Awesome
Themis
Introduction
Themis provides cross-row/cross-table transaction on HBase based on google's Percolator.
Themis guarantees the ACID characteristics of cross-row transaction by two-phase commit and conflict resolution, which is based on the single-row transaction of HBase. Themis depends on Chronos to provide global strictly incremental timestamp, which defines the global order for transactions and makes Themis could read database snapshot before given timestamp. Themis adopts HBase coprocessor framework, which could be applied without changing source code of HBase. We validate the correctness of Themis for a few months, and optimize the algorithm to achieve better performance.
Implementation
Themis contains three components: timestamp server, client library, themis coprocessor.
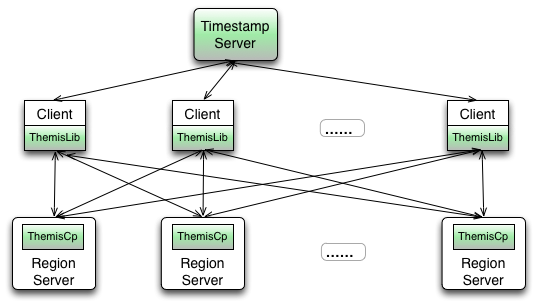
Timestamp Server
Themis uses the timestamp of HBase's KeyValue internally, and the timestamp must be global strictly incremental. Themis depends on Chronos to provide such timestamp service.
Client Library
- Provide transaction APIs.
- Fetch timestamp from Chronos.
- Issue requests to themis coprocessor in server-side.
- Resolve conflict for concurrent mutations of other clients.
Themis Coprocessor:
- Provide RPC methods for two-phase commit and read.
- Create auxiliary families and set family attributes for the algorithm automatically.
- Periodically clean the data of the aborted and expired transactions.
Usage
Build
-
Get the latest source code of Themis:
git clone https://github.com/XiaoMi/themis.git -
The master branch of Themis depends on hbase 0.94.21 with hadoop.version=2.0.0-alpha. We can download source code of hbase 0.94.21 and install it in maven local repository by:
(in the directory of hbase 0.94.21) mvn clean install -DskipTests -Dhadoop.profile=2.0 -
Build Themis and install in local repository:
cd themis mvn clean install -DskipTests
Loads themis coprocessor in HBase:
-
Add themis-coprocessor dependency in the pom of HBase:
<dependency> <groupId>com.xiaomi.infra</groupId> <artifactId>themis-coprocessor</artifactId> <version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version> </dependency> -
Add configurations for themis coprocessor in hbase-site.xml:
<property> <name>hbase.coprocessor.user.region.classes</name> <value>org.apache.hadoop.hbase.themis.cp.ThemisProtocolImpl,org.apache.hadoop.hbase.themis.cp.ThemisScanObserver,org.apache.hadoop.hbase.regionserver.ThemisRegionObserver</value> </property> <property> <name>hbase.coprocessor.master.classes</name> <value>org.apache.hadoop.hbase.master.ThemisMasterObserver</value> </property> -
Add the themis-client dependency in the pom of project which needs cross-row transactions.
Depends themis-client:
Add the themis-client dependency in the pom of project which needs cross-row transactions.
<dependency>
<groupId>com.xiaomi.infra</groupId>
<artifactId>themis-client</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
</dependency>
Run the example code
-
Start a standalone HBase cluster(0.94.21 with hadoop.version=2.0.0-alpha) and make sure themis-coprocessor is loaded as above steps.
-
After building Themis, run example code by:
cd themis-client mvn exec:java -Dexec.mainClass="org.apache.hadoop.hbase.themis.example.Example"
The screen will output the result of read and write transactions.
Example of Themis API
The APIs of Themis are defined in TransactionInterface.java, including put/delete/get/getScanner, which are similar to HBase's APIs:
public void put(byte[] tableName, ThemisPut put) throws IOException;
public void delete(byte[] tableName, ThemisDelete delete) throws IOException;
public void commit() throws IOException;
public Result get(byte[] tableName, ThemisGet get) throws IOException;
public ThemisScanner getScanner(byte[] tableName, ThemisScan scan) throws IOException;
The following code shows how to use Themis APIs:
// This class shows an example of transfer $3 from Joe to Bob in cash table, where rows of Joe and Bob are
// located in different regions. The example will use the 'put' and 'get' APIs of Themis to do transaction.
public class Example {
private static final byte[] CASHTABLE = Bytes.toBytes("CashTable"); // cash table
private static final byte[] JOE = Bytes.toBytes("Joe"); // row for Joe
private static final byte[] BOB = Bytes.toBytes("Bob"); // row for Bob
private static final byte[] FAMILY = Bytes.toBytes("Account");
private static final byte[] CASH = Bytes.toBytes("cash");
public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException {
Configuration conf = HBaseConfiguration.create();
HConnection connection = HConnectionManager.createConnection(conf);
// create table and set THEMIS_ENABLE in family 'Account'
createTable(connection);
// transfer $3 from Joe to Bob
Transaction transaction = new Transaction(conf, connection);
// firstly, read out the current cash for Joe and Bob
ThemisGet get = new ThemisGet(JOE).addColumn(FAMILY, CASH);
int cashOfJoe = Bytes.toInt(transaction.get(CASHTABLE, get).getValue(FAMILY, CASH));
get = new ThemisGet(BOB).addColumn(FAMILY, CASH);
int cashOfBob = Bytes.toInt(transaction.get(CASHTABLE, get).getValue(FAMILY, CASH));
// then, transfer $3 from Joe to Bob, the mutations will be cached in client-side
int transfer = 3;
ThemisPut put = new ThemisPut(JOE).add(FAMILY, CASH, Bytes.toBytes(cashOfJoe - transfer));
transaction.put(CASHTABLE, put);
put = new ThemisPut(BOB).add(FAMILY, CASH, Bytes.toBytes(cashOfBob + transfer));
transaction.put(CASHTABLE, put);
// commit the mutations to server-side
transaction.commit();
connection.close();
Transaction.destroy();
}
}
For the full example, please see : org.apache.hadoop.hbase.themis.example.Example.java
Schema Support
- Themis will use the timestamp of KeyValue internally, so that the timestamp and version attributes of HBase's KeyValue can't be used by the application.
- For families need Themis, set THEMIS_ENABLE to 'true' by adding "CONFIG => {'THEMIS_ENABLE', 'true'}" to the family descriptor when creating table.
- For each column, Themis will introduce two auxiliary columns : lock column and commit column. Themis saves the auxiliary columns in specific families : lock column in family 'L', and commit column in family #p(or in family #d if it is a Delete). The character '#' is preserved by Themis and application should not include it in name of the family needing Themis. Themis will create auxiliary families automically when creating table if 'THEMIS_ENABLE' is set on some family.
Themis Configuration
Client Side
Timestamp server
If users want strong consistency across client processes, the 'themis.timestamp.oracle.class' should be set to 'RemoteTimestampOracleProxy'. Then, Themis will access globally incremental timestamp from Chronos, the entry of Chronos will be registered in Zookeeper where the quorum address and entry node can be configured.
The default value of 'themis.timestamp.oracle.class' is 'LocalTimestampOracle', which provides incremental timestamp locally in one process. If users only need strong consistency in one clent process, the default value could be used.
| Key | Description | Default Value |
|---|---|---|
| themis.timestamp.oracle.class | timestamp server type | LocalTimestampOracle |
| themis.remote.timestamp.server.zk.quorum | ZK quorum where remote timestamp server registered | 127.0.0.1:2181 |
| themis.remote.timestamp.server.clustername | cluster name of remote timestamp server | default-cluster |
Lock clean
The client needs to clean lock if encountering conflict. Users can configure the ttl of lock in client-side by 'themis.client.lock.clean.ttl'. The default value of this configuration is 0, which means the lock ttl will be decided by the server side configurations.
Users can configure 'themis.worker.register.class' to 'ZookeeperWorkerRegister' to help resolve conflict faster. For details of conflict resolve, please see: Percolator paper.
| Key | Description | Default Value |
|---|---|---|
| themis.client.lock.clean.ttl | lock ttl configured in client-side | 0 |
| themis.worker.register.class | worker register class | NullWorkerRegister |
| themis.retry.count | retry count when clean lock | 10 |
| themis.pause | sleep time between retries | 100 |
Server Side
Data Clean Options
Both read and write transactions should not last too long. Users can set 'themis.transaction.ttl.enable' to enable transaction ttl. If this configuration is enabled, 'themis.read.transaction.ttl' and 'themis.write.transaction.ttl' could be used to configure the ttl for read transaction and write transaction respectively.
If users enable transaction ttl, old data may become expired and can not be read by any transaction. Users can enable 'themis.expired.data.clean.enable' to clean the old and expired data from HBase.
| Key | Description | Default Value |
|---|---|---|
| themis.transaction.ttl.enable | whether the transaction will be expired | true |
| themis.read.transaction.ttl | ttl for read transaction | 86400 |
| themis.write.transaction.ttl | ttl for write transaction | 60 |
| themis.expired.data.clean.enable | enable cleaning the old and expired data | true |
Metrics
Themis provides metrics for major APIs, which could be retrieved from JMX or sent to a file. The following configuration in hadoop-metrics.properties will send the metric to file periodically:
themis.class=org.apache.hadoop.hbase.metrics.file.TimeStampingFileContext
themis.period=10
themis.fileName=./themis_metrics.out
MapReduce Support
Themis implement InputFormat and OutputFormat interface in MapReduce framework:
-
ThemisTableInputFormat is implemented to read data from themis-enable table in Mapper. To read data from multi-tables, please use MultiThemisTableInputFormat.
-
ThemisTableOutputFormat is implemented to write data by Themis to themis-enable table in Reducer. To write data across multi-tables, please use MultiThemisTableOutputFormat.
-
ThemisTableMapReduceUtil provides utility methods to start a MapReduce job.
Global Secondary Index Support
Based on the cross table data consistency guaranteed by Themis transaction, we build an expiremental sub-project "themis-index" to support global secondary index, this sub-project is in progress.
Test
Correctness Validation
We design an AccountTransfer simulation program to validate the correctness of implementation. This program will distribute initial values in different tables, rows and columns in HBase. Each column represents an account. Then, configured client threads will be concurrently started to read out a number of account values from different tables and rows by themisGet. After this, clients will randomly transfer values among these accounts while keeping the sum unchanged, which simulates concurrent cross-table/cross-row transactions. To check the correctness of transactions, a checker thread will periodically scan account values from all columns, make sure the current total value is the same as the initial total value. We run this validation program for a period when releasing a new version for Themis.
Performance Test
Percolator Result:
Percolator tests the read/write performance for single-column transaction(represents the worst case of Percolator) and gives the relative drop compared to BigTable as follow table.
| BigTable | Percolator | Relative | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Read/s | 15513 | 14590 | 0.94 |
| Write/s | 31003 | 7232 | 0.23 |
Themis Result: We evaluate the performance of Themis under similar test conditions with Percolator's and give the relative drop compared to HBase.
Evaluation of get. Load 30g data into HBase before testing get by reading loaded rows. We set the heap size of region server to 10g and hfile.block.cache.size=0.45.
| Client Thread | GetCount | Themis AvgLatency(us) | HBase AvgLatency(us) | Relative |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 10000000 | 1029.88 | 1191.21 | 0.86 |
| 10 | 20000000 | 1230.44 | 1407.93 | 0.87 |
| 20 | 20000000 | 1848.05 | 2190.00 | 0.84 |
| 50 | 30000000 | 4529.80 | 5382.87 | 0.84 |
Evaluation of put. Load 3,000,000 rows data into HBase before testing put. We config 256M cache size to keep locks in memory for write transaction.
| Client Thread | PutCount | Themis AvgLatency(us) | HBase AvgLatency(us) | Relative |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3000000 | 1620.69 | 818.62 | 0.51 |
| 5 | 10000000 | 1695.89 | 1074.13 | 0.63 |
| 10 | 20000000 | 2057.55 | 1309.12 | 0.64 |
| 20 | 20000000 | 2761.66 | 1902.79 | 0.69 |
| 50 | 30000000 | 5441.48 | 3702.04 | 0.68 |
The above tests are all done in a single region server. From the results, we can see the performance of get is 85% of HBase's get and the performance of put is about 60% of HBase's put. For get, the result is about 10% lower to that reported in Percolator paper. The put performance is much better compared to that reported in Percolator paper. We optimize the performance of single-column transaction by the following skills:
-
In prewrite phase, we only write the lock to MemStore;
-
In commit phase, we erase corresponding lock if it exist, write data and commit information at the same time.
The aboving skills make prewrite phase not sync HLog, so that improving the write performance a lot. After applying the skills, if region server restarts after prewrite phase, the commit phase can't read the persistent lock and the transaction will fail, this won't break correctness of the algorithm.
Future Works
- Optimize the memory usage of RegionServer. Only locks of unfinished transactions should be kept in memory.
- Support different ioslation levels. Study the tradeoff between isolation levels and efficiency.
- Commit secondary rows in background to improve latency.
- Optimize the lock clean process.
- Open source the correctness validate program: AccountTransfer.
Contact Us
Any suggestion or discussion about Themis is welcomed. Please contact us by cuijianwei@xiaomi.com, or in HBase jira HBASE-10999.