Awesome
Bare Metal Tetris
Tetris for x86.
There is an improved version, in NASM, called Tetrasm.
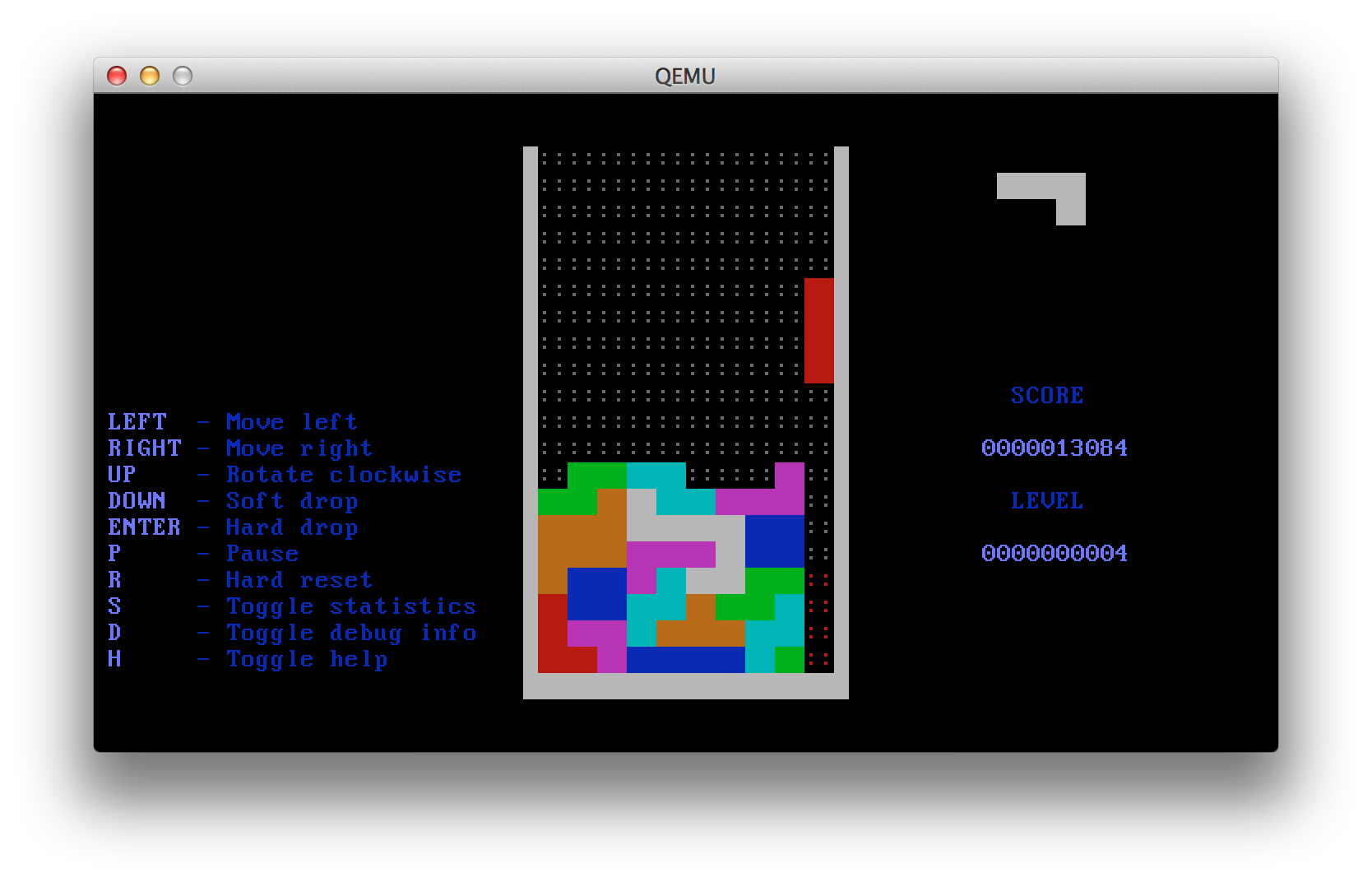
Features
- Color text display
- PC speaker sound effects
- Help screen
- Tetrimino preview
- Tetrimino ghost
- Soft & hard drop
- Pause
- Score and levels
- Increasing difficulty
- Tetrimino statistics
Technical Overview
Bare Metal Tetris does not use processor interrupts, since initializing and using them seemed too complex for a single-file Tetris game. Instead, it uses a combination of an infinite loop, CPU tick counting, and the real-time clock (RTC) to achieve timing.
The timing calibration function is called on every iteration of the main
loop. This function checks the RTC to determine if a second has passed
since the last calibration. If one has, the number of CPU ticks since
boot is retrieved using the rdtsc instruction, and the number of ticks
elapsed in the last second is calculated. This is then divided and set
as the tpms, or "ticks per millisecond" value. Timing functions then
use this value, along with the same rdtsc instruction, to determine if
a number of milliseconds have elapsed since a previous call. These
timing values can be seen in the debug screen, toggled using D.
In order to properly calibrate the tpms before the game starts, the
title screen is shown for at least one second. That is, the RTC second
value must change twice before the timing is properly calibrated and the
game can start.
The main loop also checks for keyboard input by polling on each iteration, and takes care of updating game state and redrawing the screen if any state has changed.
Building
make
Requires the NASM assembler, a C compiler and a linker.
The build tries to use an i386-elf target GCC cross-compiler by
default. To change the target tuple, pass a TARGET value to make. On
x86 or x86_64 systems that already target ELF, such as Linux, the system
compiler can be used by passing CC=gcc LD=ld to make.
The build output is a multiboot ELF file tetris.elf.
Binaries
Binary ELF files and ISO images can be found on the releases page.
Running
QEMU
make qemu
The multiboot ELF file can be booted directly by the QEMU emulator.
ISO
make tetris.iso
A bootable ISO can be created using GRUB's stage2_eltorito (included
in this repository) to boot the multiboot ELF file.
genisoimage is used to crate the ISO file. On systems without
genisoimage, mkisofs from the cdrtools package can be used instead
by passing GENISOIMAGE=mkisofs to make.
The resulting tetris.iso file can then be booted with the QEMU
emulator using make qemu-iso, attached to a virtual machine as a CD
drive, or burned to a CD and booted on real hardware.
License
Copyright © 2013–2014, Curtis McEnroe programble@gmail.com
Permission to use, copy, modify, and/or distribute this software for any purpose with or without fee is hereby granted, provided that the above copyright notice and this permission notice appear in all copies.
THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS" AND THE AUTHOR DISCLAIMS ALL WARRANTIES WITH REGARD TO THIS SOFTWARE INCLUDING ALL IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE AUTHOR BE LIABLE FOR ANY SPECIAL, DIRECT, INDIRECT, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES OR ANY DAMAGES WHATSOEVER RESULTING FROM LOSS OF USE, DATA OR PROFITS, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, NEGLIGENCE OR OTHER TORTIOUS ACTION, ARISING OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE USE OR PERFORMANCE OF THIS SOFTWARE.