Awesome
Analysys Presto-HBase-Connector
The component is implemented based on the Presto Connector interface specification and is used to add the ability to query HBase to Presto.
Our performance is 10 to 100 times faster than other open source versions of the HBase Connector.
Performance Comparison
| Environment | Detail |
|---|---|
| Data Size | The event table contains 5 million records and 90 fields |
| Workers | 3 |
| Hardware | 16 logical core 64GB memory (Presto and HBase 16GB memory respectively) 4T*2 hard disk |
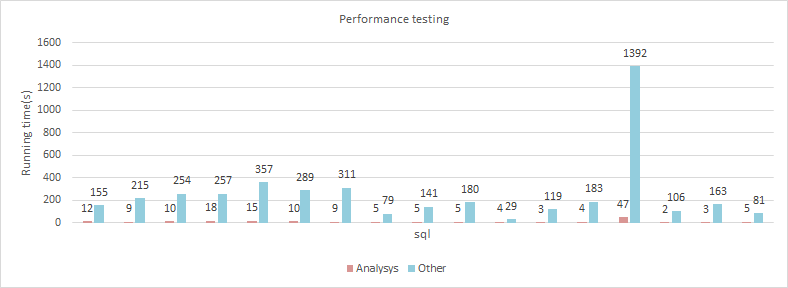
Function Point Comparison
| Fuction | Analysys | Others |
|---|---|---|
| Salted Table | SUPPORTED | UNSUPPORTED |
| Scan By StartKey & EndKey | SUPPORTED | UNSUPPORTED |
| Batch Gets | SUPPORTED | UNSUPPORTED |
| Predicate Pushdown (Filter) | SUPPORTED | UNSUPPORTED |
| ClientSideScan | SUPPORTED | SUPPORTED |
| Insert | SUPPORTED | SUPPORTED |
| Delete | SUPPORTED | SUPPORTED |
| Create Table | SUPPORT LATER | SUPPORTED |
Environment
- Mac OS X or Linux
- 8u161+, 64-bit.
- Maven 3.3.9+
- PrestoSql 315+
Building
mvn clean package
Deploying
1.hbase.properties
Create the hbase.properties file under the {Presto_Config_Dir}/catalog directory.Synchronize to all worker nodes after configuration.
The following is a relatively simple configuration sample for your reference:
connector.name=hbase
zookeeper-quorum=localhost:2181
zookeeper-client-port=2181
zookeeper-znode-parent=/hbase
hbase-cluster-distributed=true
presto-server-port=8285
random-schedule-redundant-split=false
meta-dir=/etc/presto/chbase
Parameters:
-
connector.name
Please fix this param to hbase. -
zookeeper-quorum
Please refer to hbase.zookeeper.quorum of HBase API. -
zookeeper-client-port
Please refer to hbase.zookeeper.property.clientPort of HBase API. -
hbase-cluster-distributed
Please refer to hbase.cluster.distributed of HBase API. -
presto-workers-name
Hostname of presto Worker, separated by commas(,). If param split-remove-accessible configuration is false, this parameter can be unset. -
presto-server-port
Please refer to http-server.http.port in {Presto_Config_Dir}/config.properties. -
random-schedule-redundant-split
By default, Presto dispatches the Split in the order of available workers and assigns the Split in turn. This makes it easy for the remainder of the Split set to be dispatched to workers at the beginning of the available Worker list when multi-table queries occur. Setting this parameter to true can change to randomly dispatch the remainder of the Split to a Worker for execution. -
meta-dir
The directory where the HBase table metadata information is stored. -
zookeeper-znode-parent
Please refer to zookeeper.znode.parent in hbase-site.xml. -
enable-clientSide-scan
Whether to enable HBase's ClientSide query mode.Default is false. -
clientside-querymode-tablenames
The name of table that is queried using ClientSide mode, with multiple tables separated by commas(,).
2.namespace
After configuring hbase.properties, we need to create the hbase namespace directory structure in the {meta-dir} directory. Informations:
- The {meta-dir} directory is used to store metadata information for tables.
- Under this directory, first create the directory with the namespace name of HBase.
- Each table will have a separate JSON file, named {table name}.json, to hold its table structure information. We can configure metadata information such as table fields in this JSON file.
- Tables of different namespace are stored in their respective namespace directories.
Example:
--meta-dir:
--namespace_a:
table_a1.json
table_a2.json
--namespace_b:
table_b1.json
table_b2.json
--default:
table_c.json
This example defines five tables:
namespace_a:table_a1 namespace_a:table_a2 namespace_b:table_b1 namespace_b:table_b2 default:table_c (saved in default namespace)
3.Table Structure JSON
After the namespace directory is created, we need to configure the table structure JSON file. Here are the properties in the JSON file:
| Attribute | Detail |
|---|---|
| tableName | Table name. |
| schemaName | Namespace. |
| rowKeyFormat | The RowKey is composed of which fields, separated by English commas.The fields are in order. |
| rowKeySeparator | The delimiter between the fields that make up the RowKey, which is \001 by default. |
| rowKeyFirstCharRange | If the RowKey is hashed, you can specify a range for the first letter of the RowKey, which can dramatically improve performance in the form of multiple split concurrency.The value range of the first letter can be A~ z,A~ z, 0 |
| describe | Comment of table. |
| columns | columns. |
Columns Json:
| Attribute | Detail |
|---|---|
| family | Family name. |
| columnName | Column name. |
| isRowKey | is RowKey. |
| type | Column type (Case insensitive): string, int, bigint, double, boolean(Stored with int, 0 for false, 1 for false), array< string >. |
| comment | Column comment. |
Description: isRowKey is true, which means we abstract the Rowkey of this table into a concrete field.Whether it's querying, writing, or any other complex operation, it's no different on the surface from a normal field, except that underneath the surface it has a special meaning as a row key for a table.
The RowKey field must be of type VARCHAR.
Example:
{
"tableName": "t_event_test",
"schemaName": "db_test",
"rowKeyFormat": "xwhat,xwho",
"describe": "Table for test!",
"rowKeySeparator": "-",
"rowKeyFirstCharRange": "a~z,0~9",
"columns": [{
"family": "",
"columnName": "rowkey",
"comment": "The RowKey column of table!",
"type": "varchar",
"isRowKey": true
}, {
"family": "f",
"columnName": "xwho",
"comment": "Column for test!",
"type": "varchar",
"isRowKey": false
}, {
"family": "f",
"columnName": "ds",
"comment": "Column for test!",
"type": "varchar",
"isRowKey": false
}]
}
Find its corresponding directory in {meta-dir} from the table namespace, and follow the instructions above to create a JSON file named after the table name.
4.Build Jar
- After completing the above steps, we need to compile the component JAR package:
// download source code
// using maven to build
mvn clean package
5.Deploy Component Jar
Create the plugin directory hbase (directory name can be set arbitrarily) in the {plugin.dir} directory.
Copy the presto0.20-hbase-{version.num}. Jar into this directory and synchronize it to all worker nodes.
6.Restart Presto Cluster
Insert
Write operations are supported in dev_0.1.1.
The write operation requires the user to specify the row_key for the data, either as a field concatenation or as a fixed value. As follows:
insert into hbase.db_test.test_event(row_key, xwho, distinct_id, ds, xwhen, xwhat, attri_1) select '01-test_rowkey' as row_key, xwho, distinct_id, ds, xwhen, xwhat, attri_1 from hbase.db_test.test_event_v2 where xwhen=1562057346821;
insert into hbase.db_test.test_event(row_key, xwho, distinct_id, ds, xwhen, xwhat, attri_1) select concat('01-', xwho, '-', xwhat, '-', xwhen) as row_key, xwho, distinct_id, ds, xwhen, xwhat, attri_1 from hbase.db_test.test_event_v2 where xwhat='login';
Delete
Deletion is supported in meta_0.1.1. The delete operation does not require the user to specify the value of the row_key for the data in the SQL, but requires the table being operated on to have the row_key field set in the JSON file that defines its metadata. Connector, when sieving the data to be deleted, gets the row_key for the data and then deletes the specified data based on the value of the row_key.
Example:
delete from hbase.db_test.test_event where xwhen >= 1562139516028;
Query Optimization
1.Salted Table
A salt value is a set of reverse-reducible random Numbers that are prefixed to each RowKey. This allows the data to be stored in multiple regions and queries to be searched concurrently by multiple threads. In Presto, you can use this mechanism to split the data into multiple split and run concurrently. It has been proven that using salt values can improve performance by dozens of times.
Using salt values in a component requires the following two properties to be set in the JSON file:
-
seperateSaltPart
Whether RowKey uses an INDEPENDENT salt value as a prefix.This param is set to true if the RowKey begins with a separate salt value section followed by {rowKeySeparator}.Starting with version 0.1.5, salt values can only consist of characters with values ranging from a to Z, A to Z, and 0 to 9 bits.
-
rowKeyFirstCharRange
When the first character of RowKey is hashed according to MD5 or some other algorithm, this property can be used to indicate the range of values for the first character.The Connector generates multiple split based on its value range.For the time being, the value range of the first letter only supports a
z,Az, 0~9, with commas between each other, like:a~b,D~K,3~5 3~5,c~f A~Z,p~uWhen the property is configured as A
b,DF,6~8, 8 startKey and endKey pairs are generated in turn. Each pair of startKey and endKey will give a split for data scanning, like:(a,a|) (b,b|) (D,D|) (E,E|) (F,F|) (6,6|) (7,7|) (8,8|)Sometimes, if too many split is split, the scope will be merged automatically to avoid the degradation of the performance of too many split, like:
(a,b|) (D,F|) (6,8|) -
rowKeySeparator
The delimiter between the fields that make up the RowKey, which is \001 by default.
2.Concatenate StartKey and EndKey according to the composition of the RowKey
This means to concatenate queries StartKey and EndKey based on which fields the RowKey consists of, and the predicates of the current query.
For example, when RowKey is composed as follows:
xwhat-xwho
sqls:
select xwhat, xwho, date, xwhen from t_event_test where xwhat='login' and xwho in ('drew', 'george');
This generates the following two StartKey and EndKey pairs:
(login-drew, login-drew|)
(login-george, login-george|)
To implement such a query optimization mechanism, we need to configure the following two parameters:
-
rowKeyFormat
Defines which fields the RowKey consists of in order.So in this case, it should be configured as "xwhat,xwho" -
rowKeySeparator
The delimiter between the different components of the RowKey, which is \001 by default.So in this case, it should be configured as "-"
Also, if you want to see exactly which splits the SQL has made, you can set the log level to Info to see in server.log.
3.Batch Get
Batch get is the way the HBase API encapsulates multiple rowkeys to be queried into a List< get >, and then requests the List to get the data.
This query method is very convenient to use, you can directly query the RowKey as the equivalent of the query criteria into the SQL.
select * from t_event_test where rk in ('rk1', 'rk2', 'rk3');
When the system resolves the predicate, it determines whether this query pattern will be executed based on whether the field name is consistent with the RowKey field.
Using this query pattern, you must specify the RowKey field via isRowKey in the table's JSON file.
Note: Because the RowKey field we defined is a virtual field, it makes no logical sense to do any type of query against it other than equivalent.
4.ClientSideRegionScanner
ClientSideRegionScanner is a new addition to HBase's 0.96 Scanner. It scans files on HDFS directly on the Client side without sending a request to RegionServer, which in turn scans the HDFS files. This reduced the RegionServer burden and did not affect the query even if the RegionServer was in the unavailable state.At the same time, because it is to read HDFS directly, so in the cluster with relatively balanced load, the local read strategy can avoid a lot of network load.
Here's a comparison of the component's performance using ClientSideRegionScanner vs ordinary RegionScanner. Most of the queries showed a 30% or more improvement, especially a full table scan:
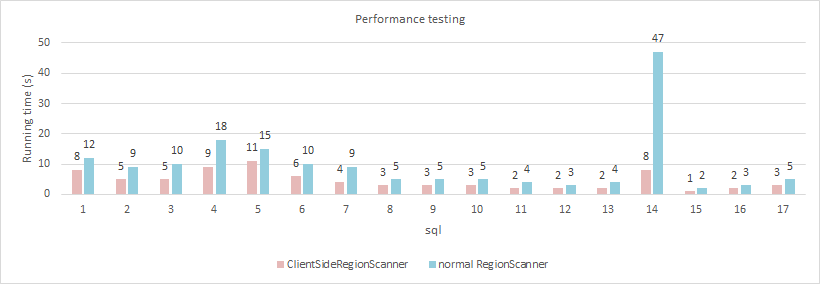
- Using ClientSide queries requires the following three parameters:
-
hbase-rootdir
This parameter is consistent with the hbase.rootdir of hbase.site.xml.
-
enable-clientSide-scan
Whether ClientSide query mode is enabled or not.
-
clientside-querymode-tablenames
Define which tables need ClientSide queries, with commas between table names, for example:
namespace_a:table_a,namespace_a:table_b,namespace_b:table_cIf all tables use ClientSide queries, you can configure it to *.
In addition to the above three parameters, the two configuration files of Hadoop in the running environment, core-site.xml and HDFs-site.xml, need to be copied to the src/main/resources directory of the project when packaging.
Note that ClientSideRegionScanner's queries rely on Snapshot, so in order for queries to get the latest data, a Snapshot is automatically created with the following naming rule for each query:
"ss-" + schemaName + "." + tableName + "-" + System.nanoTime()
The maximum number of Snapshot supported by HBase is 65,536, so it is a good idea to periodically clean out expired Snapshot when using ClientSideRegionScanner.
Problem Solving
1.How to support ClientSideRegionScanner query Snappy compressed HBase table?
You need to solve the following problems:
1) Cannot find SnappyCodec
This is due to the lack of Hadoop-common-2.7.3.jar in Presto's classPath.Since we are based on the Presto built by Ambari, we need to copy this JAR package to the directory /usr/lib/presto/lib.
2) SnappyCodec could not be converted to CompressionCodec
Presto was found to load the plugins by a custom PluginClassLoader, while SnappyCodec was loaded by AppClassLoader.Different classloaders result in no parent-child inheritance relationship between parent and child classes.
This problem was solved by modifying the code in hbase-common-1.1.2.1.jar, change SnappyCodec to load using PluginClassLoader.Need to modify the code for hbase-common module org.apache.hadoop.hbase.io.compress.Compression, modification method is as follows:
/**
* Returns the classloader to load the Codec class from.
*/
private static ClassLoader getClassLoaderForCodec() {
/* before modify:
ClassLoader cl = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader();
if (cl == null) {
cl = Compression.class.getClassLoader();
}*/
// after modify:
ClassLoader cl = Compression.class.getClassLoader();
if (cl == null) {
cl = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader();
}
if (cl == null) {
cl = ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader();
}
if (cl == null) {
throw new RuntimeException("A ClassLoader to load the Codec could not be determined");
}
Re-install the Maven repository with the modified code and repackage the component jars.
3) java.lang.UnsatisfiedLinkError: org.apache.hadoop.util.NativeCodeLoader.buildSupportsSnappy()Z
This is the Native Snappy library that needs to add Hadoop to the JVM. In Presto's jvm.config, you can add the following configuration:
-Djava.library.path={path to hadoop native lib}
4) java.io.IOException: java.lang.NoSuchMethodError: com.google.common.base.Objects.toStringHelper(Ljava/lang/Object;)Lcom/google/common/base/Objects$ToStringHelper;
This is because the guava v20.0+ version removed the inner class ToStringHelper in class com.google.common.base.Objects, and some toStringHelper method.
We can add the deleted code from the lower version to the higher version of the Guava source, recompile and update the guava-24.1-jre.jar in the Maven repository, and then rebuild the presto-hbase.jar.
And upload guava-24.1-jre.jar to PrestoWorker's lib directory.
Or use Maven's shade plugin to resolve this conflicts.
5) Cannot find constructor of Stopwatch
Change the constructor in com.google.common.base.Stopwatch from protect to public, and rebuild.
Or use Maven's shade plugin to resolve this conflicts.
6)Caused by: org.apache.hadoop.ipc.RemoteException(org.apache.hadoop.security.AccessControlException): Permission denied: user=presto, access=WRITE, inode="/apps/hbase/data/data/db_moredatatest/multifamily_90cq_7cf_500w_snappy2/dee9b34c5cd8ee34f74ff5fc5446432a/.tmp":hbase:hdfs:drwxr-xr-x
The permissions are insufficient, when we use presto user to access hbase data dir through presto query, we need to grant the presto user read permissions.
2.How to debug ClientSideRegionScanner to scan a Snappy compressed HBase table ?
You need to solve the following problems:
1) cannot find class CanUnbuff
add dependency below in module presto-hbase-connector:
<dependency>
<groupId>com.facebook.presto.hadoop</groupId>
<artifactId>hadoop-apache2</artifactId>
<version>2.7.4-1</version>
</dependency>
2) use hbase-shaded-client and hbase-shaded-server dependencies
3) According to part "SnappyCodec could not be converted to CompressionCodec", and re-install maven library. These three modules hbase-shade-client,hbase-shade-server and hbase-common must be rebuild.
4) Add -Djava.library.path in run->Edit Configuration to VM options configuration in PrestoServer. java.library.path is the native snappy library path of hadoop.
Releases Notes
1. meta-0.1.1
- Support ClientSide Query.
2. meta-0.1.2
- Support insert and delete.
- Fix failure when query table in default namespace using ClientSide.
- Change enable-clientSide-scan to false by default. Change hbase-rootdir to nullable.
- Add param zookeeper-znode-parant.
3. meta-0.1.3
- Migrate connector to PrestoSql-315.
- Provide a usable version based on PrestoDB-0.221. Branch name is dev_prestodb-0.221_0.1.2.
- Fix document.
4. meta-0.1.4
- Migrate connector API to non-legacy version.
5. meta-0.1.5
- Readjust the split logic, remove the parameter rowKeySaltUpperAndLower, and change it to rowKeyFirstCharRange.So that even if the RowKey has no salt part and no predicates available to splice StartKey, as long as the first character of the RowKey is hashed, we can still split multiple splits to increase the parallelism of the query.