExp /\w*-\w*/
ToDo tree by Gruntfuggly
Although this extension does not understand comments in COBOL source files, it can be made to by adding the following user setting:
{
"todo-tree.tree.flat": false,
"todo-tree.tree.expanded": true,
"todo-tree.regex.regex": "((//|#|<!--|;|/\\*|\\*>|^......\\*)\\s*($TAGS)|^\\s*- \\[ \\])",
"todo-tree.general.tags": [
"TODO",
"FIXME",
"!FIXME",
"CHANGED",
"BUG",
"NOTE"
],
"todo-tree.tree.filterCaseSensitive": true,
"todo-tree.highlights.customHighlight": {
"FIXME": {
"icon": "flame",
"iconColour": "#A188FF",
},
"NOTE": {
"iconColour:" : "blue"
},
"TODO": {
"iconColour:" : "cyan"
},
"CHANGED": {
"iconColour:" : "yellow"
},
"BUG": {
"icon": "bug"
}
}
}
Visual Studio Code Work>space Trust security
When in limited functionality mode the extension disables all functionality that might be use for malicious purposes.
The extension only enables features that allow basic editing, making it ideal for browsing untrusted source.
CO-Existence Rocket COBOL extension
Using two extensions that both provide the same features can be problematic but this extension tries it's best to ensure both can used used.
This extension provides commands that allow the developer to flip between the two extensions. It does this by changing the file.associations settings and changing settings for the Rocket COBOL extension to allow the two to co-exist.
| From 'Rocket COBOL extension' | From this Extensions |
|---|---|
 |  |
When a user chooses to change to the Rocket COBOL extension via the editors language dropdown button this extension will ensure the language server is enabled.
Or you can use the COBOL: Enforce extension via file.associations command.

The language COBOL is this extension and lower-case cobol is the Rocket COBOL extension.
If this behavior is not desired, then the setting coboleditor.enable_rocket_cobol_lsp_when_active can be set to false or alternatively you can disable one of the extensions on a per-workspace basis or you have a scenario then the use of profiles is another mechanism that can isolate extensions from each other.
Settings defaults for Rocket COBOL extension
"microFocusCOBOL.suppressFileAssociationsPrompt": true,
Settings defaults for GitHub Copilot Extension
"github.copilot.inlineSuggest.enable": true,
"github.copilot.editor.enableAutoCompletions": true,
"github.copilot.enable": {
"COBOL": true,
"BITLANG-COBOL": true,
"COBOLIT": true,
"ACUCOBOL": true,
"RMCOBOL": true,
"COBOL_MF_LISTFILE": false,
"COBOL_PCOB_LISTFILE": false,
"COBOL_ACU_LISTFILE": false,
"COBOL_MF_PREP": false,
"mfu": false,
"utreport": false
}
File Editor defaults
The following settings are set by default:
"files.defaultLanguage": "COBOL",
"workbench.editor.untitled.labelFormat": "name",
When files.defaultLanguage is set to COBOL any file without an extension is not guessed but is assumed to be COBOL. If you do not want this, please change the language to double quotes eg:
"files.defaultLanguage": "",
Or use an file extension, which will ensure you have the right document language for editing.
Online resources
- Online communities
- Stack Overflow topics/tags:
- COBOL Programming Language Articles on Reddit
- Linkedin Learning COBOL Resources
- wikipedia
- standards
Shortcuts
- [ALT] + [SHIFT] + [C]: Change to COBOL Syntax (default)
- [ALT] + [SHIFT] + [A]: Change to ACUCOBOL-GT Syntax
- [ALT] + [SHIFT] + [M]: Toggle margins (overrides user/workspace settings)
Contributors
I would like to thank the follow contributors for providing patches, fixes, kind words of wisdom and enhancements.
- Ted John of Berkshire, UK


