Awesome
tween.lua
tween.lua is a small library to perform tweening in Lua. It has a minimal interface, and it comes with several easing functions.
Examples
local tween = require 'tween'
-- increase the volume of music from 0 to 5 in 10 seconds
local music = { volume = 0, path = "path/to/file.mp3" }
local musicTween = tween.new(10, music, {volume = 5})
...
musicTween:update(dt)
-- make some text fall from the top of the screen, bouncing on y=300, in 4 seconds
local label = { x=200, y=0, text = "hello" }
local labelTween = tween.new(4, label, {y=300}, 'outBounce')
...
labelTween:update(dt)
-- fade background from white to black and foregrond from black to red in 2 seconds
-- Notice that you can use subtables with tween
local properties = {bgcolor = {255,255,255}, fgcolor = {0,0,0}}
local fadeTween = tween.new(2, properties, {bgcolor = {0,0,0}, fgcolor={255,0,0}}, 'linear')
...
fadeTween:update(dt)
Demo
There is a demo in the "demo" branch of this repo:
https://github.com/kikito/tween.lua/tree/demo

You will need LÖVE to execute the demo.
In the animation above, you can see how the user can move time "forwards or backwards" by pressing and releasing the space key.
Interface
Tween creation
local t = tween.new(duration, subject, target, [easing])
Creates a new tween.
durationmeans how much the change will take until it's finished. It must be a positive number.subjectmust be a table with at least one key-value. Its values will be gradually changed by the tween until they look liketarget. All the values must be numbers, or tables with numbers.targetmust be a table with at least the same keys assubject. Other keys will be ignored.easingcan be either a function or a function name (see the easing section below). It's default value is'linear'tis the object that must be used to perform the changes - see the "Tween methods" section below.
This function only creates and returns the tween. It must be captured in a variable and updated via t:update(dt) in order for the changes to take place.
Tween methods
local complete = t:update(dt)
Gradually changes the contents of subject to that it looks more like target as time passes.
tis a tween returned bytween.newdtmust be positive number. It will be added to the internal time counter of the tween. Thensubject's values will be updated so that they approachtarget's using the selected easing function.completeistrueif the tween has reached its limit (its internal clock is>= duration). It is false otherwise.
When the tween is complete, the values in subject will be equal to target's. The way they change over time will depend on the chosen easing function.
If dt is positive, the easing will be applied until the internal clock equals t.duration, at which point the easing will stop. If it is negative,
the easing will play "backwards", until it reaches the initial value.
This method is roughtly equivalent to t:set(self.clock + dt).
local complete = t:set(clock)
Moves a tween's internal clock to a particular moment.
tis a tween returned bytween.newclockis a positive number or 0. It's the new value of the tween's internal clock.completeworks like int:update; it'strueif the tween has reached its end, andfalseotherwise.
If clock is greater than t.duration, then the values in t.subject will be equal to t.target, and t.clock will
be equal to t.duration.
t:reset()
Resets the internal clock of the tween back to 0, resetting subject.
tis a tween returned bytween.new
This method is equivalent to t:set(0).
Easing functions
Easing functions are functions that express how slow/fast the interpolation happens in tween.
tween.lua comes with 45 default easing functions already built-in (adapted from Emmanuel Oga's easing library).
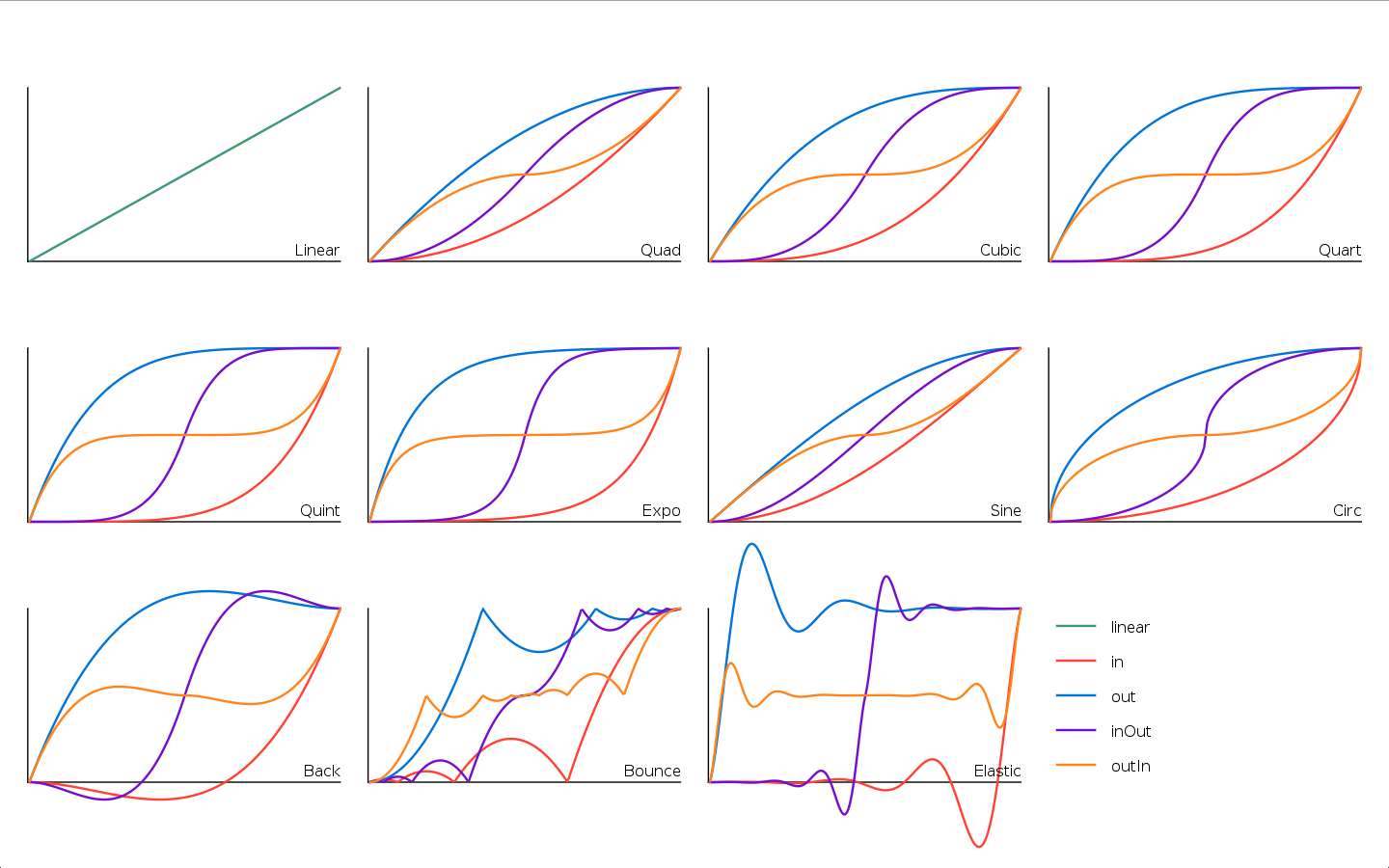
The easing functions can be found in the table tween.easing.
They can be divided into several families:
linearis the default interpolation. It's the simplest easing function.quad,cubic,quart,quint,expo,sineandcircleare all "smooth" curves that will make transitions look natural.- The
backfamily starts by moving the interpolation slightly "backwards" before moving it forward. - The
bouncefamily simulates the motion of an object bouncing. - The
elasticfamily simulates inertia in the easing, like an elastic gum.
Each family (except linear) has 4 variants:
instarts slow, and accelerates at the endoutstarts fast, and decelerates at the endinOutstarts and ends slow, but it's fast in the middleoutInstarts and ends fast, but it's slow in the middle
| family | in | out | inOut | outIn |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Linear | linear | linear | linear | linear |
| Quad | inQuad | outQuad | inOutQuad | outInQuad |
| Cubic | inCubic | outCubic | inOutCubic | outInCubic |
| Quart | inQuart | outQuart | inOutQuart | outInQuart |
| Quint | inQuint | outQuint | inOutQuint | outInQuint |
| Expo | inExpo | outExpo | inOutExpo | outInExpo |
| Sine | inSine | outSine | inOutSine | outInSine |
| Circ | inCirc | outCirc | inOutCirc | outInCirc |
| Back | inBack | outBack | inOutBack | outInBack |
| Bounce | inBounce | outBounce | inOutBounce | outInBounce |
| Elastic | inElastic | outElastic | inOutElastic | outInElastic |
When you specify an easing function, you can either give the function name as a string. The following two are equivalent:
local t1 = tween.new(10, subject, {x=10}, tween.easing.linear)
local t2 = tween.new(10, subject, {x=10}, 'linear')
But since 'linear' is the default, you can also do this:
local t3 = tween.new(10, subject, {x=10})
Custom easing functions
You are not limited to tween's easing functions; if you pass a function parameter in the easing, it will be used.
The passed function will need to take 4 parameters:
t(time): starts in 0 and usually moves towards durationb(begin): initial value of the of the property being eased.c(change): ending value of the property - starting value of the propertyd(duration): total duration of the tween
And must return the new value after the interpolation occurs.
Here's an example using LÖVE's Bezier Curve (you will need LÖVE for this example, but tween.lua does not need LÖVE in general).
local cubicbezier = function (x1, y1, x2, y2)
local curve = love.math.newBezierCurve(0, 0, x1, y1, x2, y2, 1, 1)
return function (t, b, c, d) return c * curve:evaluate(t/d) + b end
end
local label = { x=200, y=0, text = "hello" }
local labelTween = tween.new(4, label, {y=300}, cubicbezier(.35, .97, .58, .61))
Gotchas / Warnings
tweendoes not have any defined time units (seconds, milliseconds, etc). You define the units it uses by passing it adtontween.update. Ifdtis in seconds, thentweenwill work in seconds. Ifdtis in milliseconds, thentweenwill work in milliseconds.tweencan work on deeply-nested subtables (the "leaf" values have to be numbers in both the subject and the target)
Installation
Just copy the tween.lua file somewhere in your projects (maybe inside a /lib/ folder) and require it accordingly.
Remember to store the value returned by require somewhere! (I suggest a local variable named tween)
local tween = require 'tween'
You can of course specify your own easing function. Just make sure you respect the parameter format.
Specs
This project uses busted for its specs. In order to run them, install busted, and then execute it on the top folder:
busted
Credits
The easing functions have been copied from EmmanuelOga's project in
https://github.com/emmanueloga/easing
See the LICENSE.txt file for details.
Changelog
See CHANGELOG.md for a full list of changes.