Awesome
Giving Attention to Generative VAE Models for De Novo Molecular Design
 This repo contains the codebase for the attention-based implementations of VAE models for molecular design as described in this paper. The addition of attention allows models to learn longer range dependencies between input features and improves the quality and interpretability of learned molecular embeddings. The code is organized by folders that correspond to the following sections:
This repo contains the codebase for the attention-based implementations of VAE models for molecular design as described in this paper. The addition of attention allows models to learn longer range dependencies between input features and improves the quality and interpretability of learned molecular embeddings. The code is organized by folders that correspond to the following sections:
- transvae: code required to run models including model class definitions, data preparation, optimizers, etc.
- scripts: scripts for training models, generating samples and performing calculations
- notebooks: jupyter notebook tutorials and example calculations
- checkpoints: pre-trained model files
- data: token vocabularies and weights for ZINC and PubChem datasets (***note - full train and test sets for both ZINC and PubChem are available for download)
Installation
The code can be installed with pip using the following command pip install transvae. RDKit and tensor2tensor are required for certain visualizations/property calculations and must also be installed (neither of these packages are necessary for training or generating molecules so if you would prefer not to install them then you can simply remove their imports from the source code).
Training
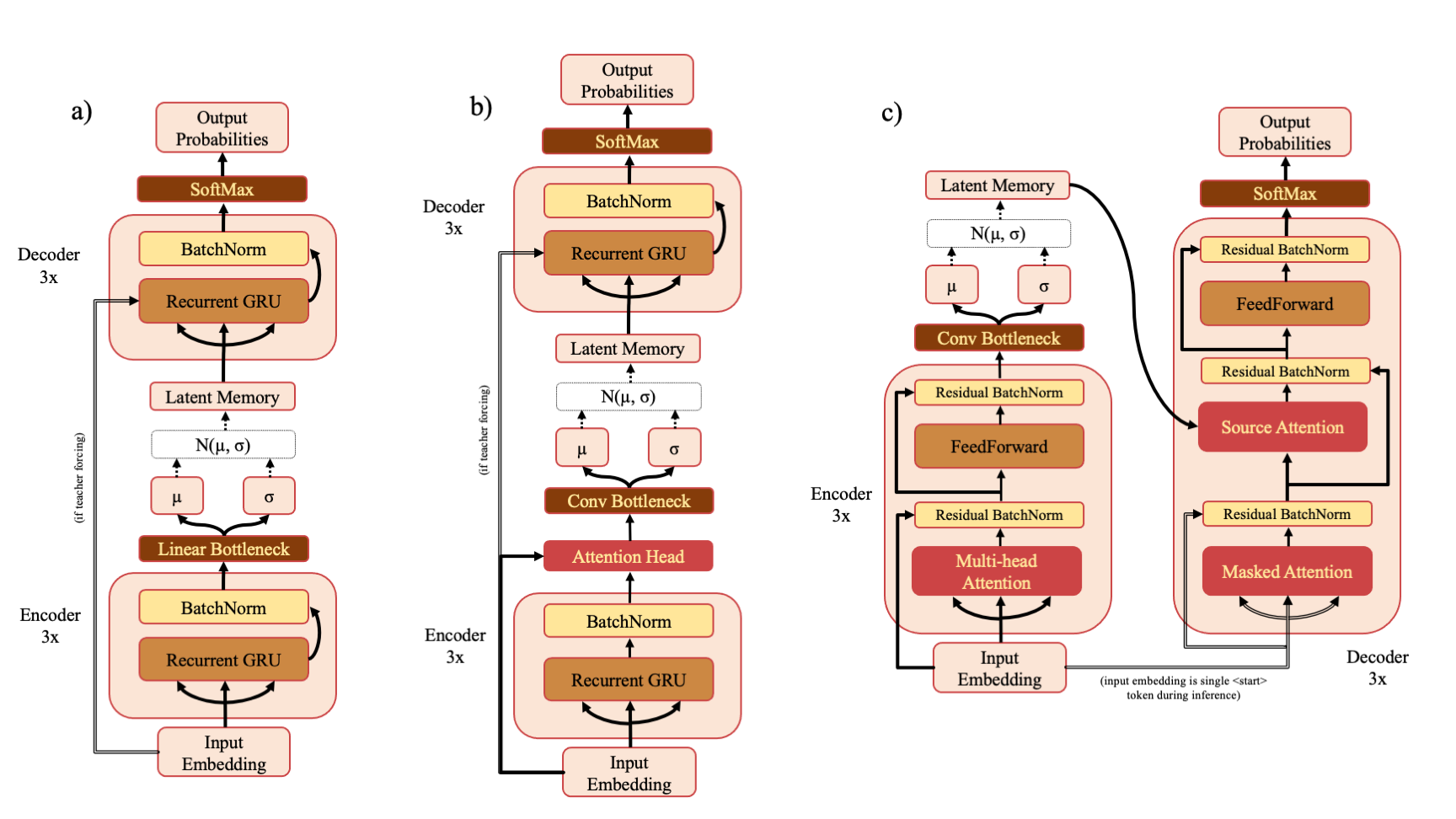
There are three model types - RNN (a), RNNAttn (b) and Transformer (c). If you've downloaded the ZINC or PubChem training sets from the drive link, you can re-train the models described in the paper with a command such as
python scripts/train.py --model transvae --data_source zinc
The default model dimension is 128 but this can also be changed at the command line
python scripts/train.py --model rnnattn --d_model 256 --data_source pubchem
You may also specify a custom train and test set like so
python scripts/train.py --model transvae --data_source custom --train_mols_path my_train_data.txt --test_mols_path my_test_data.txt --vocab_path my_vocab.pkl --char_weights_path my_char_weights.npy --save_name my_model
The vocabulary must be a pickle file that stores a dictionary that maps token -> token id and it must begin with the <start> or <bos> token. All modifiable hyperparameters can be viewed with python scripts/train.py --help.
Property Prediction
An additional set of linear layers may be appended to the latent memory to embed a property within the bottleneck using the property_predictor tag. To do so you must supply an additional set of train and test files with properties indexed at the same position as the molecules in the train and test sets. A command to train a model with this functionality might look like
python scripts/train.py --model transvae --property_predictor --data_source zinc --train_props_path train_property_data.txt --test_props_path test_property_data.txt --save_name my_props_model
Sampling
There are three sampling modes to choose from - random, high entropy or k-random high entropy. If you choose to use one of the high entropy categories, you must also supply a set of SMILES (typically the training set) to use to calculate the entropy of your model prior to sampling. An example command might look like:
python scripts/sample.py --model transvae --model_ckpt checkpoints/trans4x-256_zinc.ckpt --mols data/zinc_train.txt --sample_mode high_entropy
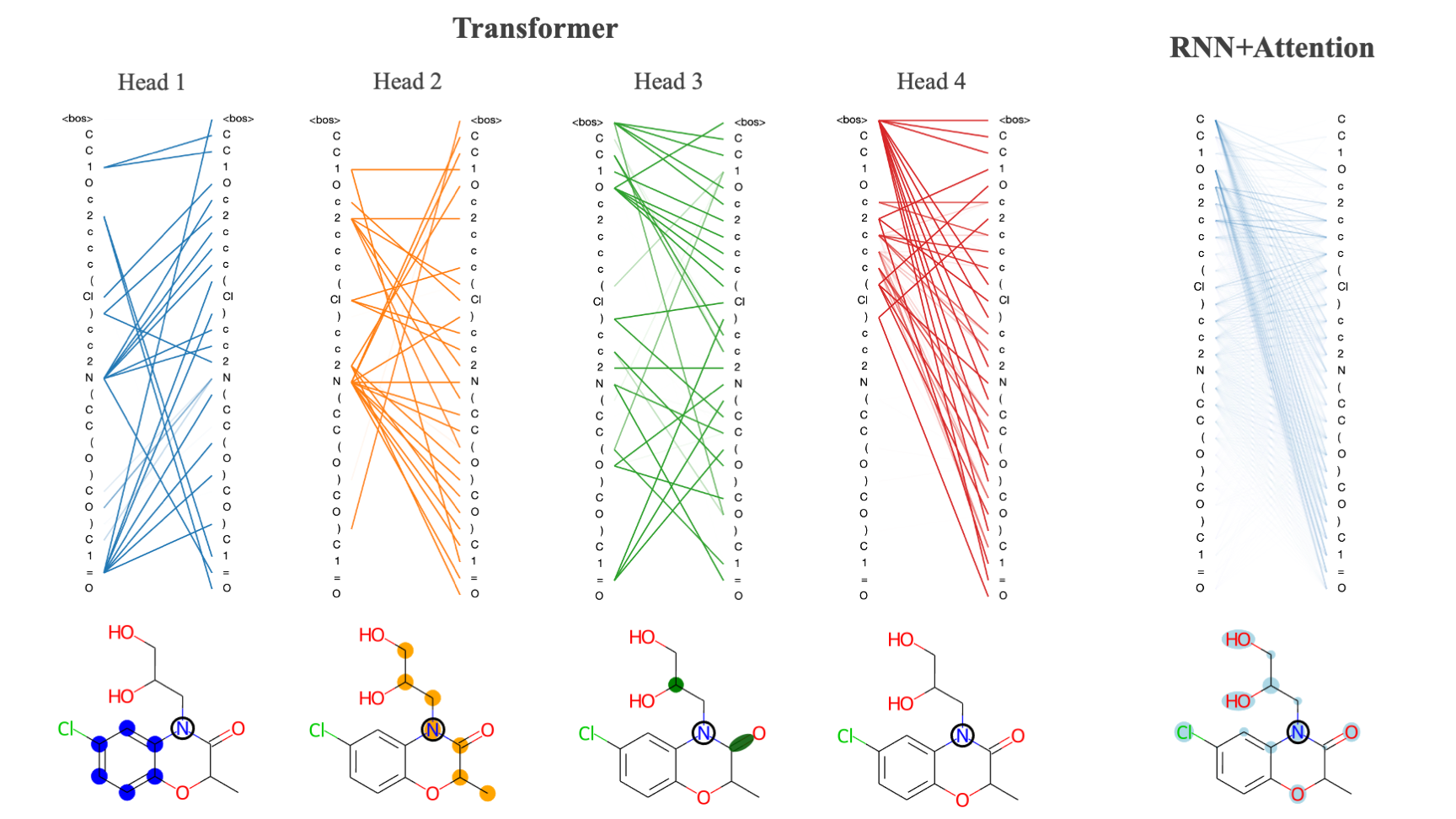
Calculating Attention
Attention can be calculated using the attention.py script. Due to the large number of attention heads and layers within the transvae model you should be careful about calculating attention for too many samples as it will generate a large amount of data. An example command for calculating attention might look like
python scripts/attention.py --model rnnattn --model_ckpt checkpoints/rnnattn-256_pubchem.ckpt --mols data/pubchem_train_(n=500).txt --save_path attn_wts/rnnattn_wts.npy
Analysis
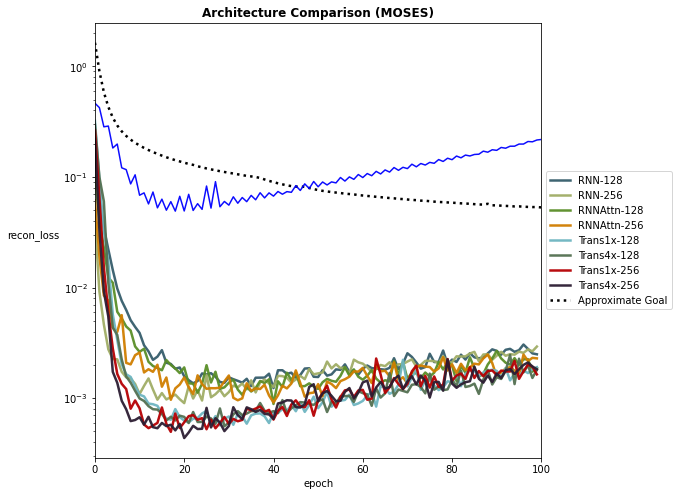
Examples of model analysis functions and how to use them are shown in notebooks/visualizing_attention.ipynb and notebooks/evaluating_models.ipynb. Additionally, there are a few helper functions in transvae/analysis.py that allow you to plot training performance curves and other useful performance metrics.