Awesome
neuraltalk2-web
Neuraltalk2 is a fantastic tool based on Torch which uses neural networks to automatically caption images.
This repository offers a Dockerfile and a web interface to run immediately the program without having to manually install the dependencies and exposing it as a simple REST interface. A basic browser page is available, too.
You can both use it from the command line and as a web service.
Does it use GPUs?
Unfortunately not. Although neuraltalk2 can use GPU I don't have the proper hardware to test it and so the Docker image runs only on CPU. Look here for a GPU-enabled image.
Installation
Linux
You only need Docker, so run as root
curl -sSL https://get.docker.com/ | sh
It's better to restart your machine aftwerwards.
Then you can run it from the CLI or usign the REST interface.
Windows or Mac OS
You will need a VM with Linux, or just install docker-machine and let it create that for you.
The default memory of 1GB is not enough, so give it more:
docker-machine create -d virtualbox --virtualbox-memory "4000" neuraltalk2
eval "$(docker-machine env neuraltalk2)"
Then use the same instructions as Linux, but note that:
- VMs usually do not have access to host GPUs
- docker-machine mounts the user folder on the VM filesystem, and that's the path you need to give ‘docker run‘
- The VM will have its own IP address, so use ‘docker-machine ssh neuraltalk2‘ to SSH in it and ‘docker-machine ip‘ to know its IP
Usage
NOTE : the application sends system metrics (free RAM, nodejs version, OS, etc. nothing like username or other personal data) to a server for my curiosity. The data is shown in the console.
If you just want to try caption an image, visit http://localhost:5000 and click or drag a file on the "drag files here to upload", then wait a few seconds and the caption will appear below. There's a known bug that requires to reload the page to caption another image.
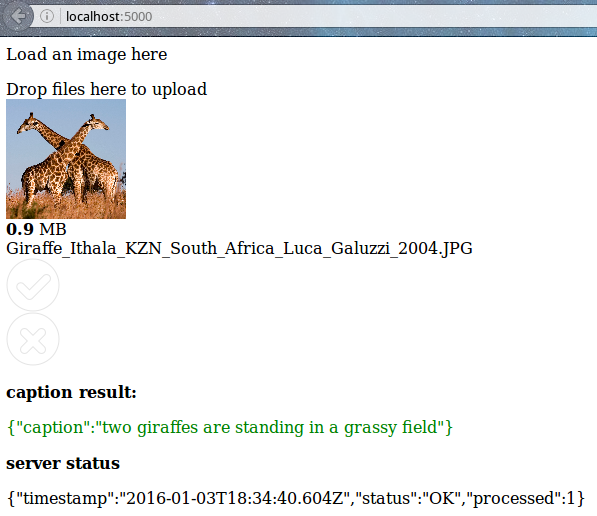
You can use the command line or the web interface, depending on your needs.
The web interface is useful to integrate captioning in other applications, just by calling a few endpoints.
In any case you will need a model file, see the neuraltalk2 page for that.
Web interface
Assuming your model file is located at /home/user/captiondata/model/model_id1-501-1448236541.t7_cpu.t7 you need to run the container with this command:
docker run --name neuraltalk2-web -p 5000:5000 -v /home/user/captiondata:/mounted jacopofar/neuraltalk2-web:latest
if you have a different model name, use -e "modelPath=/mounted/mymodel.t7" to tell the path. A check is run at startup to ensure it is found.
Now you can add an image URL to the processing queue using the addURL endpoint:
curl -X POST -H "Content-Type: application/json" -d '{"url":"https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/8/85/Garden_bench_001.jpg"}' 'http://localhost:5000/addURL'
it will return the SHA256 and the filetype of the file:
{
"extension": "jpg",
"sha256sum": "5421c617efb140e0c4967051838dc6d6b4894444b29c0bbc649399fee0b0f5ef"
}
Then call the caption endpoint using the SHA256:
curl 'http://localhost:5000/caption/5421c617efb140e0c4967051838dc6d6b4894444b29c0bbc649399fee0b0f5ef'
and retrieve the caption:
{"caption":"a wooden bench sitting on top of a lush green field"}
You can also see the status using:
curl 'http://localhost:5000/status'
Command line
If you want to use this locally, also look at these two Dockerized neuraltalk2:
-
SaMnCo/docker-neuraltalk2 has a branch for ARM machines,
-
beeva-enriqueotero/docker-neuraltalk2 has A GPU enabled version and links to script to run it live using a camera. Run
docker run -it --name neuraltalk2-web -v /home/myuser/:/mounted jacopofar/neuraltalk2-web:latest bash
assuming ‘/home/myuser/‘ contains the neuraltalk2 model and the images you want to caption. There are several options, see Docker manual for them.
This will open a shell on the container. Use ‘cd /neuraltalk2/‘ to be in the neuraltalk folder and then
th eval.lua -model /mounted/neuraltalk2models/model_id1-501-1448236541.t7_cpu.t7 -image_folder /mounted/Desktop/ -gpuid -1
will caption the images in the given folder using the given model. The captions are saved in the vis/vis.json file.