Awesome
MHFP
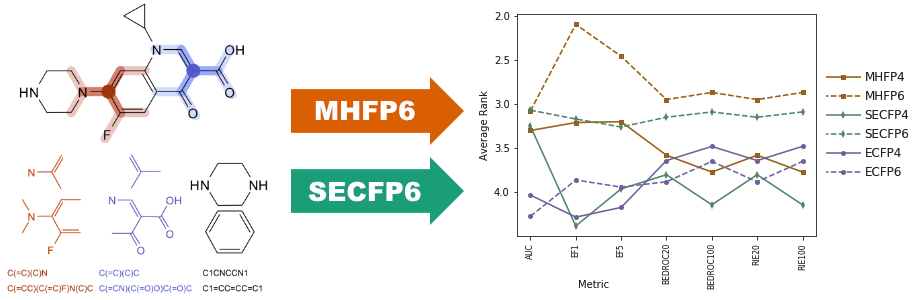
MHFP6 (MinHash fingerprint, up to six bonds) is a molecular fingerprint which encodes detailed substructures using the extended connectivity principle of ECFP in a fundamentally different manner, increasing the performance of exact nearest neighbor searches in benchmarking studies and enabling the application of locality sensitive hashing (LSH) approximate nearest neighbor search algorithms. To describe a molecule, MHFP6 extracts the SMILES of all circular substructures around each atom up to a diameter of six bonds and applies the MinHash method to the resulting set. MHFP6 outperforms ECFP4 in benchmarking analog recovery studies. Furthermore, MHFP6 outperforms ECFP4 in approximate nearest neighbor searches by two orders of magnitude in terms of speed, while decreasing the error rate.
Associated Publication: https://jcheminf.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s13321-018-0321-8
Materials
The performance of MHFP has been avaluated using Open-source platform to benchmark fingerprints for ligand-based virtual screening and ChEMBL24. Python (pyspark) scripts for the ChEMBL24 benchmark can be found in this repository.
Dependencies
MHFP requires Python 3.x and Numpy.
MHFP requires the cheminformatics library RDKit.
Installation
MHFP can be installed using the Python packet manager pip:
pip install mhfp
Usage
Usage is straightforward:
from mhfp.encoder import MHFPEncoder
mhfp_encoder = MHFPEncoder()
fp_a = mhfp_encoder.encode('CCOC1=C(C=C(C=C1)S(=O)(=O)N(C)C)C2=NC(=O)C3=C(N2)C(=NN3C)C(C)(C)C')
fp_b = mhfp_encoder.encode('CCCC1=NN(C2=C1NC(=NC2=O)C3=C(C=CC(=C3)S(=O)(=O)N4CCN(CC4)C)OCC)C')
fp_c = mhfp_encoder.encode('O=C(OC)C(C1CCCCN1)C2=CC=CC=C2')
print(MHFPEncoder.distance(fp_a, fp_a))
print(MHFPEncoder.distance(fp_a, fp_b))
print(MHFPEncoder.distance(fp_a, fp_c))
print(MHFPEncoder.distance(fp_b, fp_c))
#> 0.0
#> 0.45849609375
#> 0.97998046875
#> 0.97216796875
LSH Forest
As the fingerprints are created using the locality sensitive hashing scheme MinHash, they are ready to be used with LSH-based algorithms:
from mhfp.encoder import MHFPEncoder
from mhfp.lsh_forest import LSHForestHelper
mhfp_encoder = MHFPEncoder()
fp_a = mhfp_encoder.encode('CCOC1=C(C=C(C=C1)S(=O)(=O)N(C)C)C2=NC(=O)C3=C(N2)C(=NN3C)C(C)(C)C')
fp_b = mhfp_encoder.encode('CCCC1=NN(C2=C1NC(=NC2=O)C3=C(C=CC(=C3)S(=O)(=O)N4CCN(CC4)C)OCC)C')
fp_c = mhfp_encoder.encode('O=C(OC)C(C1CCCCN1)C2=CC=CC=C2')
fp_q = mhfp_encoder.encode('COC1=C(C=C(C=C1)S(=O)(O)N(C)C)C2=NC(=O)C3=C(N2)C(=NN3C)C(C)(C)C')
lsh_forest_helper = LSHForestHelper()
fps = [fp_a, fp_b, fp_c]
for i, fp in enumerate(fps):
lsh_forest_helper.add(i, fp)
lsh_forest_helper.index()
print(lsh_forest_helper.query(fp_q, 1, fps))
#> [0]
SECFP
SECFP (SMILES Extended Connectifity Fingerprint) creation is achieved by calling the static method MHFPEncoder.secfp_from_smiles():
from mhfp.encoder import MHFPEncoder
fp = MHFPEncoder.secfp_from_smiles('CCOC1=C(C=C(C=C1)S(=O)(=O)N(C)C)C2=NC(=O)C3=C(N2)C(=NN3C)C(C)(C)C')
Documentation
MHFPEncoder
The class for encoding SMILES and RDKit molecule instances as MHFP fingerprints.
__init__(n_permutations = 2048, seed = 42)
| Parameter | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| n_permutations | 2048 | Analogous to the number of bits ECFP fingerprints are folded into. Higher is better, lower is less exact. |
| seed | 42 | The seed for the MinHash operation. Has to be the same for comparable fingerprints. |
MHFPEncoder.encode(in_smiles, radius = 3, rings = True, kekulize = True, sanitize = True)
| Parameter | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| in_smiles | The input SMILES. | |
| radius | 3 | Analogous to the radius for the Morgan fingerprint. The default radius 3 encodes SMILES to MHFP6. |
| rings | True | Whether rings in the molecule are included in the fingerprint. As a radii of 3 fails to encode rings and there is no way to determine ring-membership in a substructure SMILES, this considerably increases performance. |
| kekulize | True | Whether or not to kekulize the molecule before extracting substructure SMILES. |
| sanitize | True | Whether or not to sanitize the molecule (using RDKit) before extracting substructure SMILES. |
Returns a numpy.ndarray containing the fingerprint hashes.
MHFPEncoder.encode_mol(in_mol, radius = 3, rings = True, kekulize = True)
| Parameter | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| in_mol | The input RDKit molecule instance. | |
| radius | 3 | Analogous to the radius for the Morgan fingerprint. The default radius 3 encodes SMILES to MHFP6. |
| rings | True | Whether rings in the molecule are included in the fingerprint. As a radii of 3 fails to encode rings and there is no way to determine ring-membership in a substructure SMILES, this considerably increases performance. |
| kekulize | True | Whether or not to kekulize the molecule before extracting substructure SMILES. |
Returns a numpy.ndarray containing the fingerprint hashes.
MHFPEncoder.distance(a, b)
| Parameter | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| a | A numpy.ndarray containing fingerprint hashes. | |
| b | A numpy.ndarray containing fingerprint hashes. |
Returns a float representing the distance between two MHFP encoded molecules.
MHFPEncoder.secfp_from_mol(in_mol, length=2048, radius=3, rings=True, kekulize=True)
| Parameter | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| in_mol | The input RDKit molecule instance. | |
| length | 2048 | The length of the folded fingerprint. |
| radius | 3 | Analogous to the radius for the Morgan fingerprint. The default radius 3 encodes SMILES to MHFP6. |
| rings | True | Whether rings in the molecule are included in the fingerprint. As a radii of 3 fails to encode rings and there is no way to determine ring-membership in a substructure SMILES, this considerably increases performance. |
| kekulize | True | Whether or not to kekulize the molecule before extracting substructure SMILES. |
Returns a numpy.ndarray containing the fingerprint values.
MHFPEncoder.secfp_from_smiles(in_smiles, length=2048, radius=3, rings=True, kekulize=True, sanitize=False)
| Parameter | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| in_smiles | The input SMILES. | |
| length | 2048 | The length of the folded fingerprint. |
| radius | 3 | Analogous to the radius for the Morgan fingerprint. The default radius 3 encodes SMILES to MHFP6. |
| rings | True | Whether rings in the molecule are included in the fingerprint. As a radii of 3 fails to encode rings and there is no way to determine ring-membership in a substructure SMILES, this considerably increases performance. |
| kekulize | True | Whether or not to kekulize the molecule before extracting substructure SMILES. |
| sanitize | False | Whether or not to sanitize the SMILES when parsing it using RDKit. |
Returns a numpy.ndarray containing the fingerprint values.
LSHForestHelper
If you know your way around Python, I suggest you use the LSHForest class directly. See code for details.
__init__(dims = 2048, n_prefix_trees = 64)
| Parameter | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| dims | 2048 | Has to be equal to the number of permutations n_permutations set when initializing MHFPEncoder |
| n_prefix_trees | 64 | The number of prefix trees. Lower number results in lower memory usage but less quality |
LSHForestHelper.add(key, mhfp):
| Parameter | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| key | The key that will be retrieved by a query. It's recommended to use integers. | |
| mhfp | The numpy.ndarray containing the fingerprint hashes. |
LSHForestHelper.index():
Has to be run after adding entities and before running queries!
MHFPEncoder.query(query_mhfp, k, data, kc=10)
| Parameter | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| query_mhfp | A numpy.ndarray containing fingerprint hashes. | |
| k | The number of nearest neighbors to be retrieved. | |
| data | Data mapping keys to fingerprints. See LSH Forest example for details. | |
| kc | 10 | Initially k is multiplied by kc and k · kc (ANN) results are returned. The top k are then selected from these k · kc using linear scan. |