Awesome
git-sim

Visually simulate Git operations in your own repos with a single terminal command.
This generates an image (default) or video visualization depicting the Git command's behavior.
Command syntax is based directly on Git's command-line syntax, so using git-sim is as familiar as possible.
Example: $ git-sim merge <branch>
<br/><br/>
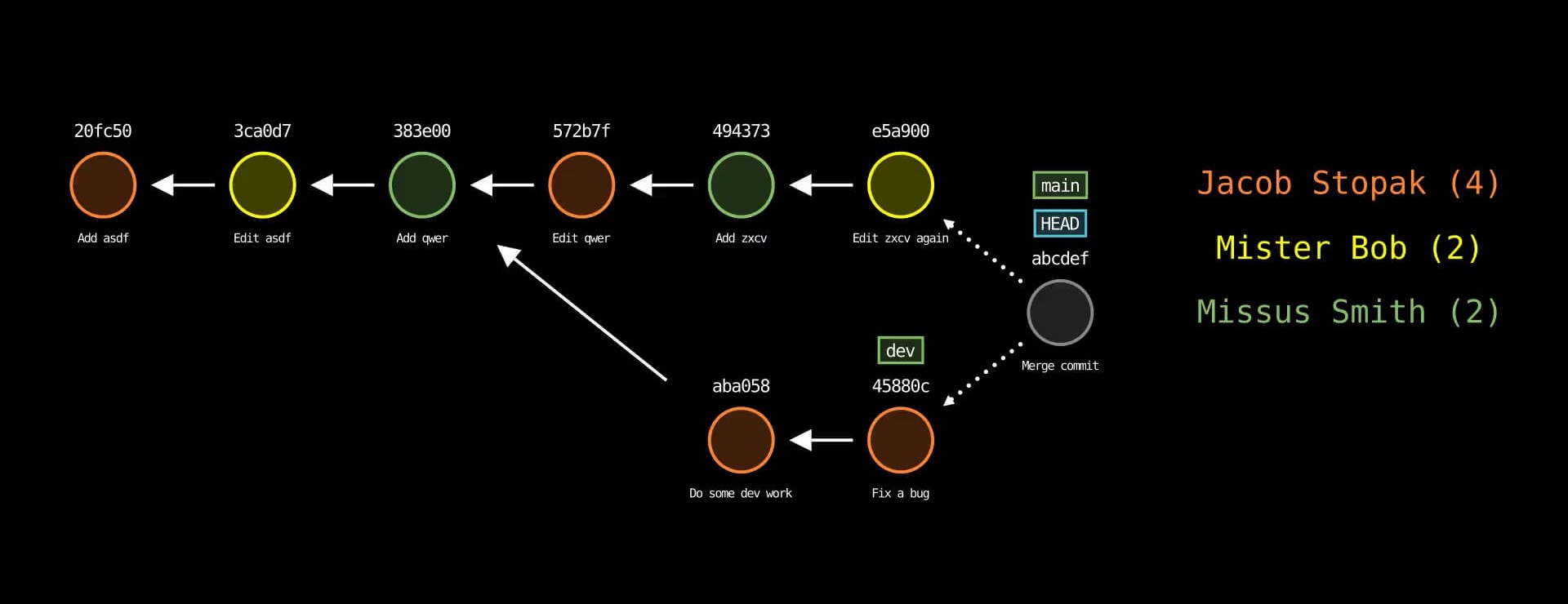
Check out the git-sim release blog post for the full scoop!
Support git-sim
Git-Sim is Free and Open-Source Software (FOSS). Your support will help me work on it (and other Git projects) full time!
Use cases
- Visualize Git commands to understand their effects on your repo before actually running them
- Prevent unexpected working directory and repository states by simulating before running
- Share visualizations (jpg/png image or mp4/webm video) of your Git commands with your team, or the world
- Save visualizations as a part of your team documentation to document workflow and prevent recurring issues
- Create static Git diagrams (jpg/png) or dynamic animated videos (mp4/webm) to speed up content creation
- Help visual learners understand how Git commands work
- Combine with bundled command git-dummy to generate a dummy Git repo and then simulate operations on it
Features
- Run a one-liner git-sim command in the terminal to generate a custom Git command visualization (.jpg) from your repo
- Supported commands:
add,branch,checkout,cherry-pick,clean,clone,commit,config,fetch,init,log,merge,mv,pull,push,rebase,remote,reset,restore,revert,rm,stash,status,switch,tag - Generate an animated video (.mp4) instead of a static image using the
--animateflag (note: significant performance slowdown, it is recommended to use--low-qualityto speed up testing and remove when ready to generate presentation-quality video) - Color commits by parameter, such as author with the
--color-by=authoroption - Choose between dark mode (default) and light mode
- Specify output formats of either jpg, png, mp4, or webm
- Combine with bundled command git-dummy to generate a dummy Git repo and then simulate operations on it
- Animation only: Add custom branded intro/outro sequences if desired
- Animation only: Speed up or slow down animation speed as desired
Quickstart
Note: If you prefer to install git-sim with Docker, skip steps (1) and (2) here and jump to the Docker installation section below, then come back here to step (3).
-
Install Manim and its dependencies for your OS / environment:
-
Install
git-sim:
$ pip3 install git-sim
Note: For MacOS, it is recommended to NOT use the system Python to install Git-Sim, and instead use Homebrew to install a version of Python to work with Git-Sim. Virtual environments should work too.
- Browse to the Git repository you want to simulate Git commands in:
$ cd path/to/git/repo
- Run the program:
$ git-sim [global options] <subcommand> [subcommand options]
Optional: If you don't have an existing Git repo to simulate commands on, use the bundled git-dummy command to generate a dummy Git repo with the desired number of branches and commits to simulate operations on with git-sim:
$ git-dummy --name="dummy-repo" --branches=3 --commits=10
$ cd dummy-repo
$ git-sim [global options] <subcommand> [subcommand options]
Or if you want to do it all in a single command:
$ git-dummy --no-subdir --branches=3 --commits=10 && git-sim [global options] <subcommand> [subcommand options]
-
Simulated output will be created as a
.jpgfile. Output files are named using the subcommand executed combined with a timestamp, and by default are stored in a subdirectory calledgit-sim_media/. The location of this subdirectory is customizable using the command line flag--media-dir=path/to/output. Note that when the--animateglobal flag is used, render times will be much longer and a.mp4video output file will be produced. -
For convenience, environment variables can be set for any global command-line option available in git-sim. All environment variables start with
git_sim_followed by the name of the option.
For example, the --media-dir option can be set as an environment variable like:
$ export git_sim_media_dir=~/Desktop
Similarly, the --speed option can be set like:
$ export git_sim_speed=2
Boolean flags can be set like:
$ export git_sim_light_mode=true
In general:
$ export git_sim_option_name=option_value
Explicitly specifying options at the command-line takes precedence over the corresponding environment variable values.
- See global help for list of global options/flags and subcommands:
$ git-sim -h
- See subcommand help for list of options/flags for a specific subcommand:
$ git-sim <subcommand> -h
Requirements
- Python 3.7 or greater
- Pip (Package manager for Python)
- Manim (Community version)
Commands
Basic usage is similar to Git itself - git-sim takes a familiar set of subcommands including "add", "branch", "checkout", "cherry-pick", "clean", "clone", "commit", "config", "fetch", "init", "log", "merge", "mv", "pull", "push", "rebase", "remote", "reset", "restore", "revert", "rm", "stash", "status", "switch", "tag" along with corresponding options.
$ git-sim [global options] <subcommand> [subcommand options]
The [global options] apply to the overarching git-sim simulation itself, including:
-n <number>: Number of commits to display from each branch head.
--all: Display all local branches in the log output.
--animate: Instead of outputting a static image, animate the Git command behavior in a .mp4 video.
--color-by author: Color commits by parameter, such as author.
--invert-branches: Invert positioning of branches by reversing order of multiple parents where applicable.
--hide-merged-branches: Hide commits from merged branches, i.e. only display mainline commits.
--media-dir: The path at which to store the simulated output media files.
-d: Disable the automatic opening of the image/video file after generation. Useful to avoid errors in console mode with no GUI.
--light-mode: Use a light mode color scheme instead of default dark mode.
--reverse, -r: Display commit history in the reverse direction.
--img-format: Output format for the image file, i.e. jpg or png. Default output format is jpg.
--stdout: Write raw image data to stdout while suppressing all other program output.
--output-only-path: Only output the path to the generated media file to stdout. Useful for other programs to ingest.
--quiet, -q: Suppress all output except errors.
--highlight-commit-messages: Make commit message text bigger and bold, and hide commit ids.
--style: Graphical style of the output image or animated video, i.e. clean (default) or thick.
Animation-only global options (to be used in conjunction with --animate):
--video-format: Output format for the video file, i.e. mp4 or webm. Default output format is mp4.
--speed=n: Set the multiple of animation speed of the output simulation, n can be an integer or float, default is 1.5.
--low-quality: Render the animation in low quality to speed up creation time, recommended for non-presentation use.
--show-intro: Add an intro sequence with custom logo and title.
--show-outro: Add an outro sequence with custom logo and text.
--title=title: Custom title to display at the beginning of the animation.
--logo=logo.png: The path to a custom logo to use in the animation intro/outro.
--outro-top-text: Custom text to display above the logo during the outro.
--outro-bottom-text: Custom text to display below the logo during the outro.
--font: Font family used to display rendered text.
The [subcommand options] are like regular Git options specific to the specified subcommand (see below for a full list).
The following is a list of Git commands that can be simulated and their corresponding options/flags.
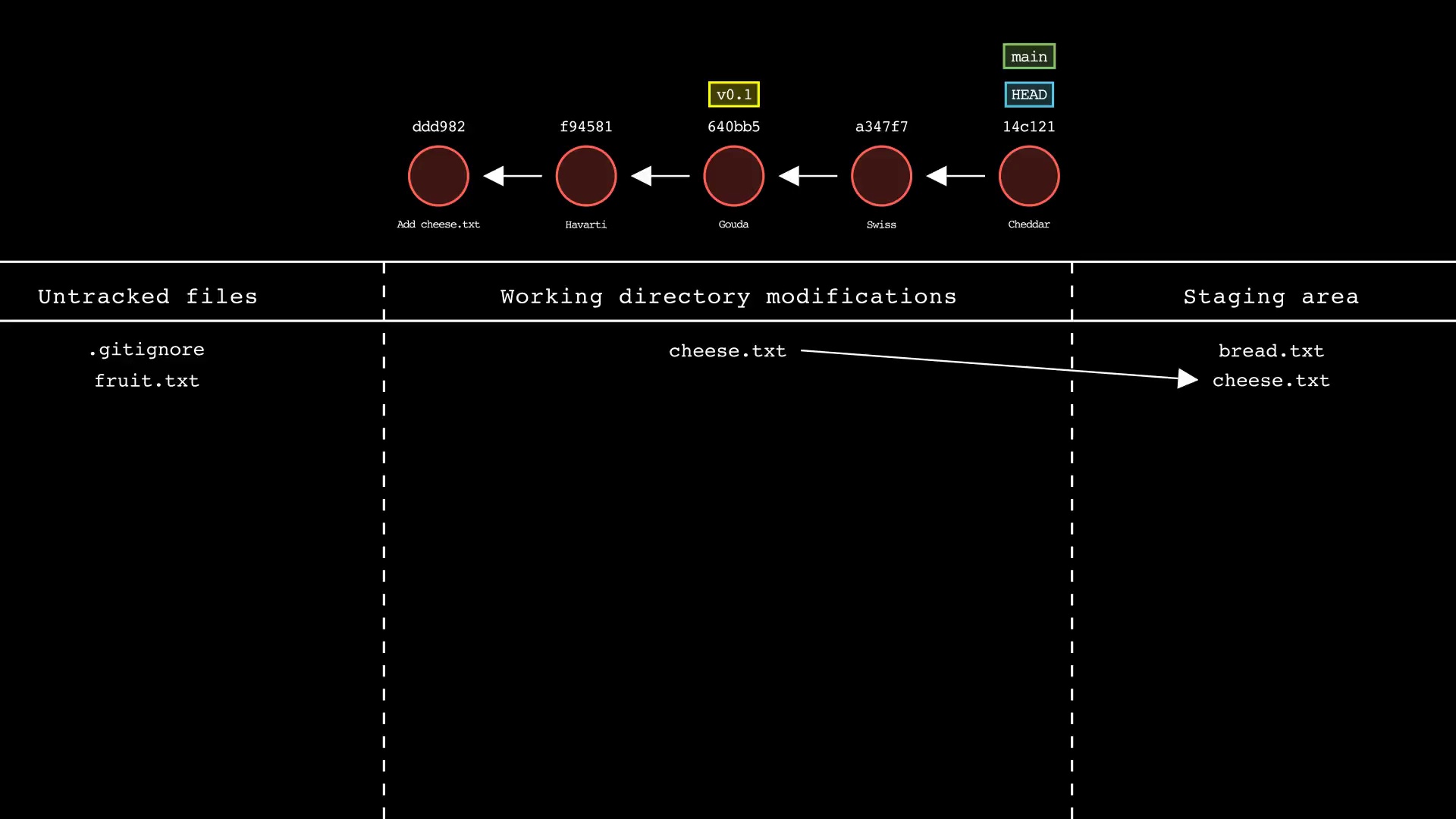
git add
Usage: git-sim add <file 1> <file 2> ... <file n>
- Specify one or more
<file>as a modified working directory file, or an untracked file - Simulated output will show files being moved to the staging area
- Note that simulated output will also show the most recent 5 commits on the active branch
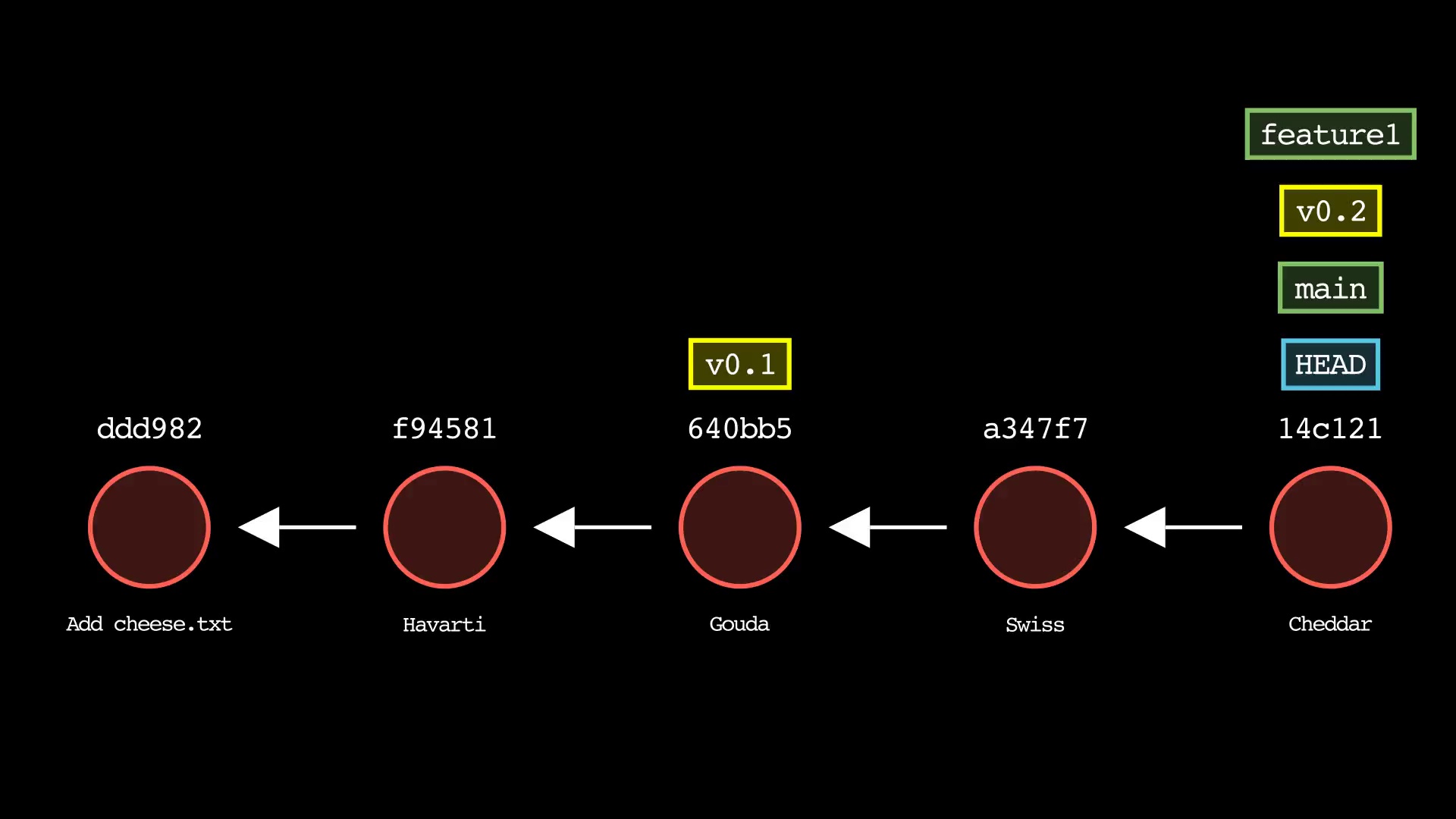
git branch
Usage: git-sim branch <new branch name>
- Specify
<new branch name>as the name of the new branch to simulate creation of - Simulated output will show the newly create branch ref along with most recent 5 commits on the active branch
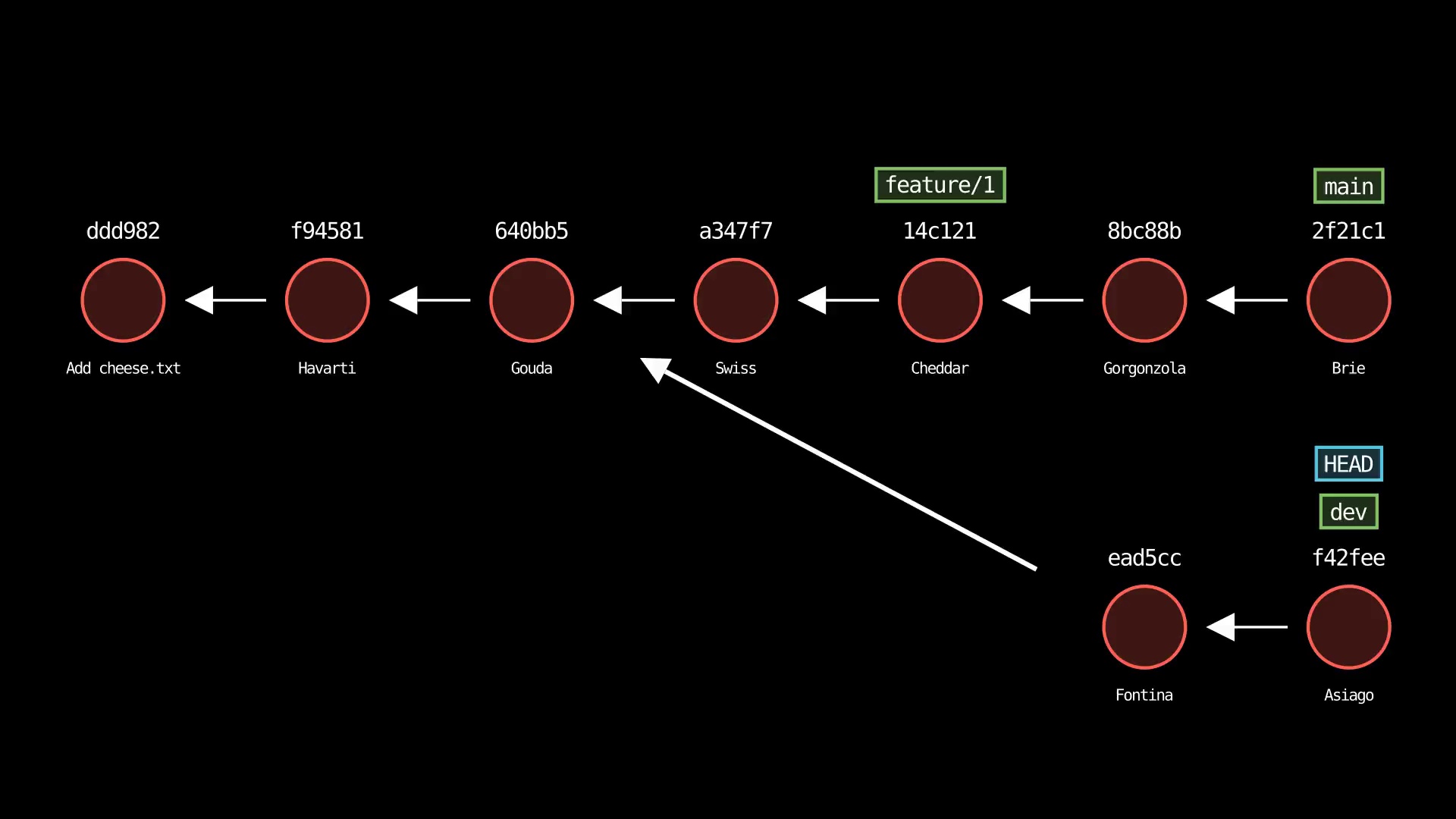
git checkout
Usage: git-sim checkout [-b] <branch>
- Checks out
<branch>into the working directory, i.e. movesHEADto the specified<branch> - The
-bflag creates a new branch with the specified name<branch>and checks it out, assuming it doesn't already exist
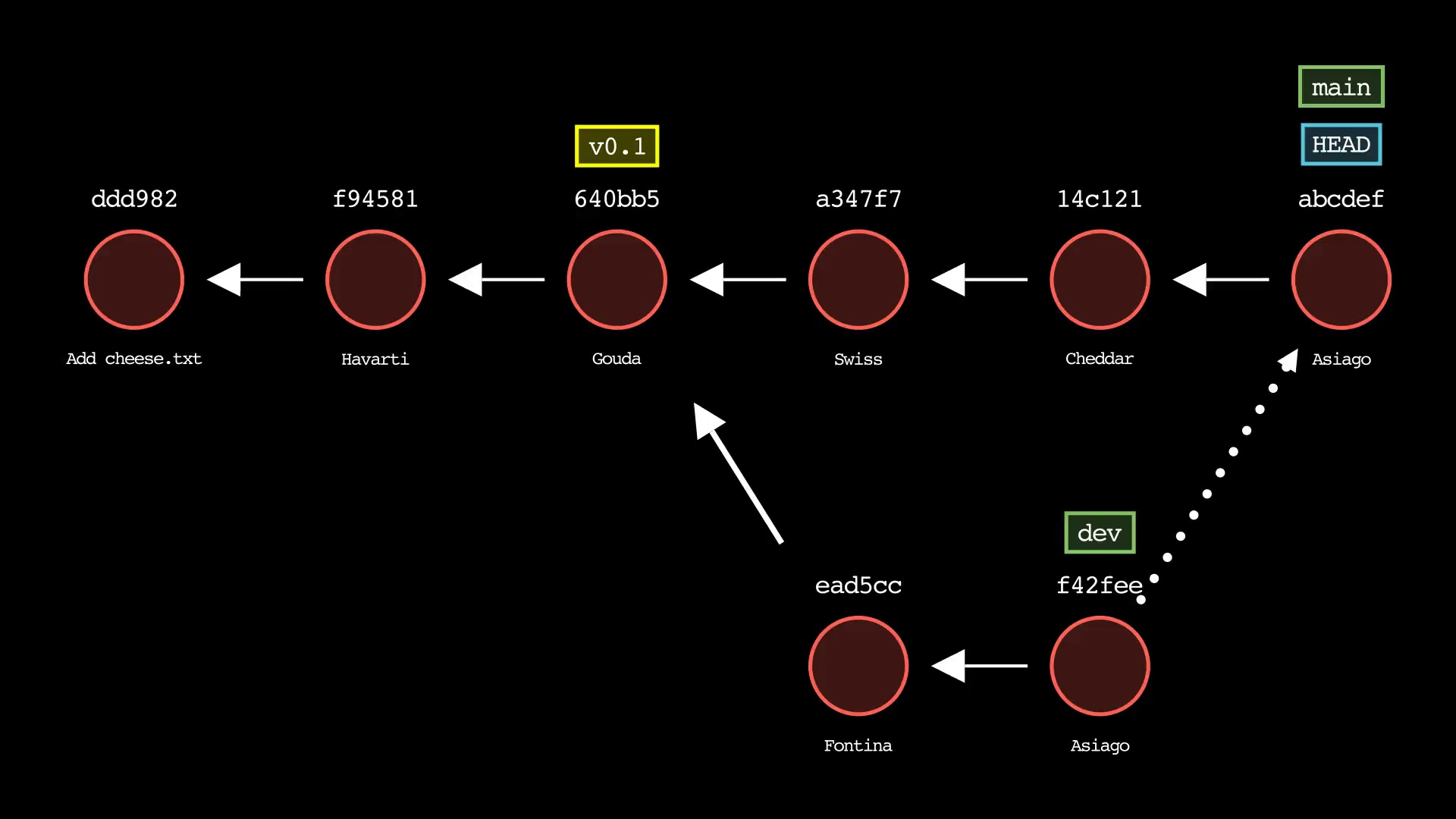
git cherry-pick
Usage: git-sim cherry-pick <commit>
- Specify
<commit>as a ref (branch name/tag) or commit ID to cherry-pick onto the active branch - Supports editing the cherry-picked commit message with:
$ git-sim cherry-pick <commit> -e "Edited commit message"
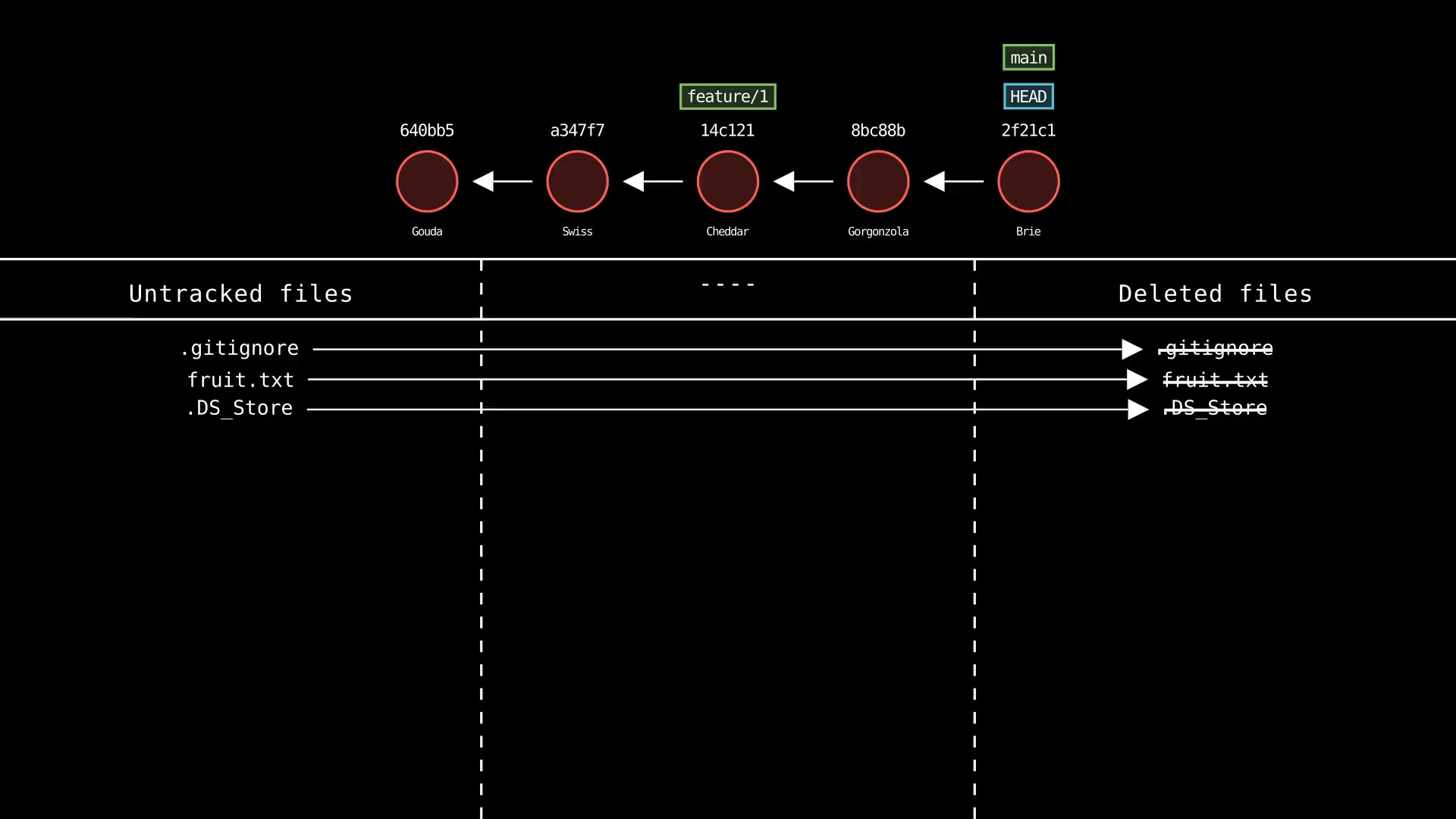
git clean
Usage: git-sim clean
- Simulated output will show untracked files being deleted
- Since this is just a simulation, no need to specify
-i,-n,-fas in regular Git - Note that simulated output will also show the most recent 5 commits on the active branch
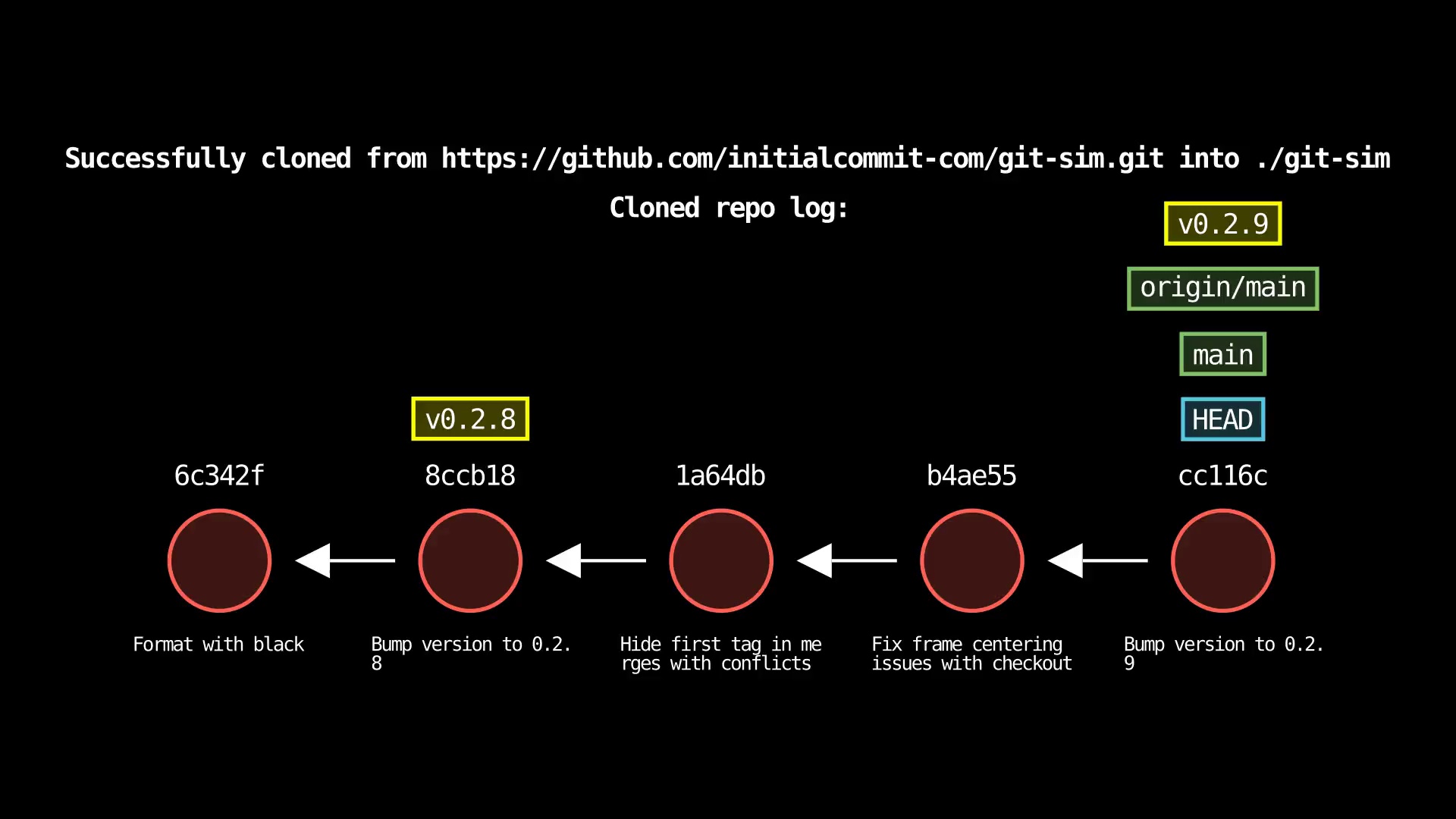
git clone
Usage: git-sim clone <url>
- Clone the remote repo from
<url>(web URL or filesystem path) to a new folder in the current directory - Output will report if clone operation is successful and show log of local clone
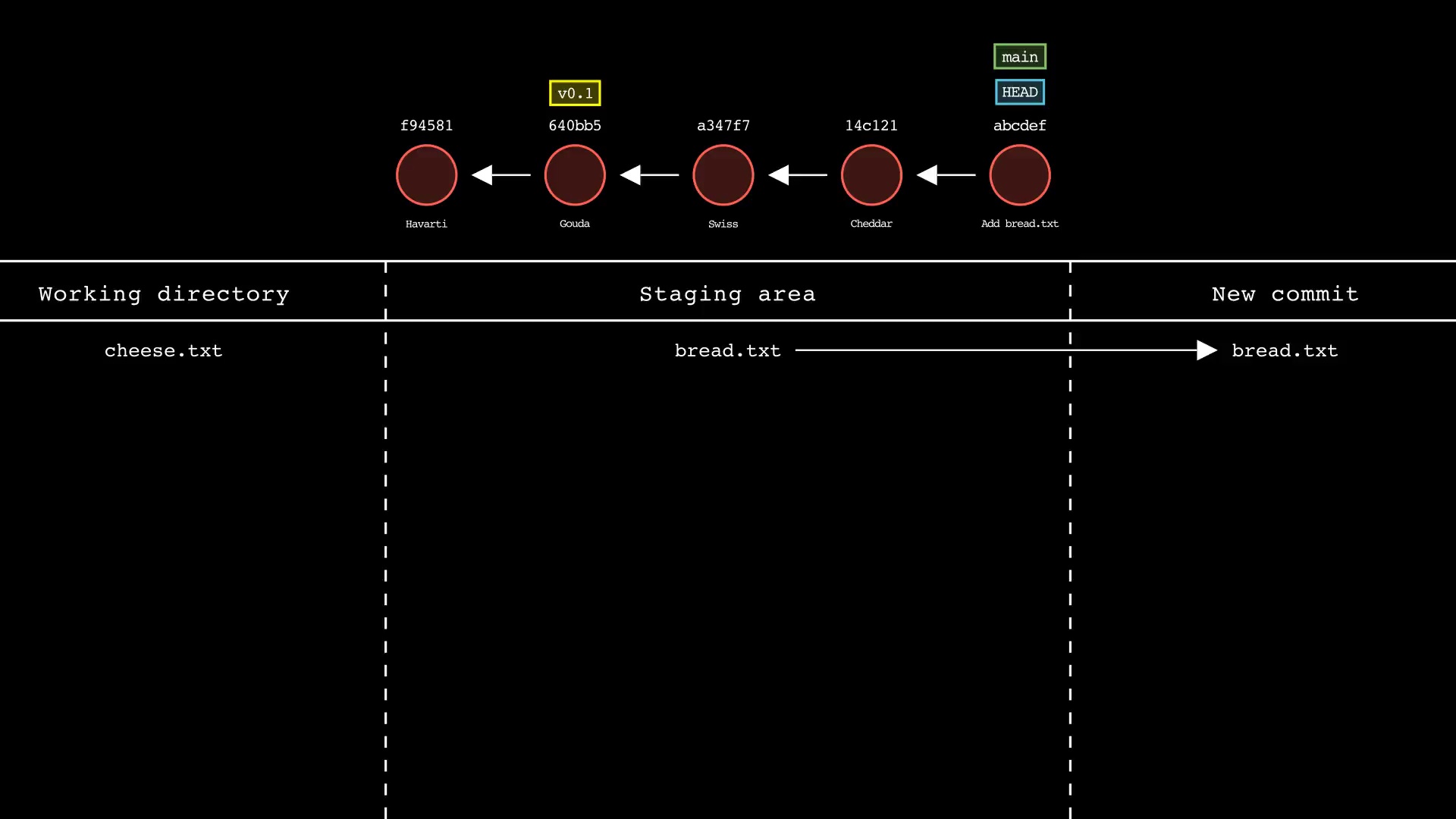
git commit
Usage: git-sim commit -m "Commit message"
- Simulated output will show the new commit added to the tip of the active branch
- Specify a commit message with the
-moption - HEAD and the active branch will be moved to the new commit
- Simulated output will show files in the staging area being included in the new commit
- Supports amending the last commit with:
$ git-sim commit --amend -m "Amended commit message"
git config
Usage: git-sim config [--list] <section.option> <value>
- Simulated output describes the specified configuration change
- Use
--listor-lto display all configuration
git fetch
Usage: git-sim fetch <remote> <branch>
- Fetches the specified
<branch>from the specified<remote>to the local repo
git init
Usage: git-sim init
- Simulated output describes the initialized
.git/directory and it's contents
git log
Usage: git-sim log [-n <number>] [--all]
- Simulated output will show the most recent 5 commits on the active branch by default
- Use
-n <number>to set number of commits to display from each branch head - Set
--allto display all local branches in the log output
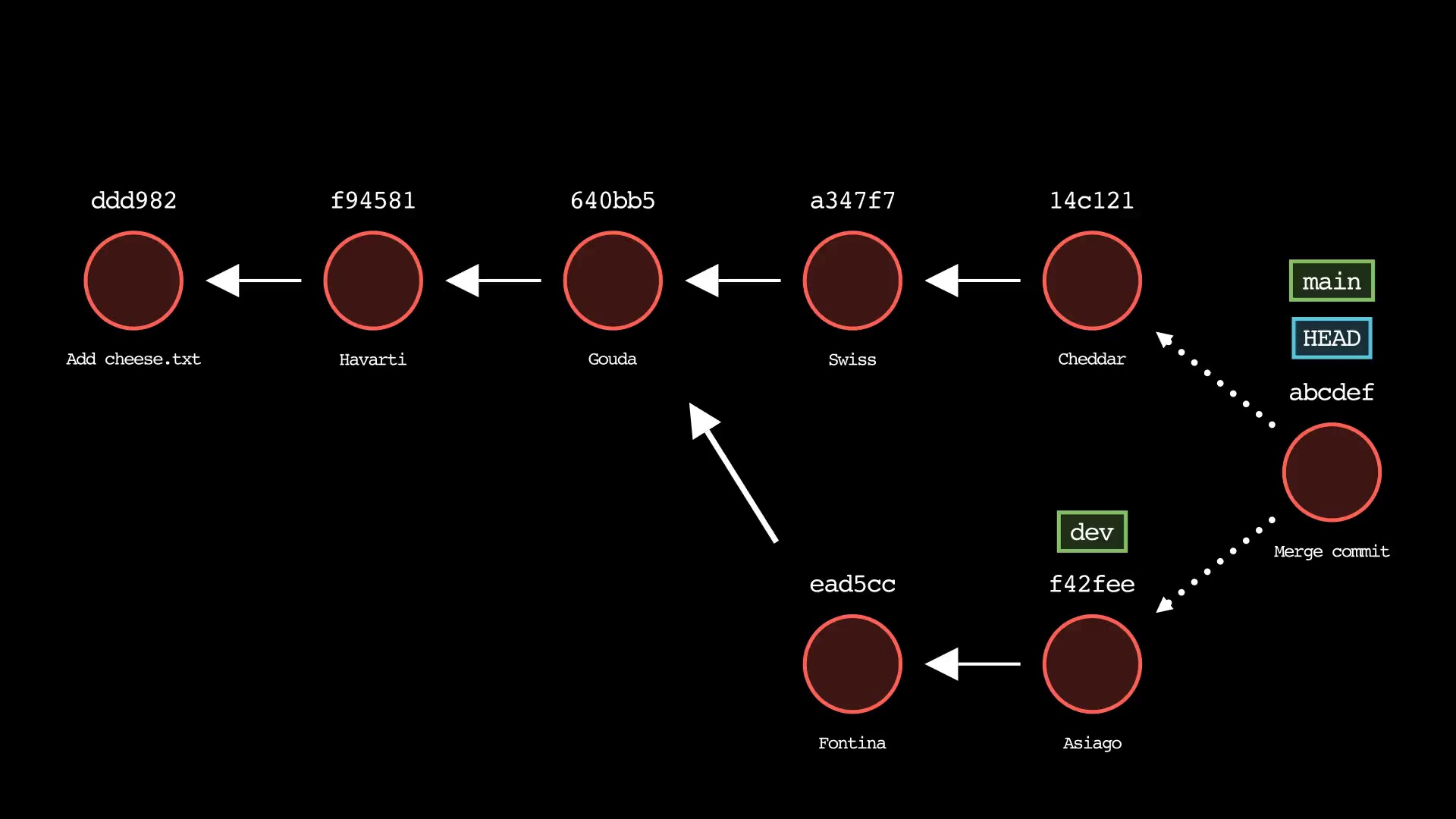
git merge
Usage: git-sim merge <branch> [-m "Commit message"] [--no-ff]
- Specify
<branch>as the branch name to merge into the active branch - If desired, specify a commit message with the
-moption - Simulated output will depict a fast-forward merge if possible
- Otherwise, a three-way merge will be depicted
- To force a merge commit when a fast-forward is possible, use
--no-ff - If merge fails due to merge conflicts, the conflicting files are displayed
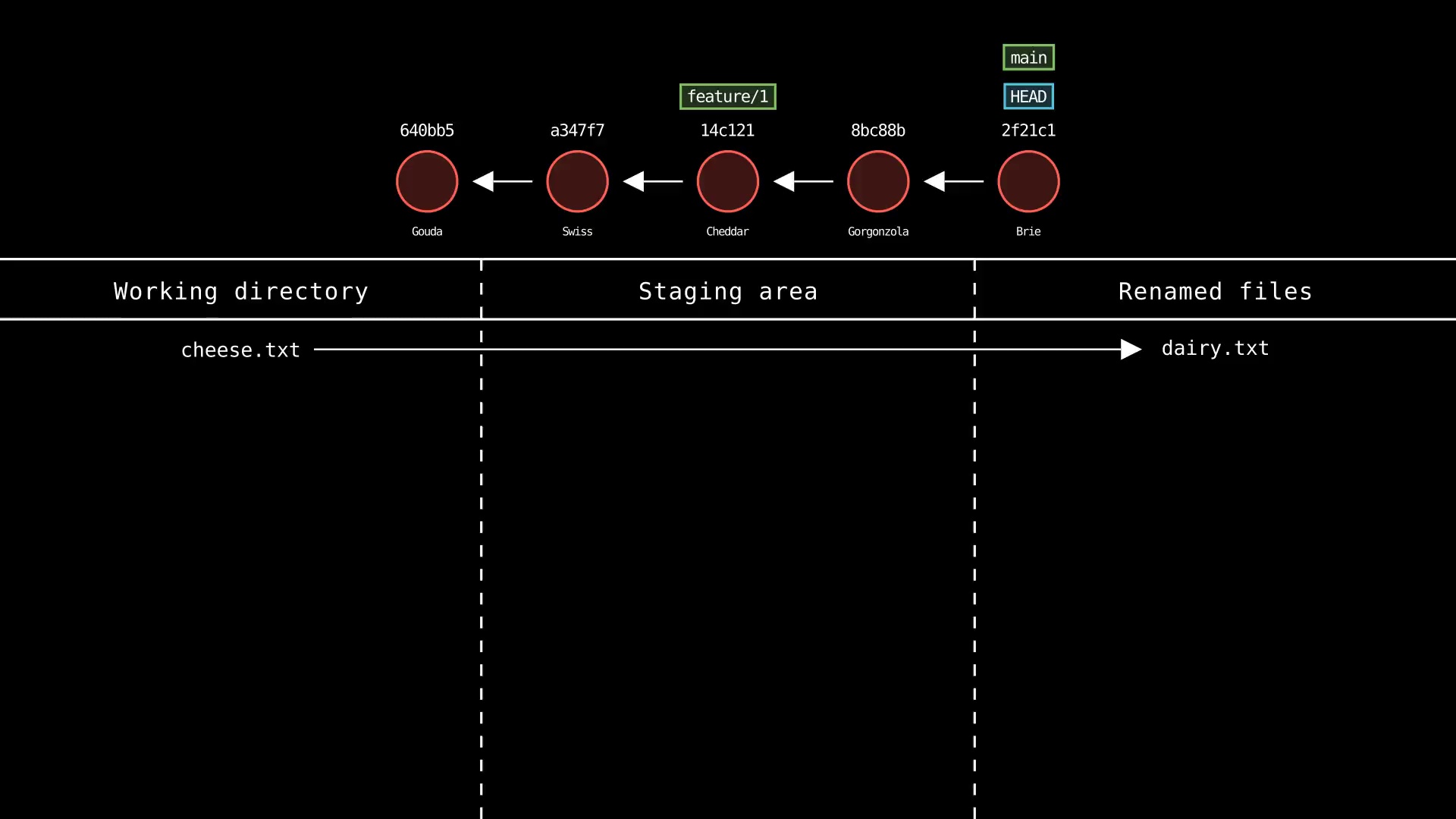
git mv
Usage: git-sim mv <file> <new file>
- Specify
<file>as file to update name/path - Specify
<new file>as new name/path of file - Simulated output will show the name/path of the file being updated
- Note that simulated output will also show the most recent 5 commits on the active branch
git pull
Usage: git-sim pull [<remote> <branch>]
- Pulls the specified
<branch>from the specified<remote>to the local repo - If
<remote>and<branch>are not specified, the active branch is pulled from the default remote - If merge conflicts occur, they are displayed in a table
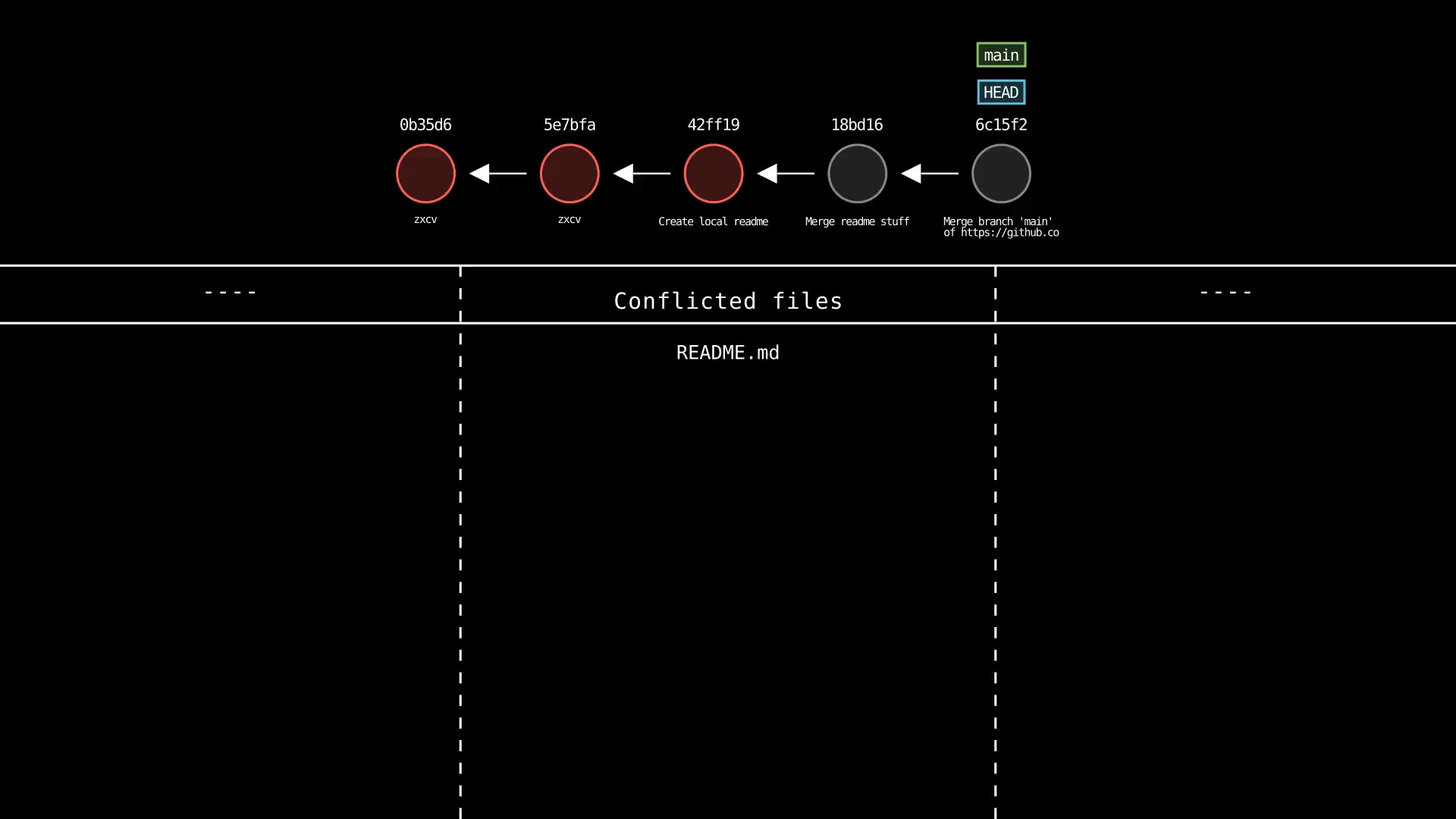
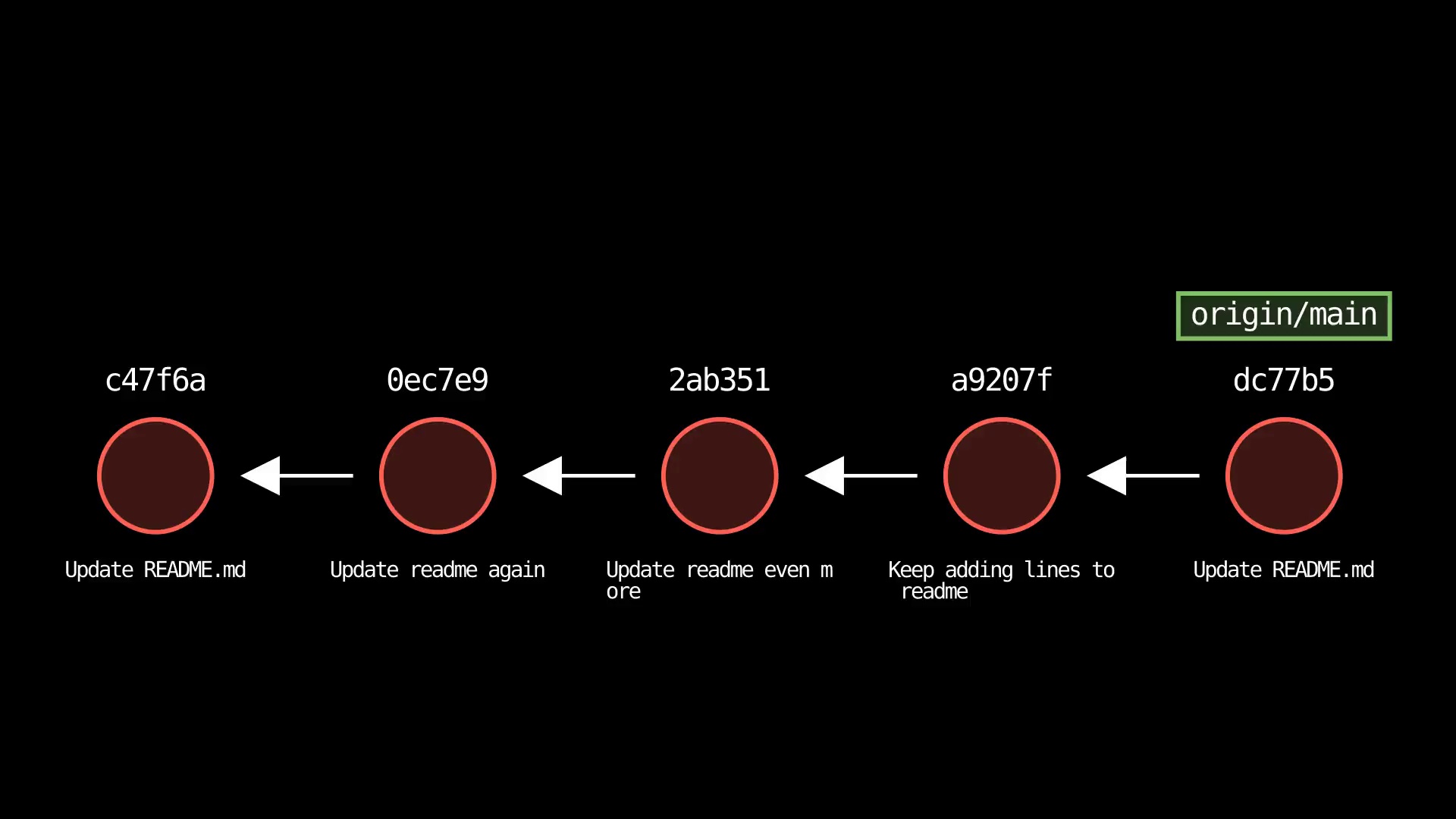
git push
Usage: git-sim push [<remote> <branch>]
- Pushes the specified
<branch>to the specified<remote>and displays the local result - If
<remote>and<branch>are not specified, the active branch is pushed to the default remote - If the push fails due to remote changes that don't exist in the local repo, a message is included telling the user to pull first, along with color coding which commits need to be pulled

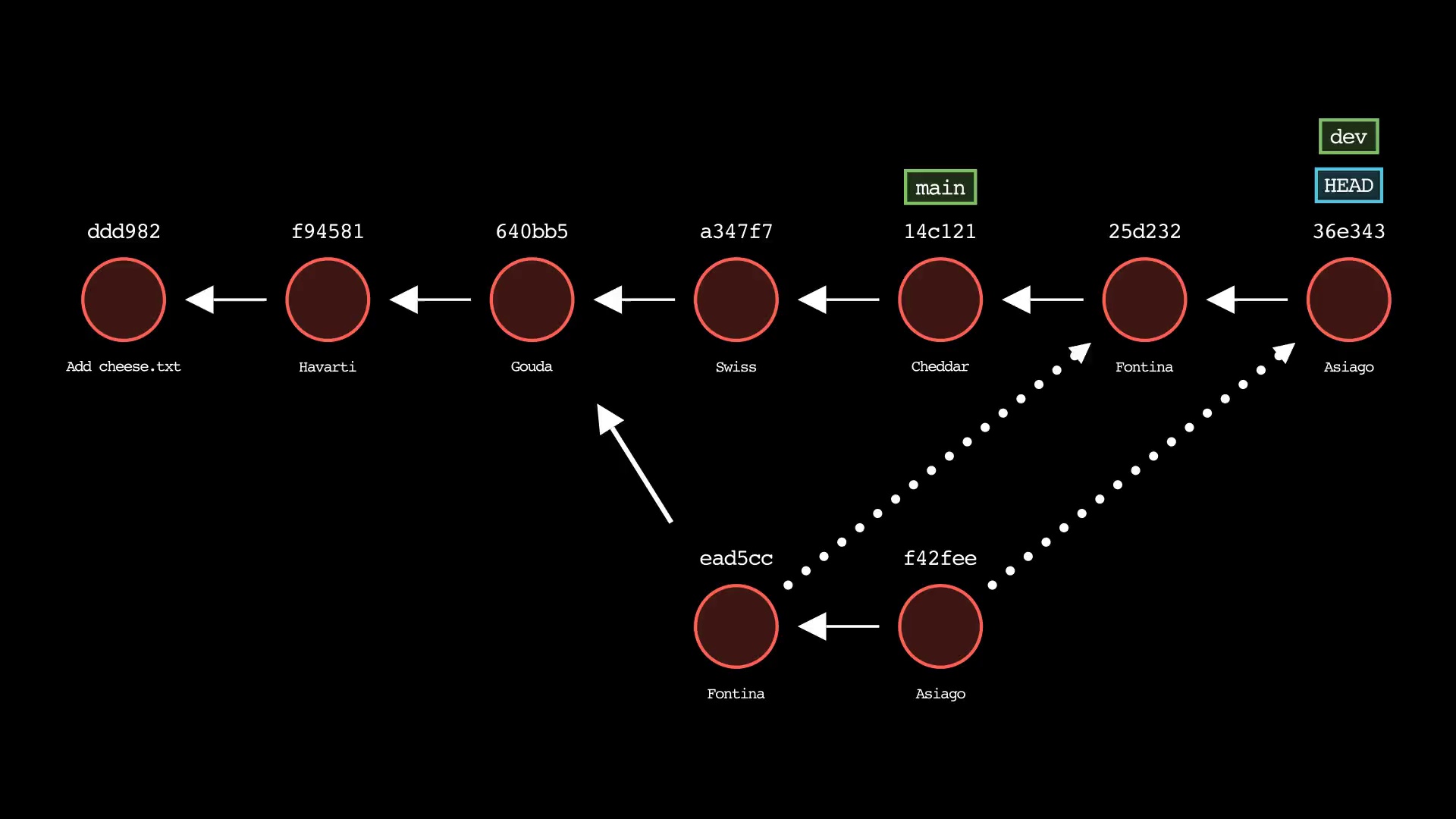
git rebase
Usage: git-sim rebase <new-base>
- Specify
<new-base>as the branch name to rebase the active branch onto
git remote
Usage: git-sim remote [add|rename|remove|get-url|set-url] [<remote>] [<url>]
- Simulated output will show remotes being added, renamed, removed, modified as indicated
- Running
git-sim remotewith no options will list all existing remotes and their details
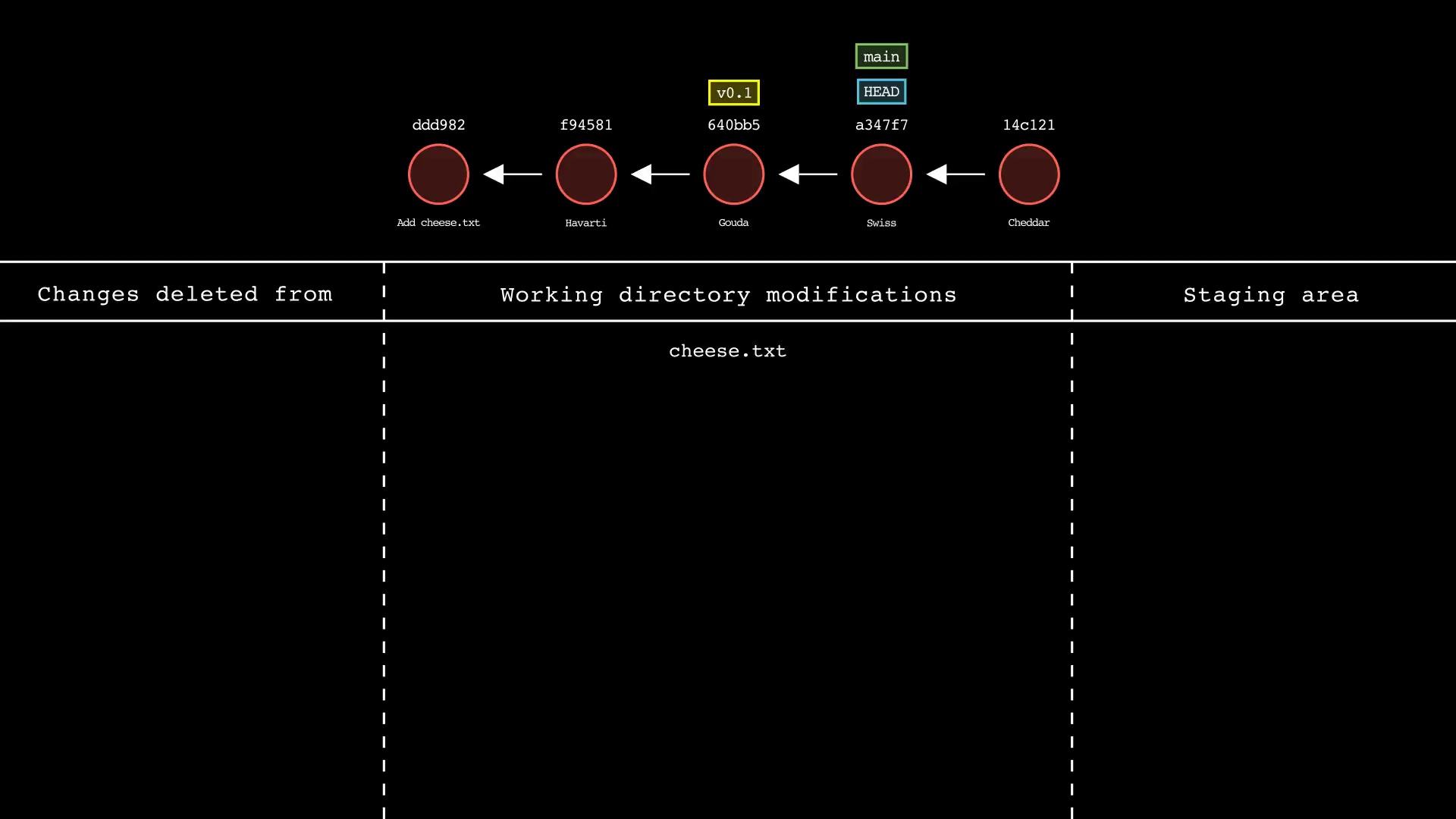
git reset
Usage: git-sim reset <reset-to> [--mixed|--soft|--hard]
- Specify
<reset-to>as any commit id, branch name, tag, or other ref to simulate reset to from the current HEAD (default:HEAD) - As with a normal git reset command, default reset mode is
--mixed, but can be specified using--soft,--hard, or--mixed - Simulated output will show branch/HEAD resets and resulting state of the working directory, staging area, and whether any file changes would be deleted by running the actual command
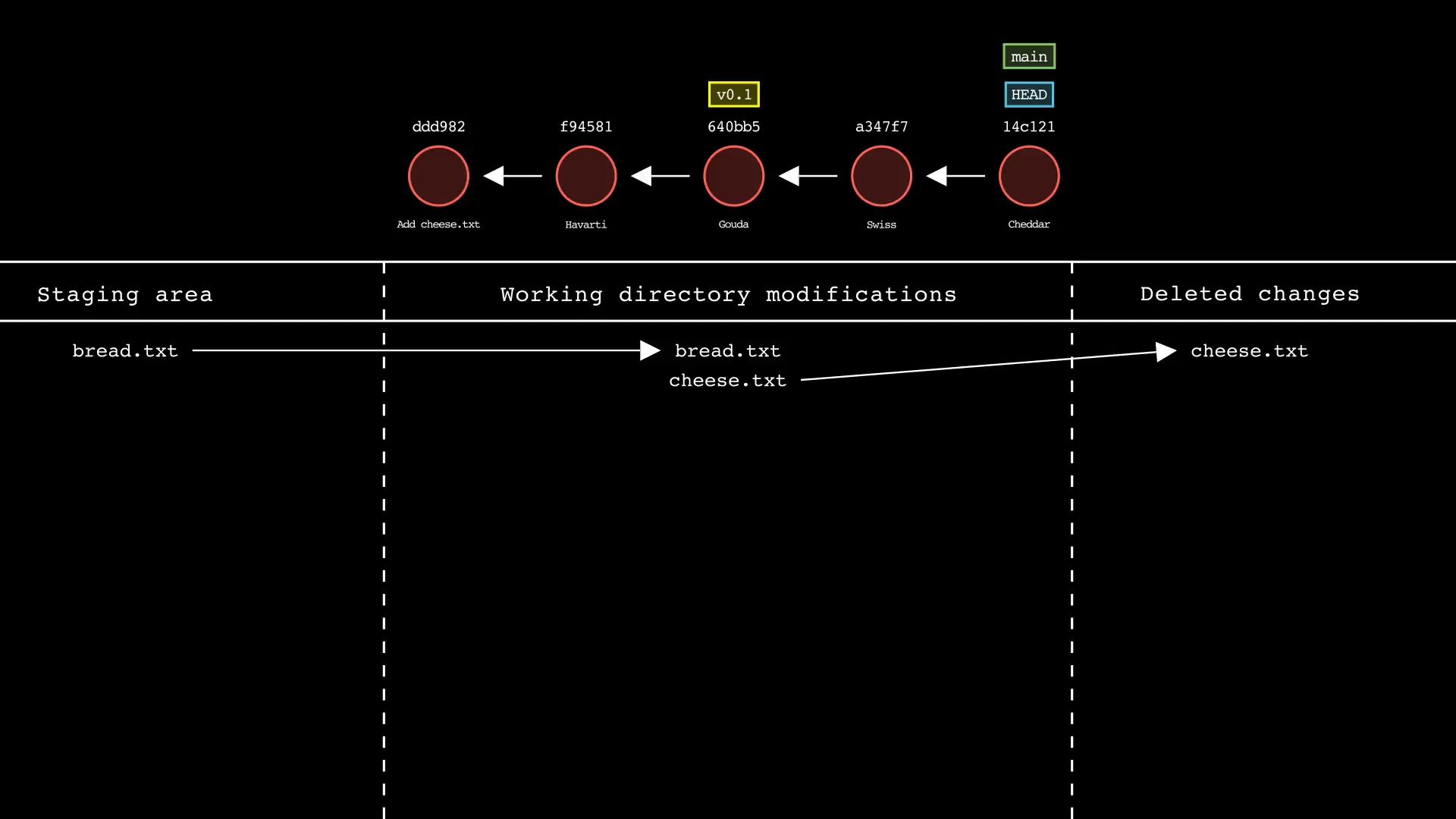
git restore
Usage: git-sim restore <file 1> <file 2> ... <file n>
- Specify one or more
<file>as a modified working directory file, or staged file - Simulated output will show files being moved back to the working directory or discarded changes
- Note that simulated output will also show the most recent 5 commits on the active branch
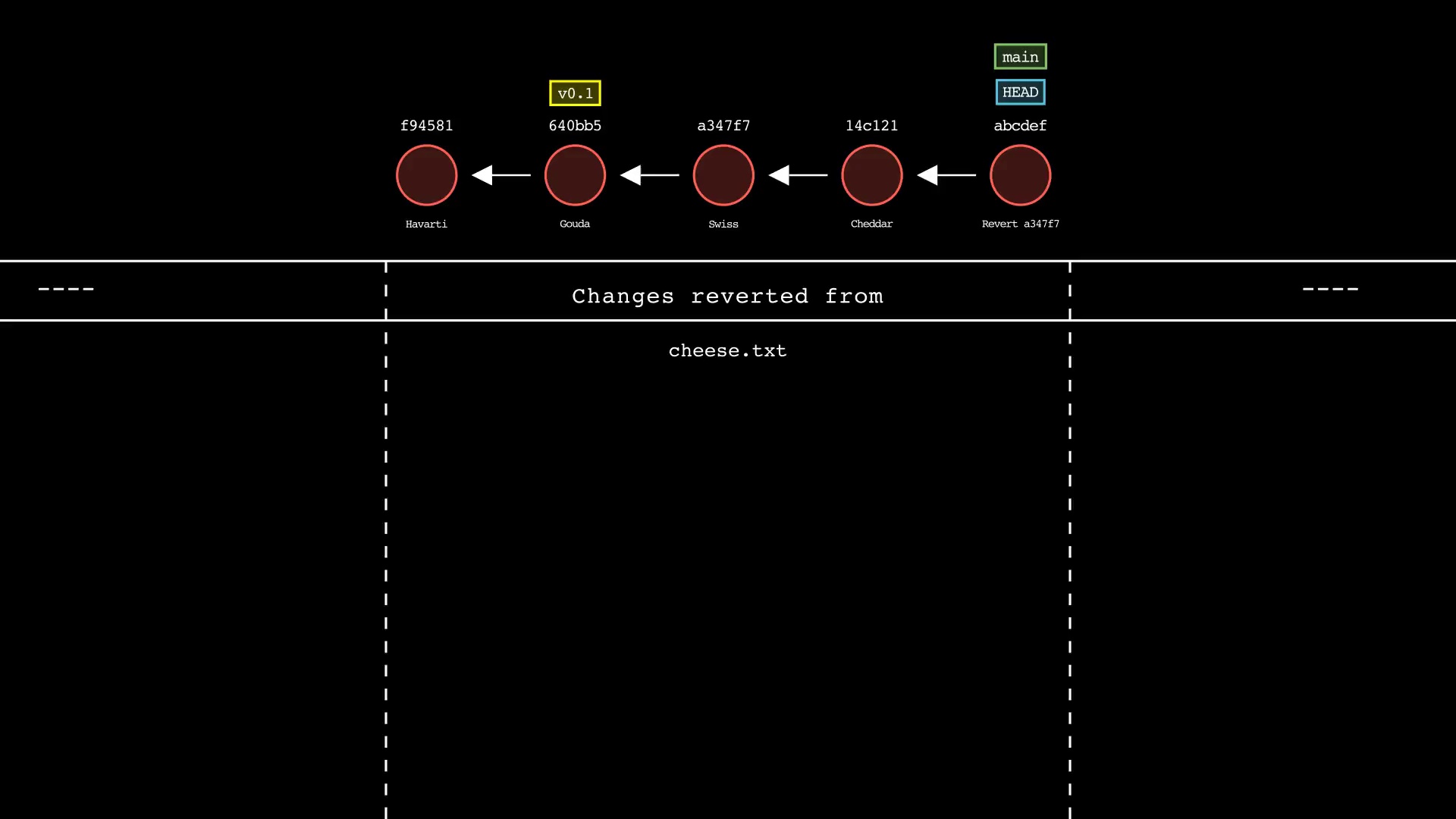
git revert
Usage: git-sim revert <to-revert>
- Specify
<to-revert>as any commit id, branch name, tag, or other ref to simulate revert for - Simulated output will show the new commit which reverts the changes from
<to-revert> - Simulated output will include the next 4 most recent commits on the active branch
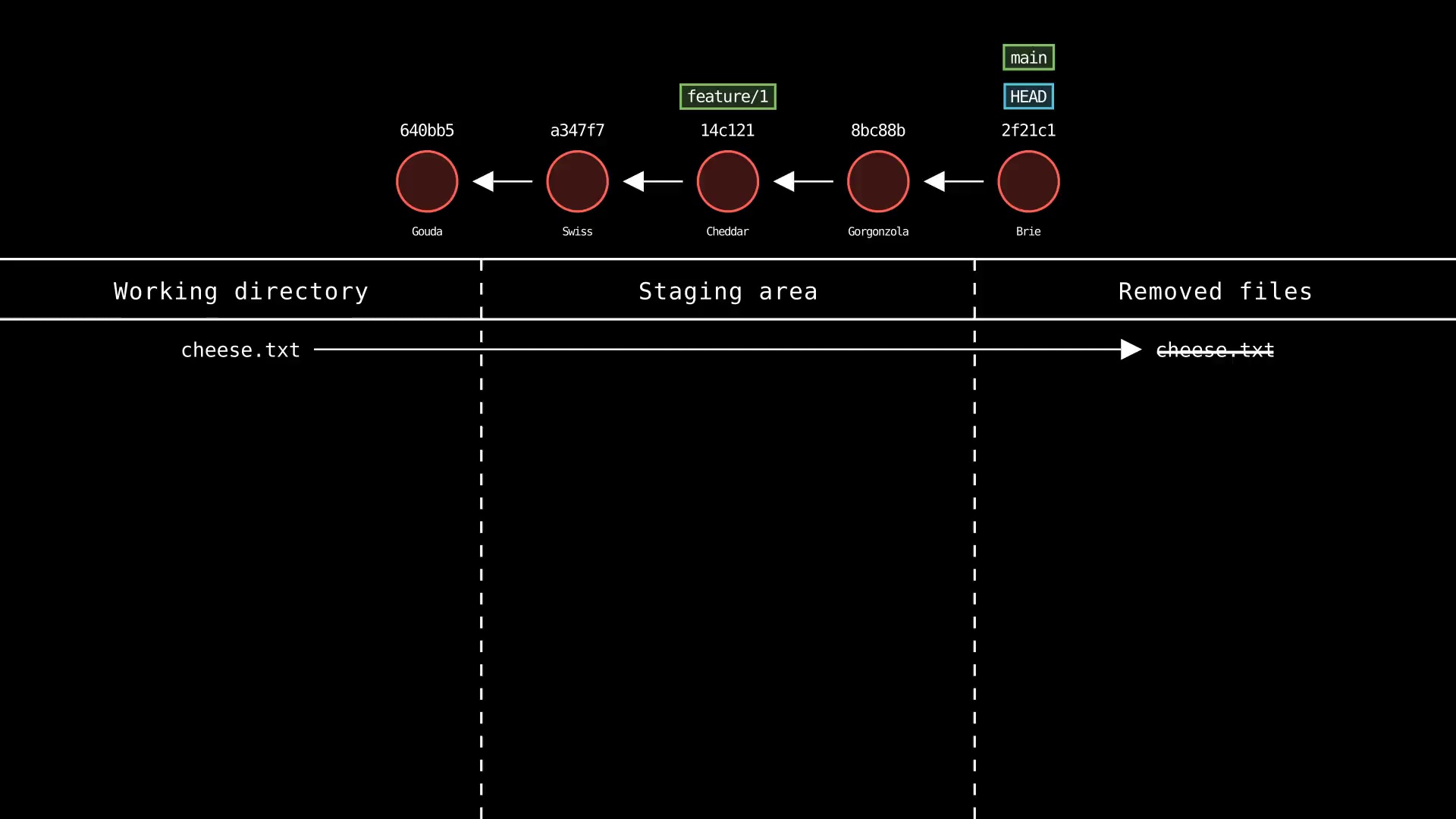
git rm
Usage: git-sim rm <file 1> <file 2> ... <file n>
- Specify one or more
<file>as a tracked file - Simulated output will show files being removed from Git tracking
- Note that simulated output will also show the most recent 5 commits on the active branch
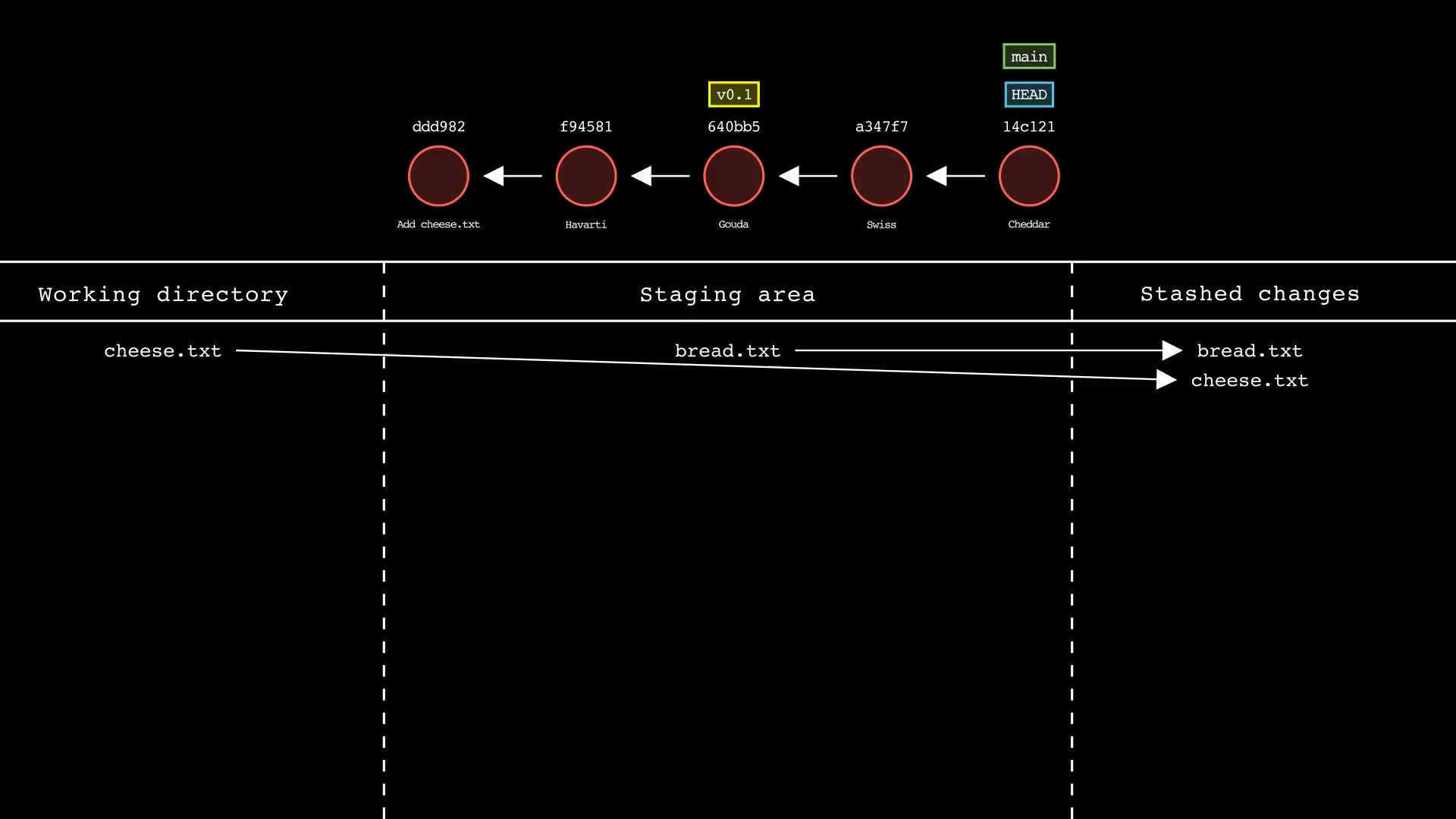
git stash
Usage: git-sim stash [push|pop|apply] <file>
- Specify one or more
<file>as a modified working directory file, or staged file - If no
<file>is specified, all available files will be included - Simulated output will show files being moved in/out of the Git stash
- Note that simulated output will also show the most recent 5 commits on the active branch
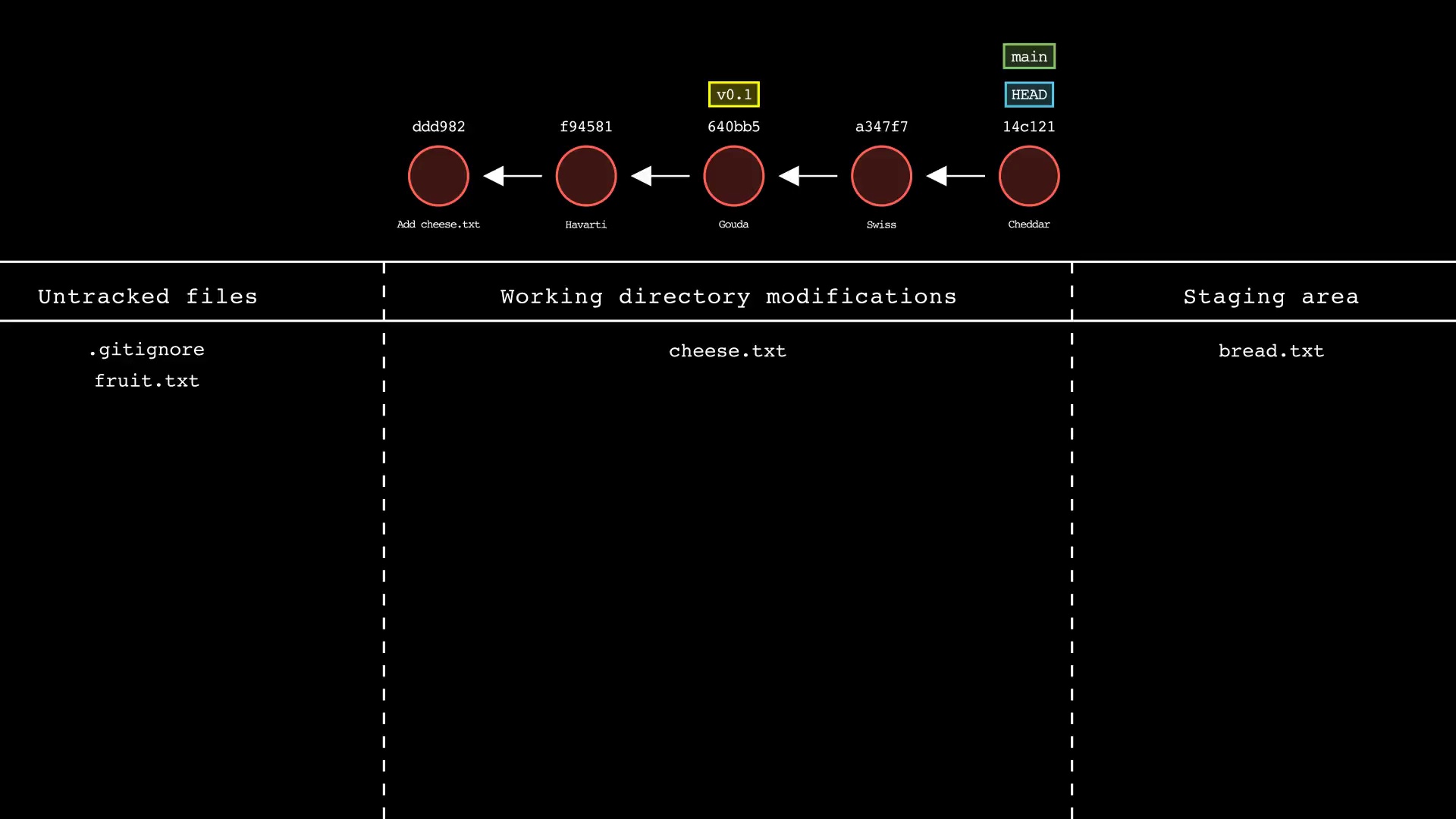
git status
Usage: git-sim status
- Simulated output will show the state of the working directory, staging area, and untracked files
- Note that simulated output will also show the most recent 5 commits on the active branch
git switch
Usage: git-sim switch [-c] <branch>
- Switches the checked-out branch to
<branch>, i.e. movesHEADto the specified<branch> - The
-cflag creates a new branch with the specified name<branch>and switches to it, assuming it doesn't already exist
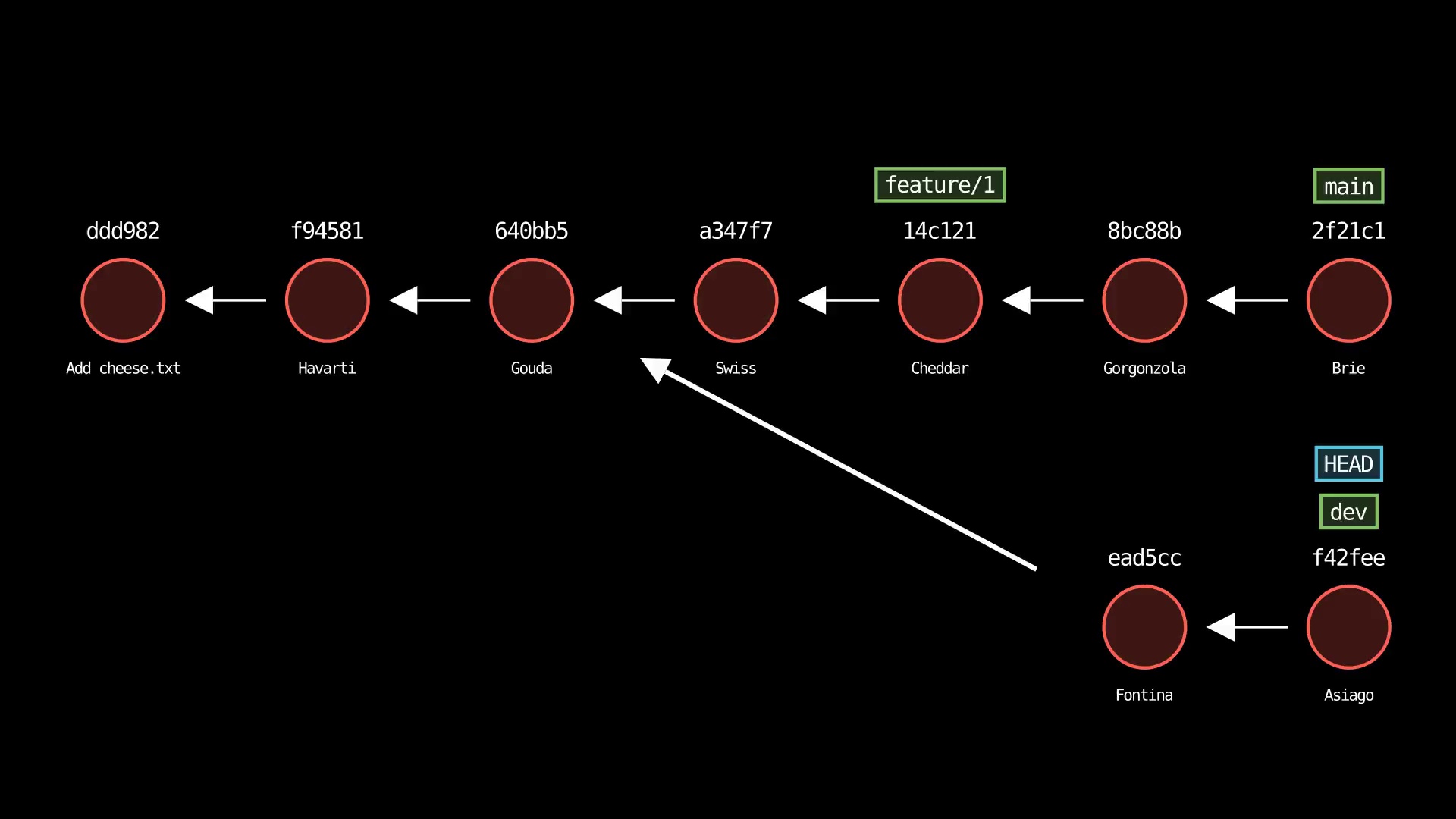
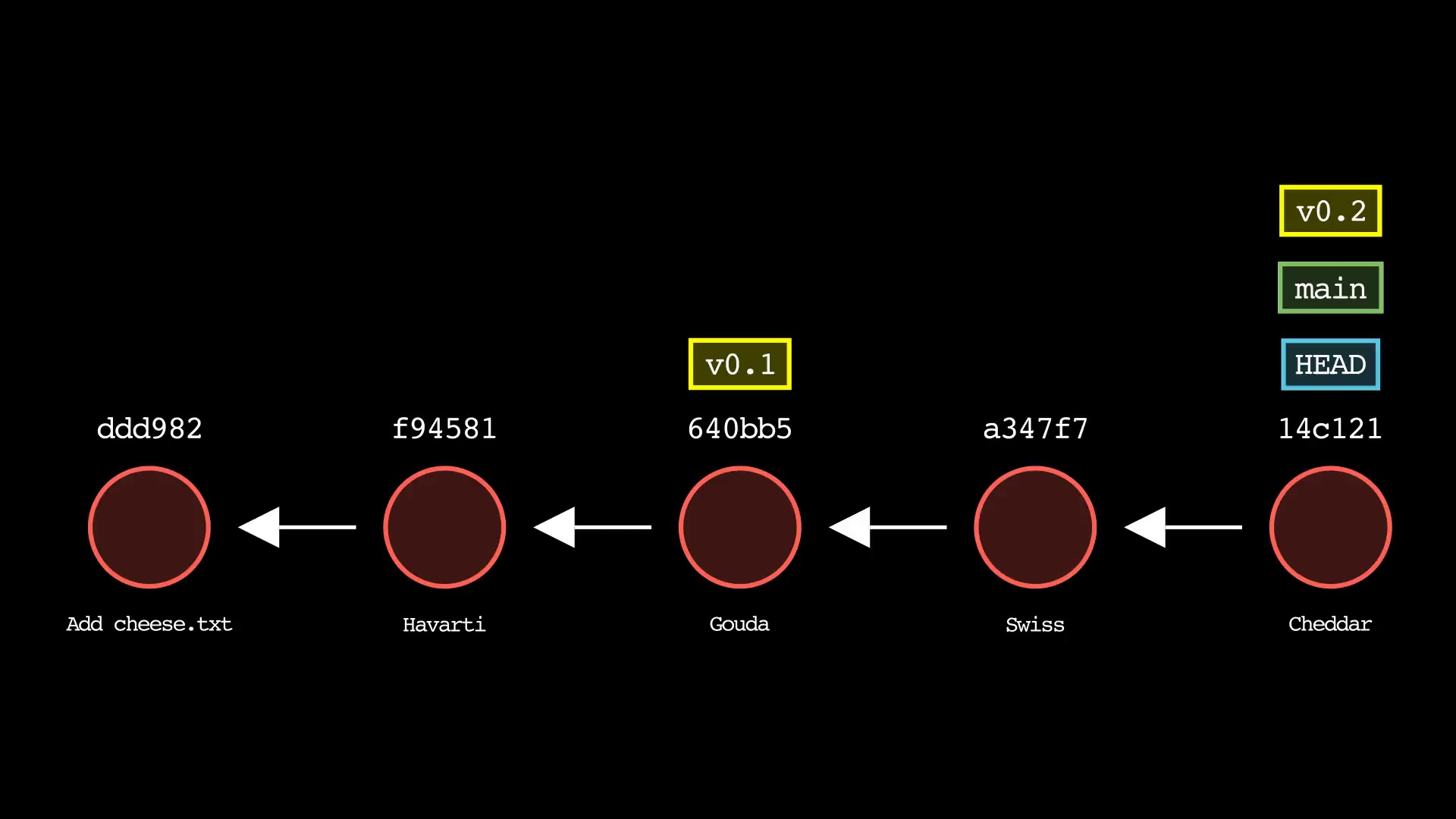
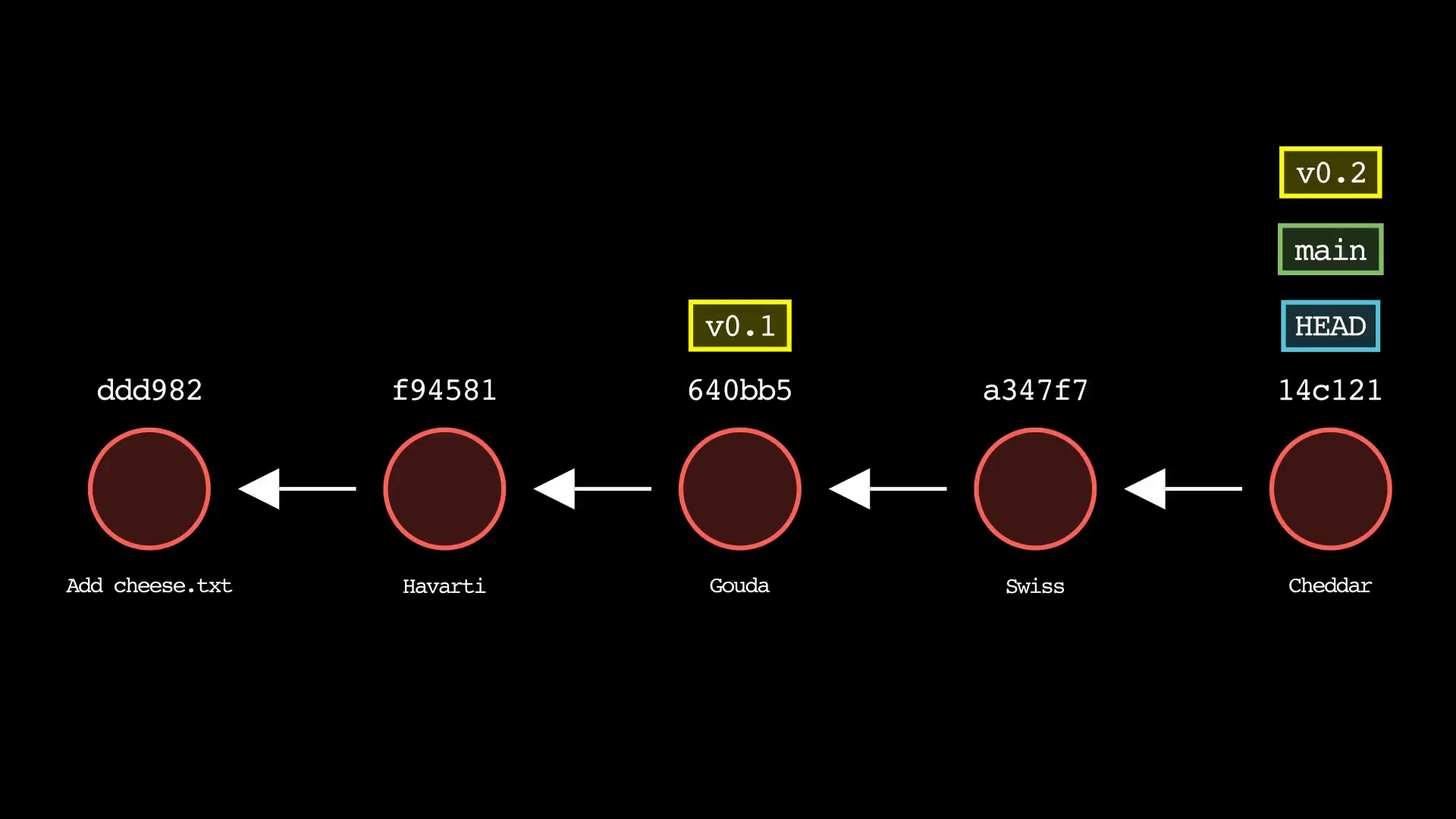
git tag
Usage: git-sim tag <new tag name>
- Specify
<new tag name>as the name of the new tag to simulate creation of - Simulated output will show the newly create tag ref along with most recent 5 commits on the active branch
Video animation examples
$ git-sim --animate reset HEAD^
$ git checkout main
$ git-sim --animate merge dev
$ git checkout dev
$ git-sim --animate rebase main
$ git checkout main
$ git-sim --animate cherry-pick dev
Basic command examples
Simulate the output of the git log command:
$ cd path/to/git/repo
$ git-sim log
Simulate the output of the git status command:
$ git-sim status
Simulate adding a file to the Git staging area:
$ git-sim add filename.ext
Simulate restoring a file from the Git staging area:
$ git-sim restore filename.ext
Simulate creating a new commit based on currently staged changes:
$ git-sim commit -m "Commit message"
Simulate stashing all working directory and staged changes:
$ git-sim stash
Simulate creating a new Git branch:
$ git-sim branch new-branch-name
Simulate creating a new Git tag:
$ git-sim tag new-tag-name
Simulate a hard reset of the current branch HEAD to the previous commit:
$ git-sim reset HEAD^ --hard
Simulate reverting the changes in an older commit:
$ git-sim revert HEAD~7
Simulate merging a branch into the active branch:
$ git-sim merge feature1
Simulate rebasing the active branch onto a new base:
$ git-sim rebase main
Simulate cherry-picking a commit from another branch onto the active branch:
$ git-sim cherry-pick 0ae641
Command examples with extra options/flags
Use light mode for white background and black text, instead of the default black background with white text:
$ git-sim --light-mode status
Animate the simulated output as a .mp4 video file:
$ git-sim --animate add filename.ext
Add an intro and outro with custom text and logo (must include --animate):
$ git-sim --animate --show-intro --show-outro --outro-top-text="My Git Repo" --outro-bottom-text="Thanks for watching!" --logo=path/to/logo.png status
Customize the output image/video directory location:
$ git-sim --media-dir=path/to/output status
Optionally, set the environment variable git_sim_media_dir to set a global default media directory, to be used if no --media-dir is provided. Simulated output images/videos will be placed in this location, in subfolders named with the corresponding repo's name.
$ export git_sim_media_dir=path/to/media/directory
$ git-sim status
Note: --media-dir takes precedence over the environment variable. If you set the environment variable and still provide the argument, you'll find the media in the path provided by --media-dir.
Generate output video in low quality to speed up rendering time (useful for repeated testing, must include --animate):
$ git-sim --animate --low-quality status
Installation
See Quickstart section for details on installing manim and other dependencies. Then run:
$ pip3 install git-sim
Docker installation
- Clone down the git-sim repository:
$ git clone https://github.com/initialcommit-com/git-sim.git
- Browse into the
git-simfolder and build the Docker image:
$ docker build -t git-sim .
- Run git-sim commands as follows:
- Windows:
docker run --rm -v %cd%:/usr/src/git-sim git-sim [global options] <subcommand> [subcommand options] - MacOS / Linux:
docker run --rm -v $(pwd):/usr/src/git-sim git-sim [global options] <subcommand> [subcommand options]
- Windows:
Optional: On MacOS / Linux / or GitBash in Windows, create an alias for the long docker command so your can run it as a normal git-sim command. To do so add the following line to your .bashrc or equivalent, then restart your terminal:
git-sim() { docker run --rm -v $(pwd):/usr/src/git-sim git-sim "$@"; }
This will enable you to run git-sim subcommands as described above.
Learn More
Learn more about this tool on the git-sim project page.
Authors
Jacob Stopak - on behalf of Initial Commit




