Awesome
puppet-canvas
puppet-canvas is a Puppeteer backed implementation of HTML Canvas API for NodeJS.
<img alt="puppet-canvas logo" src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/833927/73148934-a7de4580-4073-11ea-9956-f88bb8355d8f.png" height="200" align="right">Installation
$ npm install puppet-canvas --save
Usage
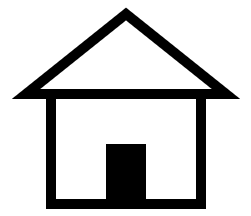
Following example draws a house and grabs the data url of the image.
import { createCanvas, close } from 'puppet-canvas';
// OR const { createCanvas, close } = require('puppet-canvas')
async(() => {
const canvas = await createCanvas(400, 400);
const ctx = await canvas.getContext('2d');
// Draw a house
ctx.lineWidth = 10;
ctx.strokeRect(75, 140, 150, 110);
ctx.fillRect(130, 190, 40, 60);
ctx.moveTo(50, 140);
ctx.lineTo(150, 60);
ctx.lineTo(250, 140);
ctx.closePath();
ctx.stroke();
// Get the image as a data url
const dataUrl = await canvas.toDataURL();
// Release
await close();
})();
Using images
To use external images in your canvas, first load the image using the loadImage method.
import { createCanvas, loadImage } from 'puppet-canvas';
const canvas = await createCanvas(400, 400);
const ctx = await canvas.getContext('2d');
const image = await loadImage('https://....', canvas);
await ctx.drawImage(image, 100, 100);
Using complex objects
Any non-serializable object returned by puppeteer is automatically proxied as well. So one can use/pass more complex objects like a gradient:
const gradient = await ctx.createLinearGradient(20, 0, 220, 0);
gradient.addColorStop(0, 'green');
gradient.addColorStop(.5, 'cyan');
gradient.addColorStop(1, 'green');
ctx.fillStyle = gradient;
ctx.fillRect(20, 20, 200, 100);
Using custom fonts
When using a custom font for rendering text, you can ensure the font is loaded by calling the loadFont methods.
import { createCanvas, loadFont } from 'puppet-canvas';
const canvas = await createCanvas(400, 400);
const ctx = await canvas.getContext('2d');
await loadFont(
'Bangers',
'https://fonts.gstatic.com/s/bangers/v12/FeVQS0BTqb0h60ACH55Q2J5hm24.woff2',
canvas
);
ctx.font = `bold 48px Bangers`;
ctx.fillText('Hello world', 50, 100);
Implementation
puppet-canvas creates a canvas on a puppeteer instance, and exposes the API via a JavaScript Proxy.
A side effect of this is that all calls, essentially become async. For normal drawing, one doesn't need to await each command unless a value is being returned.
A proxied solution is somewhat better than alternate ones because, firstly, the rendering is exactly what the browser would have rendered (Chrome). Secondly, this is mostly future-proof since all methods are just proxied to the actual instance. So, any new API added to the Canvas, should automagically work.
Implentation Shortcomings
Though a proxied implementation is simpler, smaller, and more flexible, it can be slower than alternative native implementations. For example, manipulating lots of pixels, one pixel at a time, may be slow and not recommended.
The other shortcoming is from a dev experience, everything is an async call. So it creates more code for getting child object and properties. The following code:
const imageDataLength = ctx.createImageData(10, 10).data.length;
has to be refactored as
const imageData = await ctx.createImageData(10, 10);
const imageDataLength = await (await imageData.data).length;
Why don't I just use puppeteer
Yes, you can and for some cases it may even be a better dev experience.
puppet-canvas provides a simple abstraction layer so you don't have to jump in and out of Puppeteer's execution context all the time. You treat the canvas very similar to canvas on the web, and not worry much about anything else.
Full API
createCanvas(width: number, height: number) => Promise<HTMLCanvasElement>
Creates a canvas instance with the specified width and height (in pixels)
linkCanvas(canvas: ElementHandle<HTMLCanvasElement>) => Promise<HTMLCanvasElement>
Say, you want to use this with an existing instance of puppeteer, you can pass in the ElementHandle of the canvase in your page.
close() => Promise
Close associated puppeteer instance. Usually called at the end.
releaseCanvas(canvas: HTMLCanvasElement) => Promise
Release the canvas instance, if you do not want puppet-canvas to proxy it anymore, but still want to keep the canvas instance around
screenshotCanvas(canvas: HTMLCanvasElement, options?: ScreenshotOptions) => Promise<string | Buffer>
Take a screenshot of the canvas. The method optionally takes in ScreenshotOptions which are the same options as described in Puppeteer screenshot method
loadFont(name: string, url: string, canvas: HTMLCanvasElement) => Promise
Load a font for the canvas element to use. name is the font-family name of the font. url is the url to the font file (like a woff file)
loadImage(url: string, canvas: HTMLCanvasElement, page?: Page) => Promise<HTMLImageElement>
Load an image from a URL that could be used by the canvas, e.g. for drawing the image on the canvas.