Awesome
Malware Classifier From Network Capture
Malware Classifier is a simple free software project done during an university workshop of 4 hours. The objective of the 4 hours workshop was to introduce network forensic and simple techniques to classify malware network capture (from their execution in a virtual machine). So the software was kept very simple while using and learning existing tools (networkx, redis and Gephi).
Requirements
- Python 2.7
- networkx and redis modules (pip install -r REQUIREMENTS)
- tshark (part of Wireshark)
- a Redis server
How to use the Malware Classifier
You'll need of a set of network packet captures. In the workshop, we use a dataset with more than 5000 pcap files generated from the execution of malware in virtual machines.
...
0580c82f6f90b75fcf81fd3ac779ae84.pcap
05a0f4f7a72f04bda62e3a6c92970f6e.pcap
05b4a945e5f1f7675c19b74748fd30d1.pcap
05b57374486ce8a5ce33d3b7d6c9ba48.pcap
05bbddc8edac3615754f93139cf11674.pcap
...
The filename includes the MD5 malware executed in the virtual machine.
If you want to classify malware communications based on the Server HTTP headers of the (potential) C&C communication.
cd capture
ls -1 . | parallel --gnu "cat {1} | tshark -E header=yes -E separator=, -Tfields -e http.server -r {1} | python ./bin/import.py -f {1} "
You can add additional attributes like any fields from the dissectors available within tshark (tshark -G fields). You can add additional fields in the command above. This will update the redis data structure. Then when you have enough attributes, you can dump a graph out of the relationships between the attributes and the malware packet captures.
python ./bin/graph.py
graph.py generates a GEXF file that you can import in gephi.
The output in Gephi can look like this:

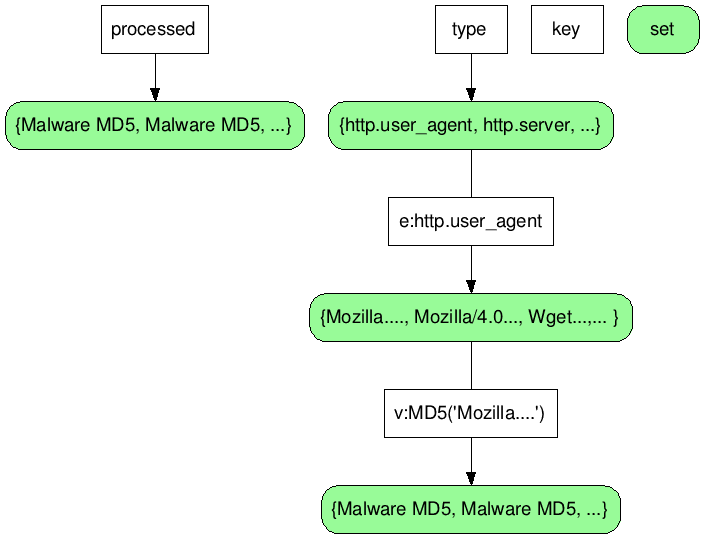
Redis data structure
Notes for the student
Check the git log and the commits, these include the steps performed during the workshop especially regarding the improvement of the Python scripts.