Awesome
Flowy
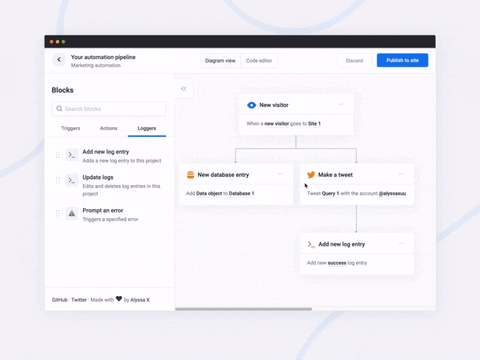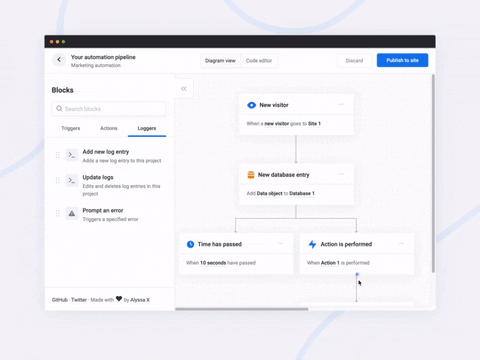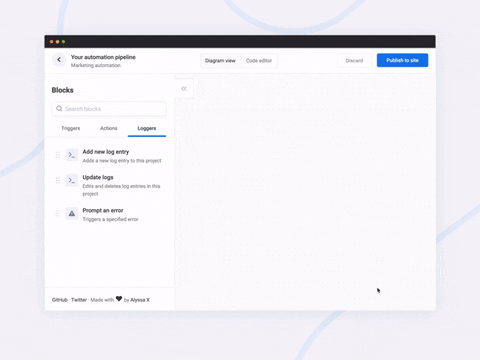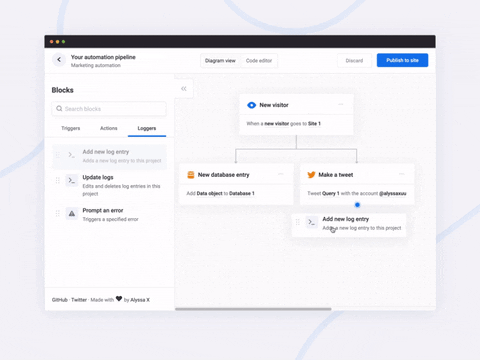 <br>A javascript library to create pretty flowcharts with ease ✨
<br>A javascript library to create pretty flowcharts with ease ✨
Dribbble | Twitter | Live demo
Flowy makes creating WebApps with flowchart functionality an incredibly simple task. Build automation software, mind mapping tools, or simple programming platforms in minutes by implementing the library into your project.
You can support this project (and many others) through GitHub Sponsors! ❤️
Made by Alyssa X
Table of contents
Features
Currently, Flowy supports the following:
- Responsive drag and drop
- Automatic snapping
- Automatic scrolling
- Block rearrangement
- Delete blocks
- Automatic block centering
- Conditional snapping
- Conditional block removal
- Import saved files
- Mobile support
- Vanilla javascript (no dependencies)
- npm install
You can suggest new features here
Installation
Adding Flowy to your WebApp is incredibly simple:
- Link
flowy.min.jsandflowy.min.cssto your project. Through jsDelivr:
<link rel="stylesheet" href="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/gh/alyssaxuu/flowy/flowy.min.css">
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/gh/alyssaxuu/flowy/flowy.min.js"></script>
- Create a canvas element that will contain the flowchart (for example,
<div id="canvas"></div>) - Create the draggable blocks with the
.create-flowyclass (for example,<div class="create-flowy">Grab me</div>)
Running Flowy
Initialization
flowy(canvas, ongrab, onrelease, onsnap, onrearrange, spacing_x, spacing_y);
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
canvas | javascript DOM element | The element that will contain the blocks |
ongrab | function (optional) | Function that gets triggered when a block is dragged |
onrelease | function (optional) | Function that gets triggered when a block is released |
onsnap | function (optional) | Function that gets triggered when a block snaps with another one |
onrearrange | function (optional) | Function that gets triggered when blocks are rearranged |
spacing_x | integer (optional) | Horizontal spacing between blocks (default 20px) |
spacing_y | integer (optional) | Vertical spacing between blocks (default 80px) |
To define the blocks that can be dragged, you need to add the class .create-flowy
Example
HTML
<div class="create-flowy">The block to be dragged</div>
<div id="canvas"></div>
Javascript
var spacing_x = 40;
var spacing_y = 100;
// Initialize Flowy
flowy(document.getElementById("canvas"), onGrab, onRelease, onSnap, onRearrange, spacing_x, spacing_y);
function onGrab(block){
// When the user grabs a block
}
function onRelease(){
// When the user releases a block
}
function onSnap(block, first, parent){
// When a block snaps with another one
}
function onRearrange(block, parent){
// When a block is rearranged
}
Callbacks
In order to use callbacks, you need to add the functions when initializing Flowy, as explained before.
On grab
function onGrab(block){
// When the user grabs a block
}
Gets triggered when a user grabs a block with the class create-flowy
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
block | javascript DOM element | The block that has been grabbed |
On release
function onRelease(){
// When the user lets go of a block
}
Gets triggered when a user lets go of a block, regardless of whether it attaches or even gets released in the canvas.
On snap
function onSnap(block, first, parent){
// When a block can attach to a parent
return true;
}
Gets triggered when a block can attach to another parent block. You can either prevent the attachment, or allow it by using return true;
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
block | javascript DOM element | The block that has been grabbed |
first | boolean | If true, the block that has been dragged is the first one in the canvas |
parent | javascript DOM element | The parent the block can attach to |
On rearrange
function onRearrange(block, parent){
// When a block is rearranged
return true;
}
Gets triggered when blocks are rearranged and are dropped anywhere in the canvas, without a parent to attach to. You can either allow the blocks to be deleted, or prevent it and thus have them re-attach to their previous parent using return true;
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
block | javascript DOM element | The block that has been grabbed |
parent | javascript DOM element | The parent the block can attach to |
Methods
Get the flowchart data
// As an object
flowy.output();
// As a JSON string
JSON.stringify(flowy.output());
The JSON object that gets outputted looks like this:
{
"html": "",
"blockarr": [],
"blocks": [
{
"id": 1,
"parent": 0,
"data": [
{
"name": "blockid",
"value": "1"
}
],
"attr": [
{
"id": "block-id",
"class": "block-class"
}
]
}
]
}
Here's what each property means:
| Key | Value type | Description |
|---|---|---|
html | string | Contains the canvas data |
blockarr | array | Contains the block array generated by the library (for import purposes) |
blocks | array | Contains the readable block array |
id | integer | Unique value that identifies a block |
parent | integer | The id of the parent a block is attached to (-1 means the block has no parent) |
data | array of objects | An array of all the inputs within a certain block |
name | string | The name attribute of the input |
value | string | The value attribute of the input |
attr | array of objects | Contains all the data attributes of a certain block |
Import the flowchart data
flowy.import(output)
Allows you to import entire flowcharts initially exported using the previous method, flowy.output()
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
output | javascript DOM element | The data from flowy.output() |
Warning
This method accepts raw HTML and does not sanitize it, therefore this method is vulnerable to XSS. The only safe use for this method is when the input is absolutely trusted, if the input is not to be trusted the use this method can introduce a vulnerability in your system.
Delete all blocks
To remove all blocks at once use:
flowy.deleteBlocks()
Currently there is no method to individually remove blocks. The only way to go about it is by splitting branches manually.
Feel free to reach out to me through email at hi@alyssax.com or on Twitter if you have any questions or feedback! Hope you find this useful 💜