Awesome
barnowl-aruba
barnowl-aruba converts the decodings of any ambient Bluetooth Low Energy & EnOcean Alliance devices by Aruba Networks access points into standard developer-friendly JSON that is vendor/technology/application-agnostic.
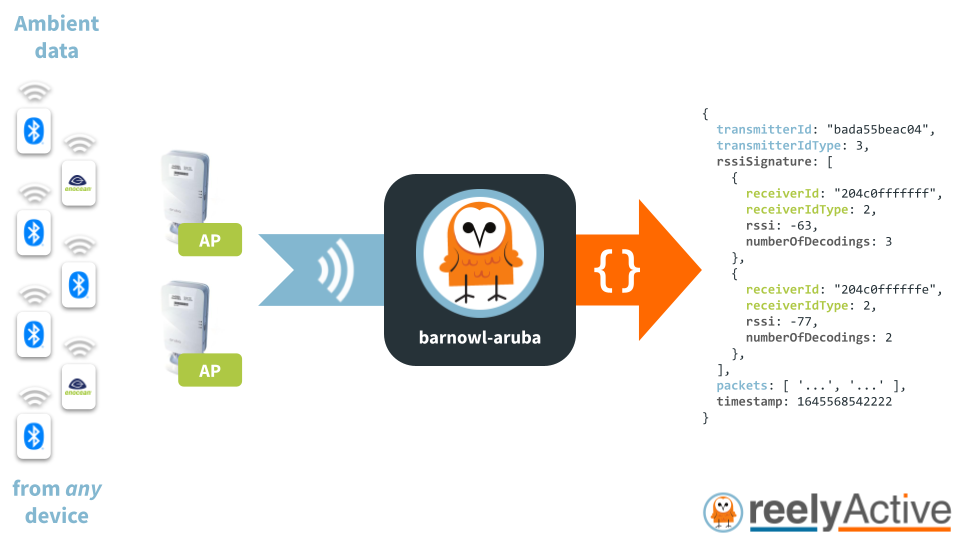
barnowl-aruba is a lightweight Node.js package that can run on resource-constrained edge devices as well as on powerful cloud servers and anything in between. It is included in reelyActive's Pareto Anywhere open source middleware suite, and can just as easily be run standalone behind a barnowl instance, as detailed in the code examples below.
Getting Started
Follow our step-by-step Configure an Aruba Instant AP tutorial to get started with barnowl-aruba or Pareto Anywhere. Or visit our HPE Aruba Networking integration page to learn about alternative configurations such as Aruba IoT Transport for Azure.
Learn "owl" about the raddec JSON data output:
Quick Start
Clone this repository, install package dependencies with npm install, and then from the root folder run at any time:
npm start
barnowl-aruba will indiscriminately accept AOS8 & AOS10 WebSocket clients and their data on localhost:3001/aruba/aos8 and localhost:3001/aruba/aos10, respectively, and output (flattened) raddec JSON to the console.
Note that AOS10 only supports secure WebSockets (wss://). See below for instructions to create a secure WebSocket in a development environment.
Hello barnowl-aruba!
Developing an application directly from barnowl-aruba? Start by pasting the code below into a file called server.js:
const Barnowl = require('barnowl');
const BarnowlAruba = require('barnowl-aruba');
let barnowl = new Barnowl({ enableMixing: true });
barnowl.addListener(BarnowlAruba, {}, BarnowlAruba.TestListener, {});
barnowl.on('raddec', (raddec) => {
console.log(raddec);
// Trigger your application logic here
});
From the same folder as the server.js file, install package dependencies with the commands npm install barnowl-aruba and npm install barnowl. Then run the code with the command node server.js and observe the simulated data stream of radio decodings (raddec objects) output to the console:
{
transmitterId: "fee150bada55",
transmitterIdType: 2,
rssiSignature: [
{
receiverId: "204c0fffffff",
receiverIdType: 2,
rssi: -77,
numberOfDecodings: 1
}
],
packets: [ '001a55daba50e1fe0201060303e1ff1216e1ffa1034affe7004500fa55daba50e1fe' ],
timestamp: 1645568542222
}
See the Supported Listener Interfaces below to adapt the code to listen for your AP(s).
Supported Listener Interfaces
The following listener interfaces are supported.
Websocket
barnowl.addListener(BarnowlAruba, {}, BarnowlAruba.WsListener, { port: 3001 });
Test
Provides a steady stream of simulated TelemetryReports for testing purposes.
barnowl.addListener(BarnowlAruba, {}, BarnowlAruba.TestListener, {});
Access Point Identification
Each AP has two or more radio identifiers:
- IP radio MAC
- Bluetooth radio MAC
- (optional) USB-connected radio identifier(s)
To the extent possible, all BLE raddecs will use the Bluetooth radio MAC as the receiverId property. As the Bluetooth radio MAC is not included in AOS8 BLE Telemetry reports, as of barnowl-aruba v1.2.1, it is instead automatically inferred from AP Health messages and, when available, BLE Data reports.
WiFi raddecs and USB-connected raddecs will use the IP radio MAC as the receiverId property.
Data vs. Telemetry
Aruba IoT Transport supports both periodic telemetry reports (ex: BLE Telemetry or Periodic Telemetry) and real-time packet reports (ex: BLE Data or Data Frames). By default, barnowl-aruba will accept only the real-time packet reports, as these include all the properties to form a raddec with rssiSignature and packets.
To process periodic telemetry reports regardless, set the listener options as follows:
{ decodingOptions: { acceptTelemetryReports: true } }
In this case, the raddec data will be limited to the transmitterId/Type, rssiSignature and timestamp properties.
For the best RTLS (real-time location) performance from telemetry reports, the following BLE Telemetry Websocket options are recommended:
- Reporting interval: 2 seconds
- RSSI reporting format: Bulk
- Report devices that have had activity in the last 30 seconds
Note that frequent telemetry reporting may significantly increase network traffic: consider the use of Filters to limit reporting only to devices of interest.
RSSI Bulk reporting provides a timestamped history of decodings which will be included in the raddec, provided they are not stale. If required, adjust the staleness threshold by setting the listener options as follows:
{ decodingOptions: { historyMilliseconds: 2000 } }
The default is 2000ms which coincides with the recommended 2s reporting interval.
Supported Transport Services
barnowl-aruba supports the following Transport Services:
AOS8
- BLE Data
- BLE Telemetry (see Data vs. Telemetry above)
- Serial Data
- EnOcean Serial Protocol (requires USB dongle)
- WiFi Telemetry & RTLS
AOS10
- BLE Data
Southbound Interface
barnowl-aruba supports the retrieval of data from Bluetooth Low Energy devices over GATT, which requires southbound interaction. When a specific payload pattern is observed, a series of southbound action messages are issued to the access point(s) and any response messages are consequently handled.
Following a completed series of actions and responses, a raddec with protocolSpecificData will be emitted, for example:
{
transmitterId: "fee150bada55",
transmitterIdType: 2,
rssiSignature: [ ... ],
packets: [ ... ],
protocolSpecificData: {
gatt: [
{
serviceUuid: "1c930003d45911e79296b8e856369374",
characteristicUuid: "1c930032d45911e79296b8e856369374",
value: "0415"
},
{
serviceUuid: "1c930003d45911e79296b8e856369374",
characteristicUuid: "1c930032d45911e79296b8e856369374",
notificationValues: [ "da7a", "da7a", "da7a", "da7a" ]
}
]
}
timestamp: 1645568542222
}
Currently, Sensor-Works BluVib devices are supported. See lib/gattmanager.js for the implementation details.
Standalone Secure WebSockets
To facilitate testing in a development environment, barnowl-aruba can run standalone using secure WebSockets with the command:
npm run secure
In this case, the startup script will attempt to create a HTTPS server using the following two files:
- /config/certificate.pem
- /config/key.pem
The APs should be configured to use the following Server URLs, substituting the xxx for the local IP address of the computer running barnowl-aruba:
- wss://xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx:3001/aruba/aos8
- wss://xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx:3001/aruba/aos10
Instructions to create these files, as well as the corresponding CA certificate for the AP(s), are provided in the following section.
Creating Certificates for Secure WebSockets on Local Network
In a development environment, it is common for barnowl-aruba to run on the same local network as the Aruba AP. In the case where transport uses secure WebSockets (wss://), barnowl-aruba can use a self-signed certificate with the IP address of the computer on which it is running as SAN (Subject Alternative Name), in place of a fully-qualified domain name. The Aruba AP(s) will use a CA certificate to establish the secure connection.
The server certificate (for barnowl-aruba) and the CA certificate (for the AP) can be generated with OpenSSL using the following procedure:
Create a server.cnf file
[req]
default_bits = 2048
distinguished_name = req_distinguished_name
req_extensions = req_ext
x509_extensions = v3_req
prompt = no
[req_distinguished_name]
countryName = CA
stateOrProvinceName = QC
localityName = Montreal
organizationName = reelyActive
commonName = 192.168.1.123
[req_ext]
subjectAltName = @alt_names
[v3_req]
subjectAltName = @alt_names
[alt_names]
IP.1 = 192.168.1.123
Update the commonName and IP.1 fields with the IP address of the computer running barnowl-aruba.
Create a CA.cnf file
[ req ]
prompt = no
distinguished_name = req_distinguished_name
[ req_distinguished_name ]
C = CA
ST = QC
L = Montreal
O = reelyActive
OU = Develop
CN = 192.168.1.123
Update the CN field with the IP address of the computer running barnowl-aruba.
Create the .pem files using OpenSSL
First, generate a CA private key & certificate:
openssl req -nodes -new -x509 -keyout CA_key.pem -out CA_certificate.pem -days 1825 -config CA.cnf
Second, generate the web server's secret key & CSR:
openssl req -sha256 -nodes -newkey rsa:2048 -keyout key.pem -out server.csr -config server.cnf
Third, create the web server's certificate, signing it with its own certificate authority:
openssl x509 -req -days 398 -in server.csr -CA CA_certificate.pem -CAkey CA_key.pem -CAcreateserial -out certificate.pem -extensions req_ext -extfile server.cnf
Assign the certificates
Configure barnowl-aruba by copying the certificate.pem and key.pem files to the /config folder, as described in Standalone Secure WebSockets above.
Upload the CA_certificate.pem file to the AP (ex: via Central) and ensure it is assigned to IoT Transport (ex: Security - Certificate Usage - IoT CA Cert).
Compiling Protocol Buffer JavaScript bundles
Aruba IoT Transport encodes data using Protocol Buffers, and, to decode the data, barnowl-aruba uses a JavaScript bundle of the proto definitions. The proto definitions, which are different for AOS 8 and AOS 10, can be found on the Aruba Support Portal (ASP), and also in the /proto folder of this repository.
The AOS 8 and AOS 10 proto definitions are already compiled and bundled in this repository in the /lib folder. An automated procedure for updating these bundles, should new versions of the proto definitions be released, is documented below.
Compiling the proto definitions into a JavaScript bundle requires pbjs from the protobuf-cli, which must first be installed as follows:
npm install -g protobuf-cli
AOS 8 protobuf
Compile the AOS 8 proto definitions (v1) with the following command:
npm run aos8v1proto
which will compile and bundle, using pbjs, the defintions from /proto/aos8v1 into the file /lib/aos8v1proto.js.
AOS 10 protobuf
Compile the AOS 10 proto definitions (v1) with the following command:
npm run aos10v1proto
which will compile and bundle, using pbjs, the defintions from /proto/aos10v1 into the file /lib/aos10v1proto.js.
Aruba IoT Transport Profile Configuration
This section only applies in the case where it is not possible to use the GUI in Instant or Central to configure the AP(s). In this rare case, the command-line configuration settings and commands will resemble the following:
| Config Option | Value |
|---|---|
| bleDataForwarding | (TRUE) |
| endpointType | telemetry-websocket |
| endpointURL | ws://xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx:3001/aruba |
| endpointToken | token (cannot be left blank) |
| payloadContent | all |
| transportInterval | 1 (seconds) |
| rssiReporting | average |
For example, this can be achieved by SSHing into the AP and executing the following commands:
# configure terminal(config) # iot transportProfile test(IoT Transport Profile "test") # bleDataForwarding(IoT Transport Profile "test") # endpointType telemetry-websocket(IoT Transport Profile "test") # endpointURL ws://xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx:3001/aruba(IoT Transport Profile "test") # endpointToken token(IoT Transport Profile "test") # payloadContent all(IoT Transport Profile "test") # transportInterval 1(IoT Transport Profile "test") # rssiReporting average(IoT Transport Profile "test") # end# commit apply
The configuration can be validated with the command:
# show iot transportProfile test
Is that owl you can do?
While barnowl-aruba may suffice standalone for simple real-time applications, its functionality can be greatly extended with the following software packages:
- advlib to decode the individual packets from hexadecimal strings into JSON
- barnowl to combine parallel streams of RF decoding data in a technology-and-vendor-agnostic way
These packages and more are bundled together as the Pareto Anywhere open source middleware suite, which includes a variety of barnowl-x listeners, APIs and interactive web apps.
Project History
barnowl-aruba v1.4.0 adds support for the AOS 10 WebSocket transport on the /aruba/aos10 path, with AOS 8 support on both the /aruba/aos8 (recommended) and /aruba (legacy) paths.
barnowl-aruba v1.0.0 was released in August 2023 with an upgrade from the AOS 8.8 to the AOS 8.10 protobuf. The latter includes the AP's Bluetooth MAC which is used as the receiverId property in place of the AP's WiFi MAC which was used in previous versions.
Contributing
Discover how to contribute to this open source project which upholds a standard code of conduct.
Security
Consult our security policy for best practices using this open source software and to report vulnerabilities.
License
MIT License
Copyright (c) 2020-2024 reelyActive
Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all copies or substantial portions of the Software.
THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM, OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE SOFTWARE.