Awesome

Scatter is an Inversion of Control (IoC) container for Node.js. Scatter allows you to split your project in particles (components), and then uses Dependency Injection and Service locator to link your modules together.
Applications created with Scatter are extensible out-of-the box. Since every dependency is "virtual", you can override and extend every module. In addition by using Scatter Services you can provide explicit extension points to your application.
Every module created for Scatter is totally agnostic to the IoC container and can be used even without it. Scatter modules are POJOs (Plain Old Javascript Objects), simply objects, factories and constructors that accept their dependencies as input. The only difference from a plain module is that Scatter reads an annotation named __module to extract the information to initialize the module and inject dependencies.
Full Guide | API docs | Plugins
Scatter virtual directory federation
Although Scatter can be used as a "traditional" IoC container and has many usage patterns, the main reason for his existence is to allow the federation of multiple project directories into one. Dependency Injection, in fact, is not the reason Scatter was created but only a tool which allows to transparently map multiple components, called particles (which may also be distributed as npm pagackes), into one virtual namespace. It doesn't matter where a module is created, when used with Scatter it will always have a federated view over all the other modules in the project.
Where is the advantage of this you may ask...well imagine those components as plugins, you app would become immediately extensible with minimal effort and no boilerplate code to support the plugin infrastructure.
The use cases? Here are some:
- Create a CRM (or any other business app) and need to customize it for some clients whitout branching the code
- Create a blog/forum/CMS and want people to extend it using plugins
- Add all the use cases where an IoC container can improve decoupling and testing.
Features
- Split your project into components (particles) and wire modules using Dependency Injection.
- Define your modules as you want: factories, constructors or plain objects.
- Your modules do not need to know who is instantiating them or wiring them, they are totally decoupled from Scatter and will work even without it.
- Instantiate and initialize modules asynchronously (just return a promise).
- Services framework built on top of the IoC container (with sync and async execution)
Examples
If you prefer to go straight to the code then take a look at some examples.
Sample usage
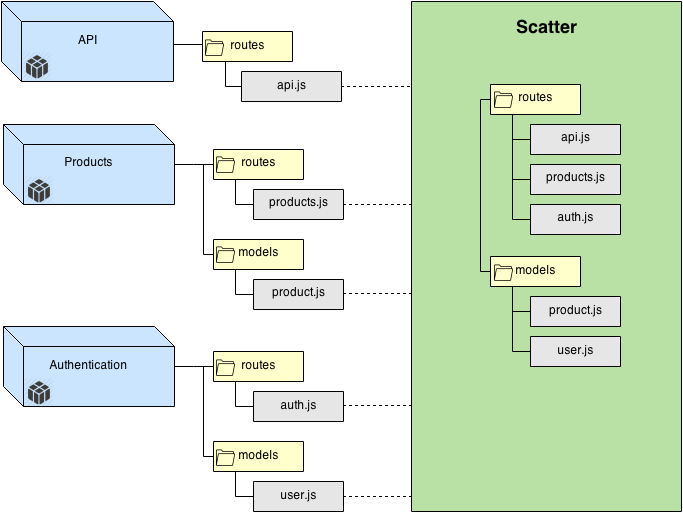
The directory structure below shows 3 particles (Scatter components):
corethe the main application- 2 plugins:
privateProfilesadmin
All the 3 components define some routes. The Scatter container allows you to write each component as if it they were all included in a single app root, as if all the sources were actually contained in a single directory (and not scattered across different components).
In this examples routes is for Scatter a namespace not a physical directory, it is a federated container of modules.
app.js
core
|-- particle.json
|-- expressApp.js
|-- routes <--- Routes
|-- home.js
`-- profiles.js
|-- data
`-- db.js
plugins
|-- privateProfiles
|-- particle.json
`-- routes <--- Routes
|-- profiles.js <--- an override
`-- private.js
|-- admin
|-- particle.json
`-- routes <--- Routes
`-- admin.js
Now if we wanted to register all the routes in our express application, the file core/expressApp.js.js would look like:
// file "core/expressApp.js.js"
var express = require('express'),
http = require('http');
module.exports = function(homeRouter, profileRouter, privateRouter, adminRouter) {
return {
start: function() {
var app = express();
app.use(...);
[... middleware ...]
app.use(app.router);
//now we register our routes
homeRouter.register(app);
profileRouter.register(app);
privateRouter.register(app);
adminRouter.register(app);
http.createServer(app).listen(app.get('port'), function () {
console.log('Express server listening on port ' + app.get('port'));
});
}
};
};
//The Scatter annotation
module.exports.__module = {
//Inject this modules as arguments
args: ["routes/home", "routes/profiles", "routes/private", "routes/admin"]
};
Then at last the file app.js would bootstrap the Scatter container and start the express app:
var scatter = new Scatter();
scatter.registerParticles([
__dirname + '/plugins/*',
__dirname + '/core'
]);
//The application entry point, the dependency is loaded explicitly
scatter.load("expressApp").then(function(expressApp) {
expressApp.start();
});
More decoupling: Services
You will notice in the example above that if a new plugins is added and a new route is introduced it will not be
registered, because we reference directly the routes in the file core/expressApp. To solve this problem Scatter
supports a pattern that is a mix between DI and service locator.
The svc (Service) plugin will allow you to require a method defined in multiple modules as a dependency!
Using Scatter Services the core/expressApp would now look like:
// file "core/expressApp.js.js"
var express = require('express'),
http = require('http');
module.exports = function(registerAllRoutes) {
return {
start: function() {
var app = express();
app.use(...);
[... middleware ...]
app.use(app.router);
//now we register our routes
registerAllRoutes(app);
http.createServer(app).listen(app.get('port'), function () {
console.log('Express server listening on port ' + app.get('port'));
});
}
};
};
//The Scatter annotation
module.exports.__module = {
//Inject a service as dependency
args: ["svc!routes/register"]
};
Documentation
There is a lot more to know! Take a look at the guide and the API docs.
Full Guide
API docs
What's new
0.7
- Support for relative paths in module dependencies.
- Breaking changes:
- Services must now be defined using the full service namespace.
Now becomes:provides: 'aService'provides: 'full/namespace/aService' - When requiring services without arguments (e.g.
svc!aService) thesequenceservice invocator will be returned instead of the full service object. In practice nowsvc!aService===svc|sequence!aService.
- Services must now be defined using the full service namespace.
0.6
- Several internal improvement, including plugin system refactoring, new benchmarking framework, performance optimizations.
- Breaking changes:
- The
logobject provided to the Scatter constructor must expecttrace, debug, info, warn, erroras levels instead ofsilly, verbose, info, warn, error.
- The
Stability
2 - Unstable
The API is in the process of settling, but has not yet had sufficient real-world testing to be considered stable.
Contributors
- Mario Casciaro - Twitter @mariocasciaro - Creator
- Zbigniew Mrowinski - Twitter @MrowinskiZ - Scatter logo





