Awesome
Whitespace
A whitespace compiler for R
1.1 About the language
Whitespace is an imperative, stack based esoteric regular programming language. It only allows three symbols: [Space](" ","S"), [Tab]("\t","T") and [Newline]("\n","L"), which makes the source code invisible.
1.2 Syntax
The full documentation can be found here: http://compsoc.dur.ac.uk/whitespace/tutorial.html, but here is a general breakdown:
[Instruction Modification Parameter][Command][Parameter ended by L]
1.2.1 Instruction Modification parameter
- Space : Stack Manipulation
1.2.2 Stack Commands
- Space number : Push the number onto the stack
- Newline Space : Duplicate the top item on the stack
- Newline Tab : Swap the top two items on the stack
- Newline Newline : Delete the top item on the stack
- Tab Space : Arithmetic
1.2.3 Arithmetic Commands
- Space Space : +: Second element from top of stack + First element on top of stack
- Space Tab : -: Second element from top of stack - First element on top of stack
- Space Newline : *: Second element from top of stack * First element on top of stack
- Tab Space : /: Second element from top of stack / First element on top of stack
- Tab Tab : %: Second element from top of stack mod First element on top of stack
- Tab Tab : Heap access
1.2.3 Heap Commands
- Space : Put element in heap: second from top of stack: address, first on top of stack: value
- Tab : Get element from heap and put on stack: first element on top of stack: address
- Newline : Flow Control
1.2.3 Flow Commands
- Space Space label : Mark current location with label
- Space Tab label : Call subrouting at label
- Space Newline label : Jump unconditionally to label
- Tab Space label : Jump to label if first item on top of stack == 0
- Tab Tab label : Jump to label if first item on top of stack < 0
- Tab Newline : Return subroutine to main code
- Newline Newline : End program
- Tab Newline : Input/Output
1.2.3 I/O Commands
- Space Space : Print character on top of stack
- Space Tab : Print number on top of stack
- Tab Space : Read character and store it in label specified by top of stack
- Tab Tab : Read number and store it in label specified by top of stack
Here is a nicer and more intuitive representation:
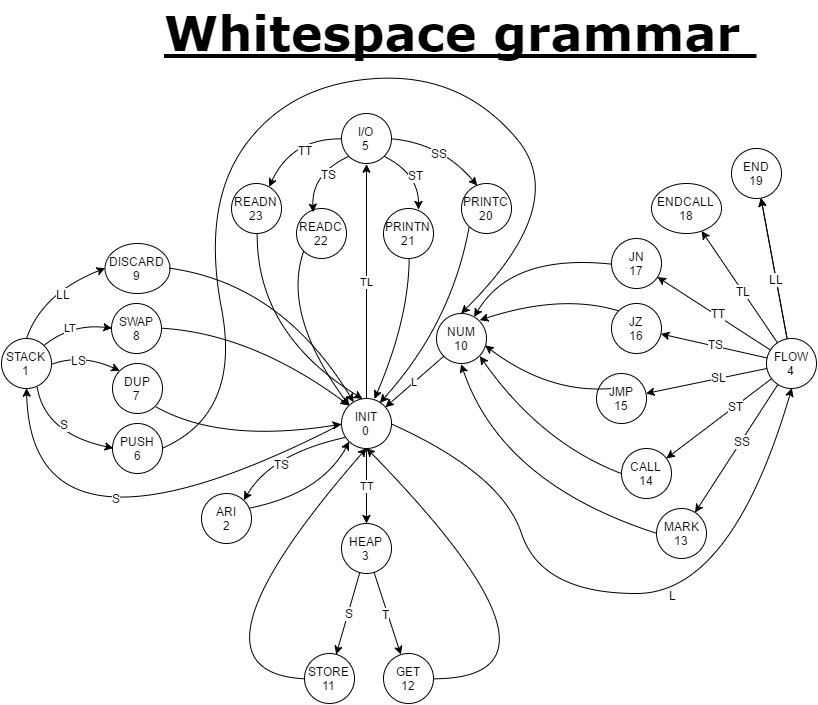
1.3 Installation
Simply do:
install.packages("devtools")
library(devtools)
install_github("artificialbreeze/whitespace")
1.4 Use
Create a DFA (Deterministic Finite-State automaton) with code=your code argument:
dfa1=dfa(" \t\t\t\t\t\t\n\t\n \n\n\n")
Now, parse the syntax:
dfa1.parsed=parse(dfa1)
Finally, compile and run the example:
dfa1.compiled=compile(dfa1.parse)
The above code should output:
# Program output: ?
# Program stop