Awesome
ide-purescript package for VS Code
This package provides editor support for PureScript projects in Visual Studio Code, based on the PureScript language server.
Features:
- Build and error reporting
- Quick-fix support for certain warnings
- Autocompletion
- Type info tooltips
- Go to symbol
- Go to definition
- Case split
- Add clause
- Pursuit lookup
- PSCI
- Formatting (via
purty)
The extension language-purescript provides basic syntax highlighting support - it is required but should be installed automatically as a dependency. This package will start on opening a .purs file, and automatically trigger a rebuild on saving a .purs file.
See troubleshooting in case of issues.
Installation and General Use
This package makes use of the purs ide server (previously psc-ide) for most functionality, with purs compile (by default via spago) for the explicit
build command. All this is via a Language Server Protocol implementation, purescript-language-server. Multi-root workspaces should be supported via a multiple language server approach.
This package will launch a purescript-language-server process, which will automatically (but this is configurable) start purs ide server in your project directory and kill it when closing. Start/stop and restart commands are provided for the IDE server in case required (eg after changing config or updating compiler version).
Functionality provided by the IDE server won't work until you build your project. This can either be via the built-in
build command, or via an external tool - but if you do build externally, you should be sure to Restart/Reconnect purs IDE server (accessed through CTRL+SHIFT+P/CMD+SHIFT+P) afterwards, or the IDE server will not be able to pick up any changes.
You can configure building with pulp (optionally with psc-package) or spago by following the configuration steps below, after which you should also Restart/Reconnect purs IDE server.
Version support policy
PureScript compiler version support is as follows:
- The current minor version of the compiler is supported at all patch versions (e.g. 0.14.xx)
- The previous minor version of the compiler is supported at the latest patch version (e.g. 0.13.8) for new functionality, and where possible all patch versions for existing functionality
- Any older compiler versions are not officially supported - they may continue to work and will not be intentionally broken, but no particular effort will be made for continued support in the face of API changes
With Spago (default)
PureScript: Build command will build your project using the command line spago build --purs-args --json-errors.
Note that prior to spago version 0.10.0.0, -- was used to separate purs args at the end of the command line.
For spago with psc-package, add the following configuration to your settings.json:
{
"purescript.addSpagoSources": true,
"purescript.addNpmPath": true,
"purescript.buildCommand": "spago build --purs-args --json-errors"
}
With Pulp
PureScript: Build command will build your project using the command line pulp build -- --json-errors.
Version 0.8.0+ of the PureScript compiler is required, as well as version 10.0.0 of pulp (with earlier versions remove --).
For pulp with psc-package, add the following configuration to your settings.json:
{
"purescript.addNpmPath": true,
"purescript.buildCommand": "pulp --psc-package build -- --json-errors"
}
Suggested extensions
See input-assist for Unicode input assistance on autocomplete which is known to work with this extension, alternatively unicode-latex which offers similar LaTeX based input vi a lookup command.
Suggested configuration
Watching directories like .spago, output can be slow and on occasion cause issues. Consider also files.exclude and search.exclude.
"files.watcherExclude": {
"**/.spago/**": true
}
Key bindings
The only key binding supplied out of the box is Shift+Ctrl+B (or Shift+Cmd+B) for the full "Build" command. Although this is only enabled inside PureScript-language text editors, it does conflict with the built-in Build command. This can be edited, and other keybinds added, in the VS Code Keyboard Shortcuts preferences.
The following default vscode bindings are helpful for processing build errors:
F8cycles through errors.CTRL + .orCMD + .shows suggested fixes. The compiler sometimes provides these suggestions.
We will suggest you to add keyboard bindings for commands that you use frequently, which you can do through the menu item File > Properties > Keyboard Shortcuts.
Access to commands
To see all the commands provided by this package,
locate the View > Command palette in menu and type 'purescript'.
The contents vary but you'll get something like this.
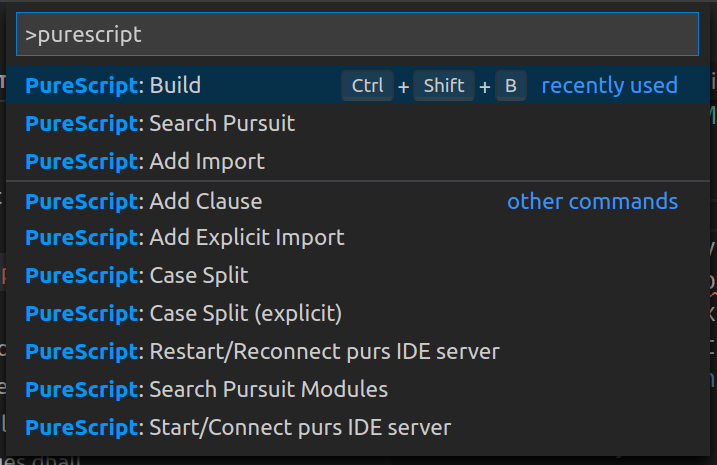
Build and error reporting
After you've added settings.json for your build system,
Shift+Ctrl+B builds it.
if you are not sure which settings.json it is, pick the Spago -one.
Autocomplete
Provided from purs ide server. Make sure your project is built first.
Completions will be sourced from modules imported in the current file.
Tooltips
Hovering over an identifier will show a tooltip with its type. Over a qualifier of a qualified identifier it will show the associated module name.
This feature disregards a context where the word appears, which means you will get some false positives (eg doesn't see local definitions, just the globals that should be visible in a given module).
Go to symbol
'Go to symbol' locates definition of a symbol by its name.
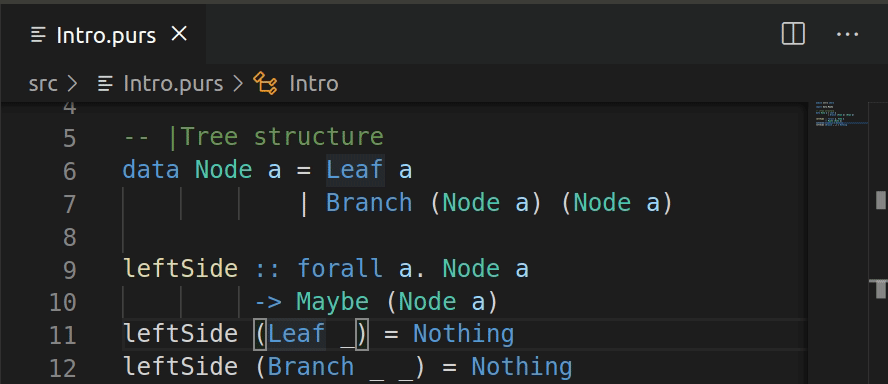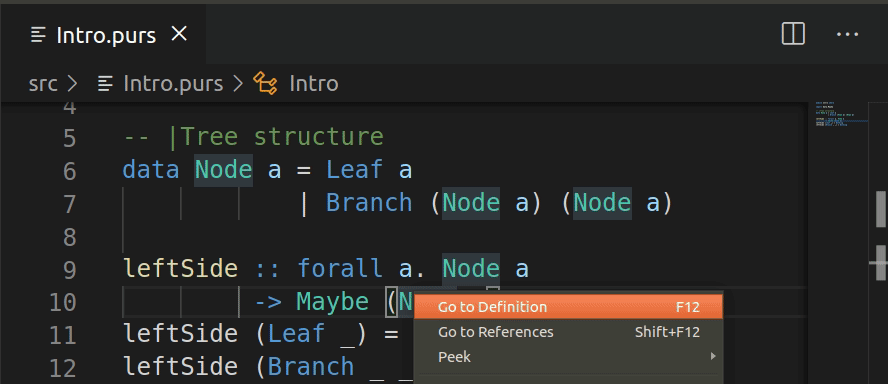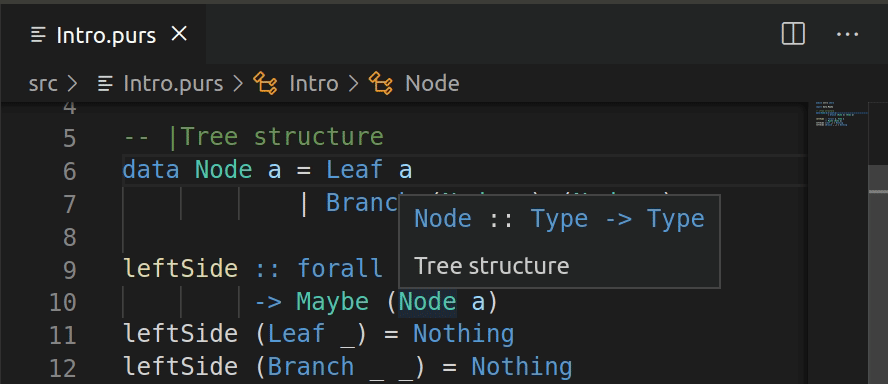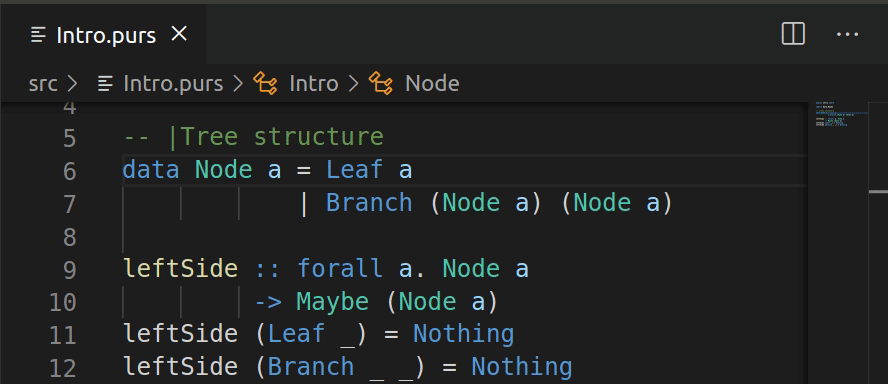
Go to definition
Hyperclick goto-definition functionality is supported. This is available with purs version
0.9.2 and above, and like tooltips/autocomplete works on identifiers bound at the top level.
In case source positions are not up to date, they may not be updated on rebuild, try rebuilding or restarting psc-ide server.
Case split
The case split expands the case under the cursor. It allows you to auto-complete large case clauses.
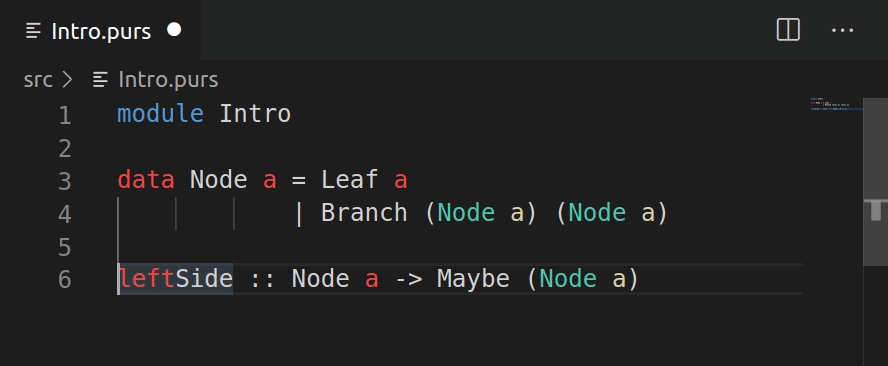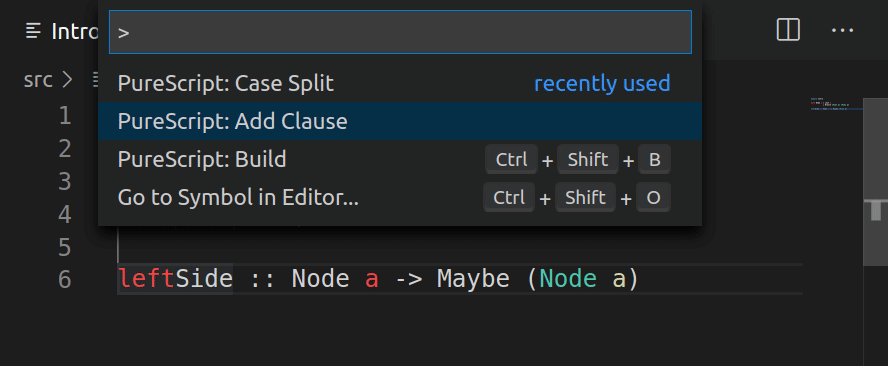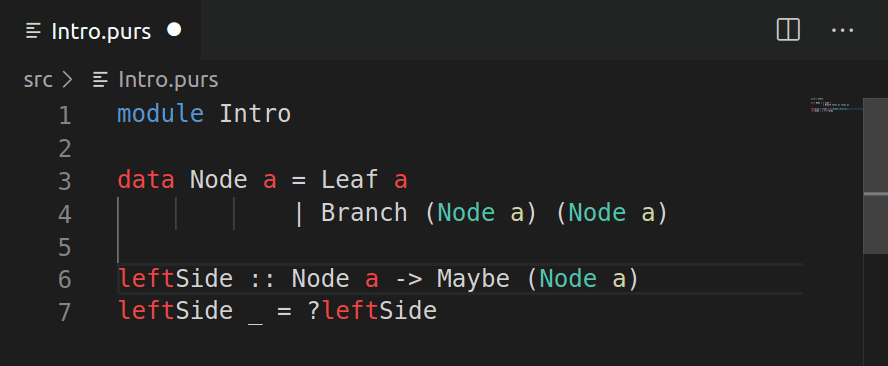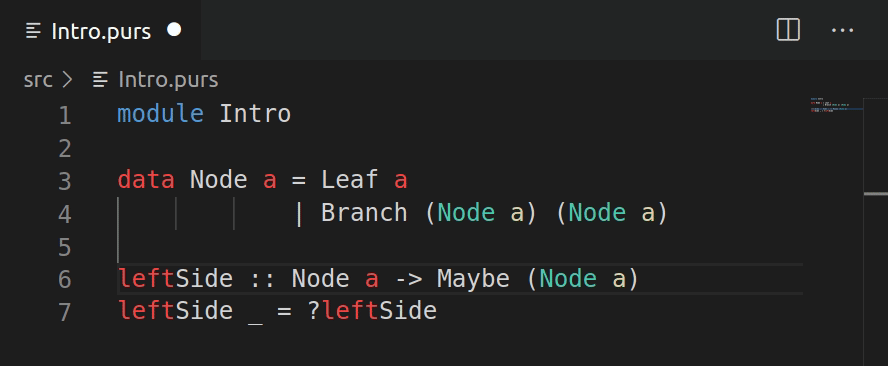
Add clause
The add clause reads the type declaration under the cursor and inserts an empty template.
Pursuit lookup
Commands "Search Pursuit" and "Search Pursuit Modules" are available to search for identifiers or modules/packages on Pursuit.
PSCI
No particular support. Suggest you open a PSCI in the integrated terminal.
Troubleshooting
Generally the Output pane ("IDE PureScript" option in the dropdown) may give useful information if something is going wrong. Useful concepts:
Rebuilding
To ensure the latest information is available to the Language Server, rebuilding may be required. This can either be the "Build Command" in VS Code, or an external build followed by "Restart/Reconnect purs IDE server".
Common errors
Module not found
This normally means either the code is not built, or there is a version mismatch. To rebuild, see above.
In some cases your build process and VS Code may be hitting different purs versions. The VS Code extension/language server will find purs in your PATH, but that includes the npm local path if the corresponding option is set, which may differ from an external build process. You may need to launch code from a terminal containing the correct PATH.
Check the "Output" pane, at the very top after the Language Server starts it will list out the purs binary being used, you can check it's the one you expect.
API for downstream extensions
VSCode makes it possible for extensions to expose methods to other extensions for cross-extension interaction. The following methods are exposed by ide-purescript.
{
// set middleware for the language client. for an example of
// how to use VSCode language client middleware, see
// https://code.visualstudio.com/api/language-extensions/embedded-languages
// the full middleware API is documented at
// https://github.com/microsoft/vscode-languageserver-node/blob/main/client/src/common/client.ts
registerMiddleware: (m: Middleware) => void;
// remove a given middleware, using the same string used to register it
unregisterMiddleware: (m: Middleware) => void;
// a callback of type () => void that is called when diagnostics begin
// diagnostics are triggered whenever compilation of one or several files begins,
// ie via a save event or by calling the `purescript.build` command
setDiagnosticsBegin: (f: EffectUnit) => void;
// a callback of type () => void that is called when diagnostics end
setDiagnosticsEnd: (f: EffectUnit) => void;
// a callback of type () => void that is called when cleaning a project begins
// cleaning is triggered by calling the `purescript.clean` command
setCleanBegin: (f: EffectUnit) => void;
// a callback of type () => void that is called when cleaning a project ends
setCleanEnd: (f: EffectUnit) => void;
}
To call these methods from your own extension, do something like:
export function activate(context: vscode.ExtensionContext) {
const ext = vscode.extensions.getExtension('nwolverson.ide-purescript');
const importedApi = ext.exports;
importedApi.setDiagnosticsBegin(() => { console.log('Did I just hear diagnostics begin?'); });
// some other stuff
}
Development
To develop (rather than use) this extension, see the instructions in purescript-language-server.