Awesome
A Powerline style prompt for your shell
A Powerline like prompt for Bash, ZSH and Fish. Based on Powerline-Shell by @banga. Ported to golang by @justjanne.
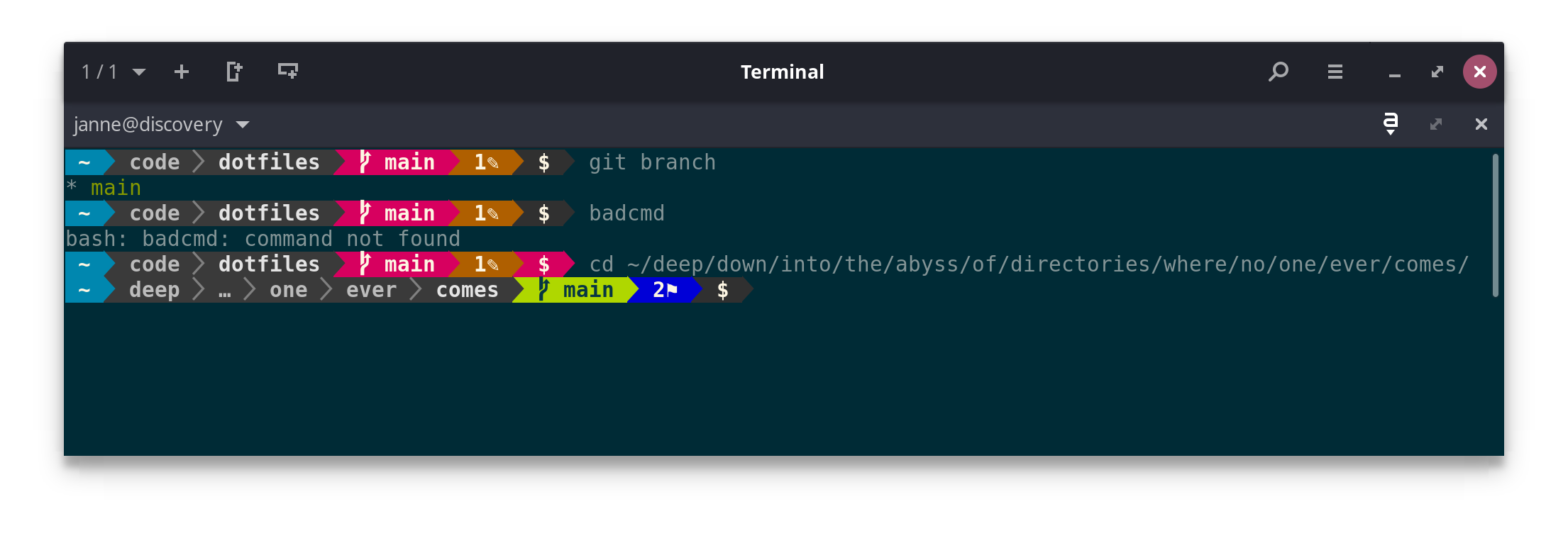
- Shows some important details about the git/hg branch (see below)
- Changes color if the last command exited with a failure code
- If you're too deep into a directory tree, shortens the displayed path with an ellipsis
- Shows the current Python virtualenv environment
- Shows the current Ruby version using rbenv or rvm
- Shows if you are in a nix shell
- It's easy to customize and extend. See below for details.
Table of Contents
Version Control
All of the version control systems supported by powerline shell give you a quick look into the state of your repo:
- The current branch is displayed and changes background color when the branch is dirty.
- When the local branch differs from the remote, the difference in number
of commits is shown along with
⇡or⇣indicating whether a git push or pull is pending
In addition, git has a few extra symbols:
✎-- a file has been modified, but not staged for commit✔-- a file is staged for commit✼-- a file has conflicts+-- untracked files are present⚑-- stash is present
Each of these will have a number next to it if more than one file matches.
Installation
Requires Go 1.15+
powerline-go uses ANSI color codes, these should nowadays work everywhere,
but you may have to set your $TERM to xterm-256color for it to work.
If you want to use the "patched" mode (which is the default, and provides improved UI), you'll need to install a powerline font, either as fallback, or by patching the font you use for your terminal: see powerline-fonts. Alternatively you can use "compatible" or "flat" mode.
Precompiled Binaries
I provide precompiled binaries for x64 Linux and macOS in the releases tab
Other Platforms
- Install (and update) the package with
go install github.com/justjanne/powerline-go@latest
- By default it will be in
$GOPATH/bin, if you want to change that, you can set your$GOPATHand/or$GOBIN, but will need to change the path in the following scripts, too.
Bash
Add the following to your .bashrc:
function _update_ps1() {
PS1="$($GOPATH/bin/powerline-go -error $? -jobs $(jobs -p | wc -l))"
# Uncomment the following line to automatically clear errors after showing
# them once. This not only clears the error for powerline-go, but also for
# everything else you run in that shell. Don't enable this if you're not
# sure this is what you want.
#set "?"
}
if [ "$TERM" != "linux" ] && [ -f "$GOPATH/bin/powerline-go" ]; then
PROMPT_COMMAND="_update_ps1; $PROMPT_COMMAND"
fi
Currently, right prompt support is not available when using bash.
ZSH
Add the following to your .zshrc:
function powerline_precmd() {
PS1="$($GOPATH/bin/powerline-go -error $? -jobs ${${(%):%j}:-0})"
# Uncomment the following line to automatically clear errors after showing
# them once. This not only clears the error for powerline-go, but also for
# everything else you run in that shell. Don't enable this if you're not
# sure this is what you want.
#set "?"
}
function install_powerline_precmd() {
for s in "${precmd_functions[@]}"; do
if [ "$s" = "powerline_precmd" ]; then
return
fi
done
precmd_functions+=(powerline_precmd)
}
if [ "$TERM" != "linux" ] && [ -f "$GOPATH/bin/powerline-go" ]; then
install_powerline_precmd
fi
Fish
Redefine fish_prompt in ~/.config/fish/config.fish:
function fish_prompt
eval $GOPATH/bin/powerline-go -error $status -jobs (count (jobs -p))
end
Nix
When using nix-shell --pure, powerline-go will not be accessible, and
your prompt will disappear.
To work around this you can add this snippet to your .bashrc,
which should re-enable the prompt in most cases:
# Workaround for nix-shell --pure
if [ "$IN_NIX_SHELL" == "pure" ]; then
if [ -x "$HOME/.nix-profile/bin/powerline-go" ]; then
alias powerline-go="$HOME/.nix-profile/bin/powerline-go"
elif [ -x "/run/current-system/sw/bin/powerline-go" ]; then
alias powerline-go="/run/current-system/sw/bin/powerline-go"
fi
fi
Powershell
Redefine prompt function on your profile:
# Load powerline-go prompt
function global:prompt {
$pwd = $ExecutionContext.SessionState.Path.CurrentLocation
$startInfo = New-Object System.Diagnostics.ProcessStartInfo
$startInfo.FileName = "powerline-go"
$startInfo.Arguments = "-shell bare"
$startInfo.Environment["TERM"] = "xterm-256color"
$startInfo.CreateNoWindow = $true
$startInfo.StandardOutputEncoding = [System.Text.Encoding]::UTF8
$startInfo.RedirectStandardOutput = $true
$startInfo.UseShellExecute = $false
$startInfo.WorkingDirectory = $pwd
$process = New-Object System.Diagnostics.Process
$process.StartInfo = $startInfo
$process.Start() | Out-Null
$standardOut = $process.StandardOutput.ReadToEnd()
$process.WaitForExit()
$standardOut
}
Use ProcessStartInfo is needed to allow fill the enviromnet variables required by powerline-go.
Customization
There are a few optional arguments which can be seen by running
powerline-go -help. These can be used by changing the command you have set
in your shell’s init file.
Usage of powerline-go:
-alternate-ssh-icon
Show the older, original icon for SSH connections
-colorize-hostname
Colorize the hostname based on a hash of itself, or use the PLGO_HOSTNAMEFG and PLGO_HOSTNAMEBG env vars (both need to be set).
-condensed
Remove spacing between segments
-cwd-max-depth int
Maximum number of directories to show in path
(default 5)
-cwd-max-dir-size int
Maximum number of letters displayed for each directory in the path
(default -1)
-cwd-mode string
How to display the current directory
(valid choices: fancy, semifancy, plain, dironly)
(default "fancy")
-duration string
The elapsed clock-time of the previous command
-duration-min string
The minimal time a command has to take before the duration segment is shown (default "0")
-east-asian-width
Use East Asian Ambiguous Widths
-error int
Exit code of previously executed command
-eval
Output prompt in 'eval' format.
-git-assume-unchanged-size int
Disable checking for changed/edited files in git repositories where the index is larger than this size (in KB), improves performance (default 2048)
-git-disable-stats string
Comma-separated list to disable individual git statuses
(valid choices: ahead, behind, staged, notStaged, untracked, conflicted, stashed)
-git-mode string
How to display git status
(valid choices: fancy, compact, simple)
(default "fancy")
-hostname-only-if-ssh
Show hostname only for SSH connections
-ignore-repos string
A list of git repos to ignore. Separate with ','.
Repos are identified by their root directory.
-ignore-warnings
Ignores all warnings regarding unset or broken variables
-jobs int
Number of jobs currently running
-max-width int
Maximum width of the shell that the prompt may use, in percent. Setting this to 0 disables the shrinking subsystem.
-mode string
The characters used to make separators between segments.
(valid choices: patched, compatible, flat)
(default "patched")
-modules string
The list of modules to load, separated by ','
(valid choices: aws, bzr, cwd, direnv, docker, docker-context, dotenv, duration, exit, fossil, gcp, git, gitlite, goenv, hg, host, jobs, kube, load, newline, nix-shell, node, perlbrew, perms, plenv, rbenv, root, rvm, shell-var, shenv, ssh, svn, termtitle, terraform-workspace, time, user, venv, vgo, vi-mode, wsl)
Unrecognized modules will be invoked as 'powerline-go-MODULE' executable plugins and should output a (possibly empty) list of JSON objects that unmarshal to powerline-go's Segment structs.
(default "venv,user,host,ssh,cwd,perms,git,hg,jobs,exit,root")
-modules-right string
The list of modules to load anchored to the right, for shells that support it, separated by ','
(valid choices: aws, bzr, cwd, direnv, docker, docker-context, dotenv, duration, exit, fossil, gcp, git, gitlite, goenv, hg, host, jobs, kube, load, newline, nix-shell, node, perlbrew, perms, plenv, rbenv, root, rvm, shell-var, shenv, ssh, svn, termtitle, terraform-workspace, time, user, venv, vgo, wsl)
Unrecognized modules will be invoked as 'powerline-go-MODULE' executable plugins and should output a (possibly empty) list of JSON objects that unmarshal to powerline-go's Segment structs.
-newline
Show the prompt on a new line
-numeric-exit-codes
Shows numeric exit codes for errors.
-path-aliases string
One or more aliases from a path to a short name. Separate with ','.
An alias maps a path like foo/bar/baz to a short name like FBB.
Specify these as key/value pairs like foo/bar/baz=FBB.
Use '~' for your home dir. You may need to escape this character to avoid shell substitution.
-priority string
Segments sorted by priority, if not enough space exists, the least priorized segments are removed first. Separate with ','
(valid choices: aws, bzr, cwd, direnv, docker, docker-context, dotenv, duration, exit, fossil, gcp, git, gitlite, goenv, hg, host, jobs, kube, load, newline, nix-shell, node, perlbrew, perms, plenv, rbenv, root, rvm, shell-var, shenv, ssh, svn, termtitle, terraform-workspace, time, user, venv, vgo, vi-mode, wsl)
(default "root,cwd,user,host,ssh,perms,git-branch,git-status,hg,jobs,exit,cwd-path")
-shell string
Set this to your shell type
(valid choices: autodetect, bare, bash, zsh)
(default "autodetect")
-shell-var string
A shell variable to add to the segments.
-shell-var-no-warn-empty
Disables warning for empty shell variable.
-shorten-eks-names
Shortens names for EKS Kube clusters.
-shorten-gke-names
Shortens names for GKE Kube clusters.
-static-prompt-indicator
Always show the prompt indicator with the default color, never with the error color
-theme string
Set this to the theme you want to use
(valid choices: default, low-contrast, gruvbox, solarized-dark16, solarized-light16)
(default "default")
-trim-ad-domain
Trim the Domainname from the AD username.
-truncate-segment-width int
Maximum width of a segment, segments longer than this will be shortened if space is limited. Setting this to 0 disables it.
(default 16)
-venv-name-size-limit int
Show indicator instead of virtualenv name if name is longer than this limit (defaults to 0, which is unlimited)
-vi-mode string
The current vi-mode (eg. KEYMAP for zsh) for vi-module module
Eval
If using eval and -modules-right is desired, the shell setup must be modified slightly, as shown below:
Bash
Add the following to your .bashrc:
function _update_ps1() {
eval "$($GOPATH/bin/powerline-go -error $? -shell bash -eval -modules-right git)"
}
if [ "$TERM" != "linux" ] && [ -f "$GOPATH/bin/powerline-go" ]; then
PROMPT_COMMAND="_update_ps1; $PROMPT_COMMAND"
fi
ZSH
Add the following to your .zshrc:
function powerline_precmd() {
eval "$($GOPATH/bin/powerline-go -error $? -shell zsh -eval -modules-right git)"
}
function install_powerline_precmd() {
for s in "${precmd_functions[@]}"; do
if [ "$s" = "powerline_precmd" ]; then
return
fi
done
precmd_functions+=(powerline_precmd)
}
if [ "$TERM" != "linux" ]; then
install_powerline_precmd
fi
Fish
Eval mode (and modules-right support) for Fish is not currently available.
Path Aliases
The point of the path aliases feature is to allow you to replace long paths with a shorter string that you can understand more quickly. This is useful if you're often in deep path hierarchies that end up consuming most of your terminal width, even when some portions are replaced by an ellipsis.
For example, you might want to replace the string $GOPATH/src/github.com with
@GOPATH-GH. When you're in a directory like
$GOPATH/src/github.com/justjanne/powerline-go, you'll instead see @GOPATH-GH > justjanne > powerline-go in the shell prompt.
Aliases are defined as comma-separated key value pairs, like this:
powerline-go ... -path-aliases \$GOPATH/src/github.com=@GOPATH-GH,\~/work/projects/foo=@FOO,\~/work/projects/bar=@BAR
Note that you should use ~ instead of /home/username when specifying the
path. Also make sure to escape the ~ character. Otherwise your shell will
perform interpolation on it before powerline-go can see it!
Duration
The duration segment requires some assistance from the shell. The shell must have a hook that gets executed immediately before the command.
Bash
Bash 4.4 includes an easy way to get a start-time, using $PS0. However, not all operating systems come with a sufficiently recent version of Bash installed. This example only has seconds precision. Add or modify your .bashrc file to include the following:
INTERACTIVE_BASHPID_TIMER="/tmp/${USER}.START.$$"
PS0='$(echo $SECONDS > "$INTERACTIVE_BASHPID_TIMER")'
function _update_ps1() {
local __ERRCODE=$?
local __DURATION=0
if [ -e $INTERACTIVE_BASHPID_TIMER ]; then
local __END=$SECONDS
local __START=$(cat "$INTERACTIVE_BASHPID_TIMER")
__DURATION="$(($__END - ${__START:-__END}))"
rm -f "$INTERACTIVE_BASHPID_TIMER"
fi
PS1="$($GOPATH/bin/powerline-go -modules duration -duration $__DURATION -error $__ERRCODE -shell bash)"
}
if [ "$TERM" != "linux" ] && [ -f "$GOPATH/bin/powerline-go" ]; then
PROMPT_COMMAND="_update_ps1; $PROMPT_COMMAND"
fi
Zsh
Using $EPOCHREALTIME requires loading the 'datetime' module in your .zshrc file, for example:
zmodload zsh/datetime
function preexec() {
__TIMER=$EPOCHREALTIME
}
function powerline_precmd() {
local __ERRCODE=$?
local __DURATION=0
if [ -n $__TIMER ]; then
local __ERT=$EPOCHREALTIME
__DURATION="$(($__ERT - ${__TIMER:-__ERT}))"
fi
PS1="$(powerline-go -modules duration -duration $__DURATION -error $__ERRCODE -shell zsh)"
unset __TIMER
}
If the 'datetime' module is unavailable or unwanted, you may replace $EPOCHREALTIME with $SECONDS, at the loss of precision.
Fish
The fish prompt, in ~/.config/fish/config.fish, will require a minimum of changes, as Fish automatically provides $CMD_DURATION, although with only milliseconds accuracy.
function fish_prompt
set duration (math -s6 "$CMD_DURATION / 1000")
$GOPATH/bin/powerline-go -modules duration -duration $duration -error $status -shell bare
end
License
This program is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or (at your option) any later version.
This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU General Public License for more details.
You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License along with this program. If not, see http://www.gnu.org/licenses/.