Awesome
PETEP (PEnetration TEsting Proxy) is an open-source Java application for creating proxies for traffic analysis & modification. Main goal of PETEP is to provide a useful tool for performing penetration tests of applications with various protocols (on TCP/UDP) by setting up proxies and interceptors to manage the traffic transmitted between the client and the server.
Links
- 🌐 Official Website
- 🔽 Download
- 📖 User Guide
- 📚 Methodology
- 👩💻 Developer Guide
- 🎬 Youtube PETEP - Tutorial (TCP Proxy for Hacking)
Installation & Usage
Requirements: Java 11+ (for M1, M2 Mac use Java 17+)
Running PETEP for the first time
- Download latest PETEP release
- Extract PETEP zip file
- Run PETEP using
petep.sh(Linux, Mac) orpetep.bat(Windows)# Linux / Mac chmod +x petep.sh ./petep.sh # Windows petep.bat
Tip: Provided run scripts contain useful variables,
including working directory (for petep.json file), and path to Java executable.
You might need to change it if you do not have it in PATH or you use multiple Java versions
on your machine.
Setting up your first project
- Start PETEP
- Create a new project using the FULL preset and click Run
- In Settings, setup TCP/UDP proxy and optionally configure interceptors
- Click START and start hacking
Tip: Most changes to the project are not automatically persistent. Use Project → Save to save the changes, when PETEP is running.
Features
Latest PETEP version has the following protocol support:
- TCP proxy with SSL/TLS support - application protocols built on TCP
- UDP proxy - application protocols built on UDP
- Deluder - integration with Deluder for proxy unaware applications
And there are the following functionalities:
- External HTTP proxy - support for tunneling the TCP traffic through HTTP proxies like Zaproxy, Burp Suite, etc
- Logger - basic text file logging of intercepted traffic
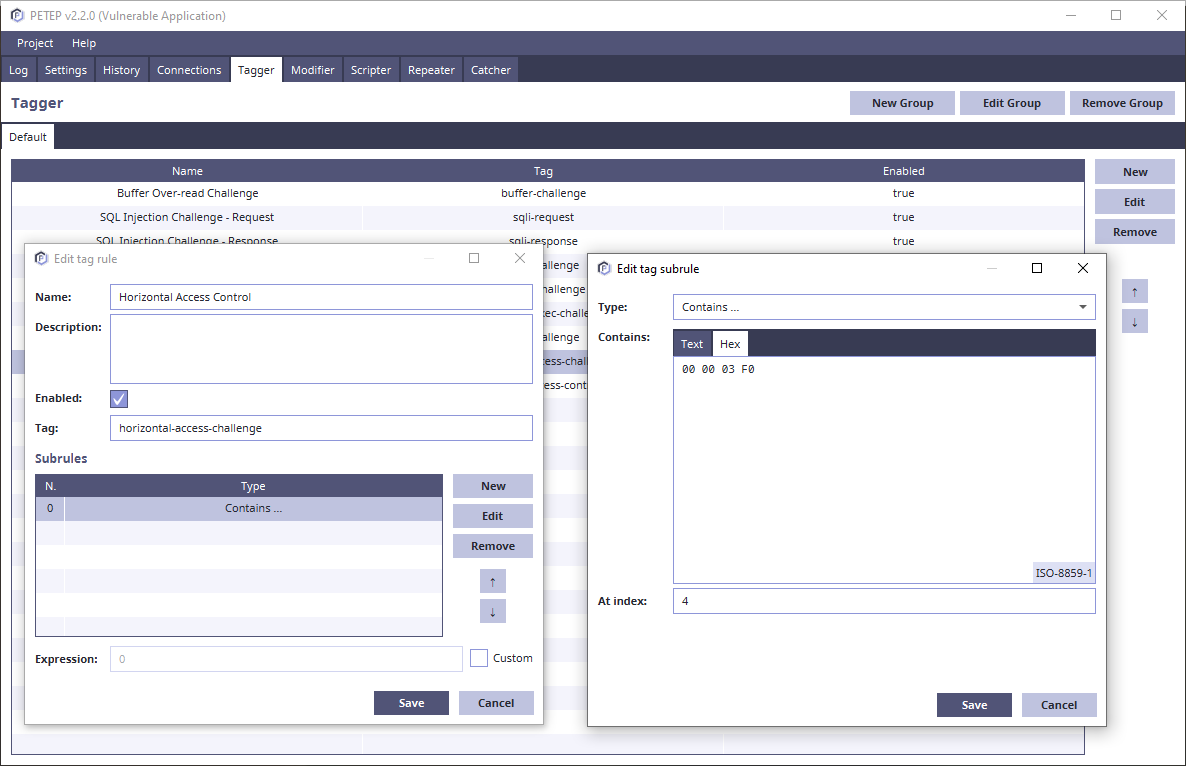
- Tagger - rules for tagging protocol data units for easier modification rules and history filtering
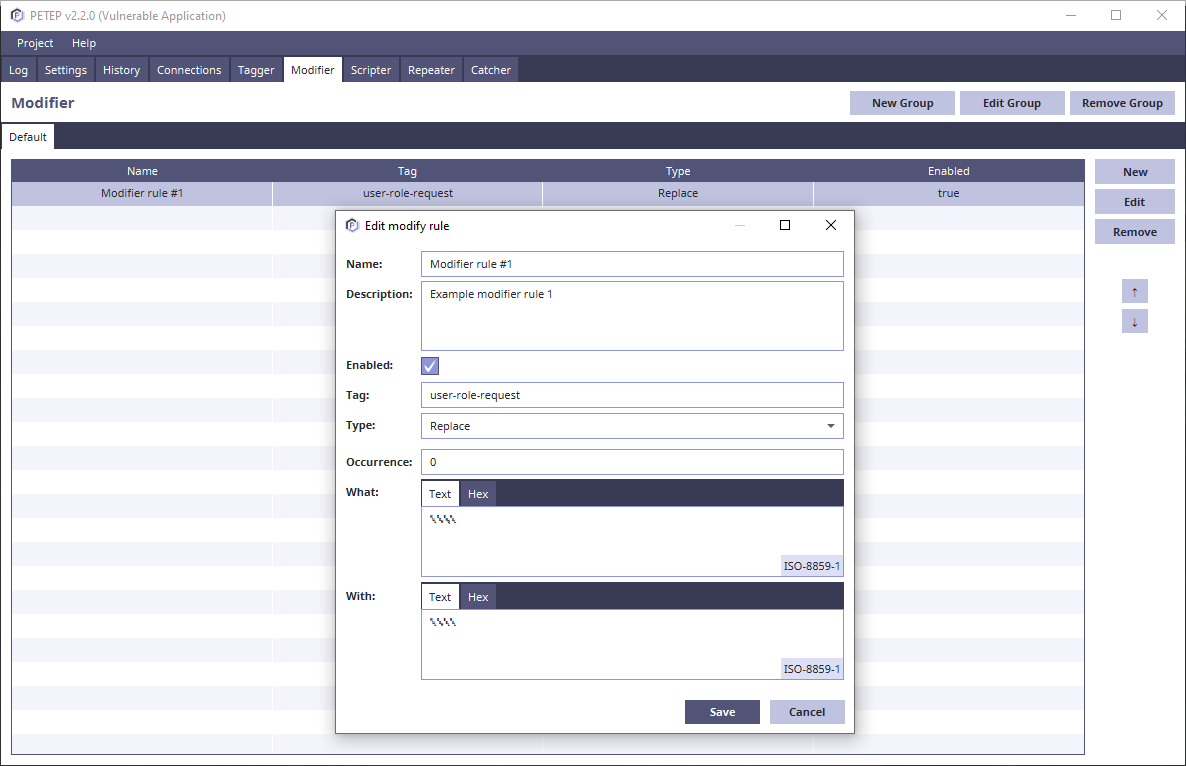
- Modifier - rules for automatic traffic modification (e.g. replacing bytes)
- Catcher - manual traffic interception and modification
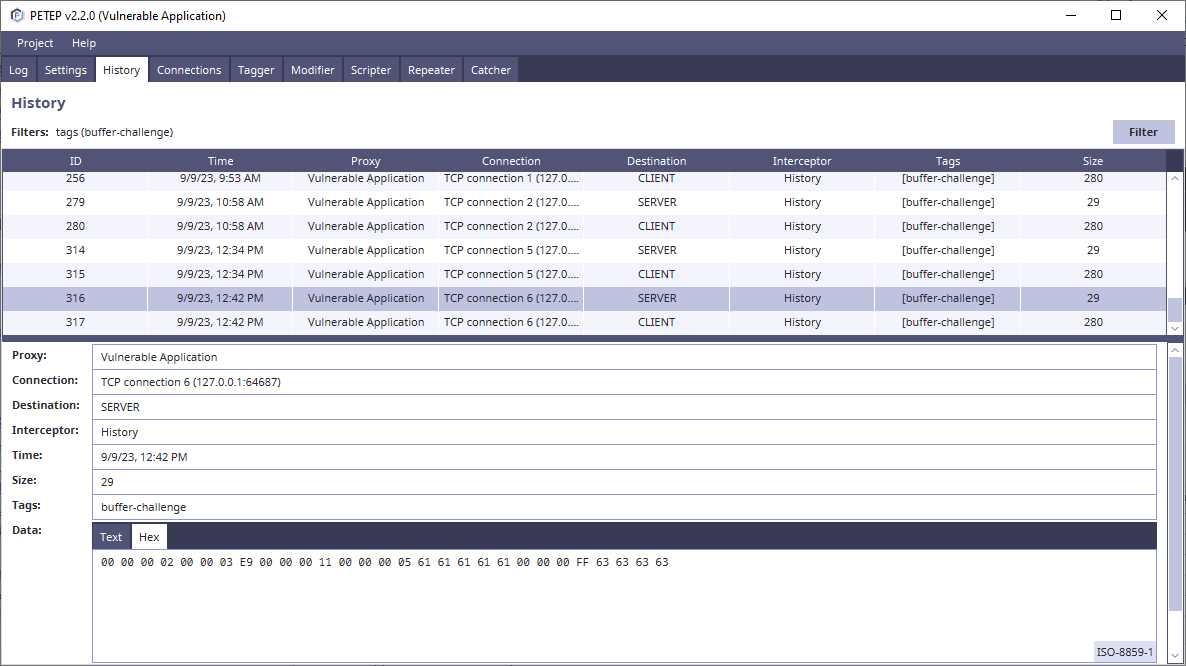
- History - history of traffic that was intercepted by PETEP with filtering support
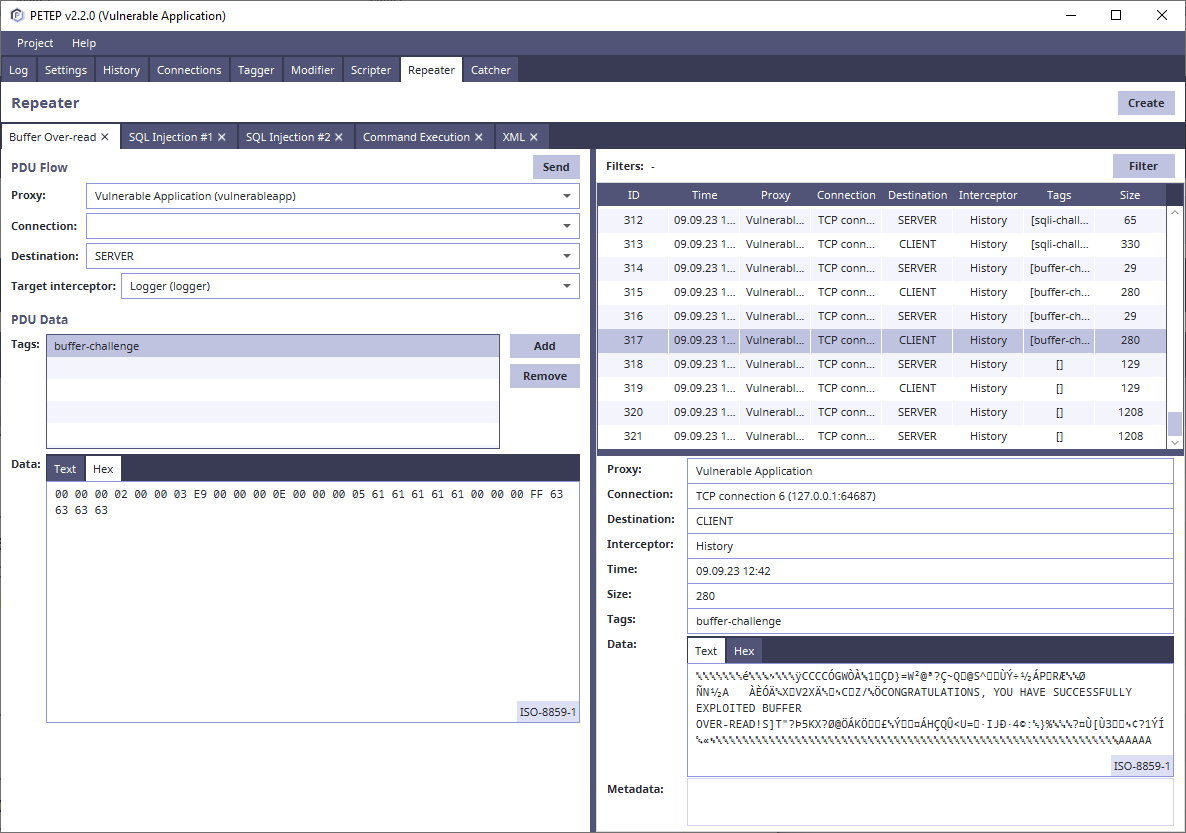
- Repeater - manual sending and editing of protocol data units
- Scripter - basic support for JS scripts for custom traffic processing
- Connections - management of active connections
Detailed descriptions of all modules can be found in the official User Guide.
TCP/UDP proxy
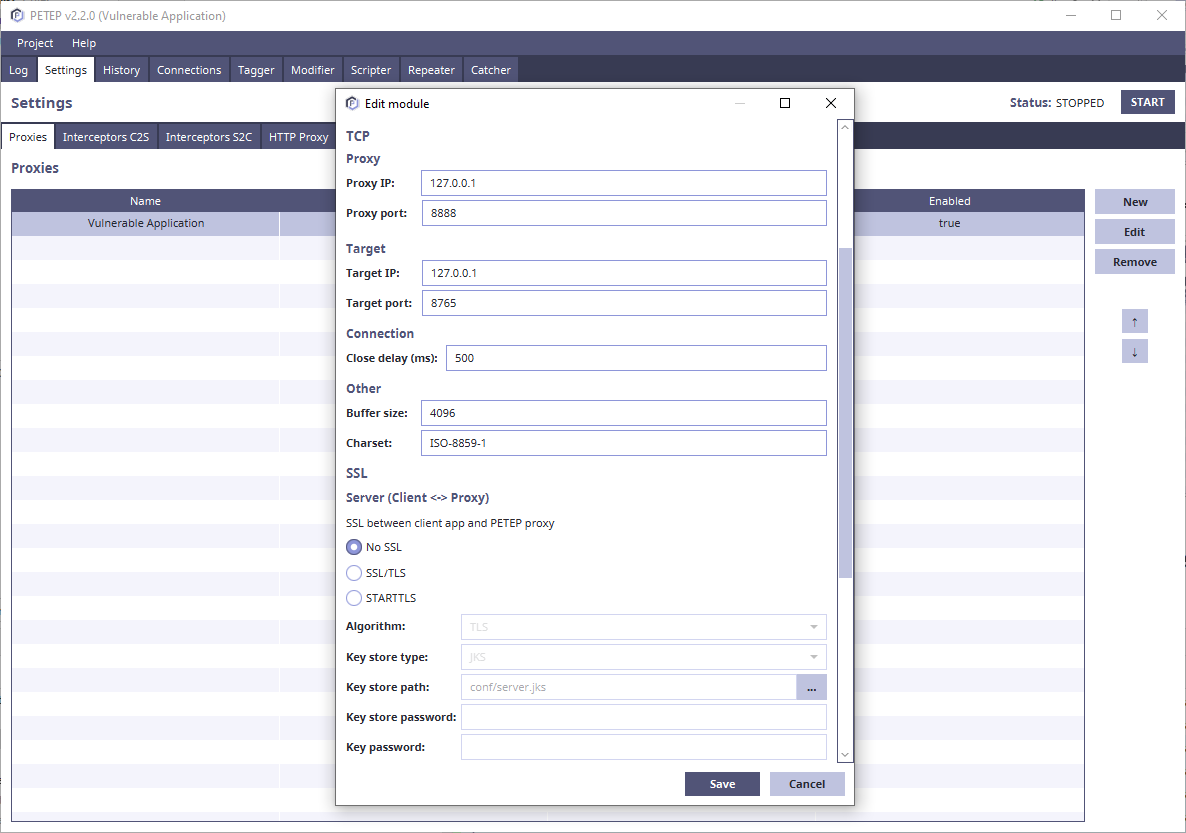
PETEP is made to be a proxy for application protocols built on TCP/UDP. In order to use PETEP as a proxy for your application, there are usually one the following options:
- Target application can be configured to use specific IP address and port for communication.
- In this case, simply configure PETEP to communicate with the target server and configure the target application to use PETEP's IP address and port.
- Target application uses domain resolution in order to connect to the target server.
- In this case, you can usually configure
/etc/hostsfile and override the IP address for the target domain. - Note that for SSL applications, you sometimes have to add the PETEP certificate to your computers trusted certificates.
- In this case, you can usually configure
Deluder for proxy unaware applications
If the target application is not proxy aware and/or it is not possible to use other approaches (e.g. /etc/hosts)
to make the application communicate through PETEP, you can use Deluder.
Deluder is a Python utility, which uses dynamic instrumentation to intercept function calls in common networking and encryption libraries. See Deluder GitHub.
Scripter extension
In order to use Scripter extension, it is recommended to use GraalVM, since the implementation is built
using GraalVM Polyglot. Since GraalVM 22.2, you might need to install the scripting language in the GraalVM using
gu install js.
Tunnel TCP through HTTP proxy like Burp or Zaproxy
In order to test TCP communication using existing HTTP proxies like Burp Suite, OWASP Zap etc.), you can use PETEP external HTTP proxy module, which allows you tunnel the TCP communication through these proxies.
External HTTP proxy module wraps the TCP communication inside HTTP, which is sent through the proxy. Repeating the packets is also supported as long as the connection is alive, so Burp Intruder/Repeater and Zaproxy Requester/Fuzzer can also be used for the TCP communication.
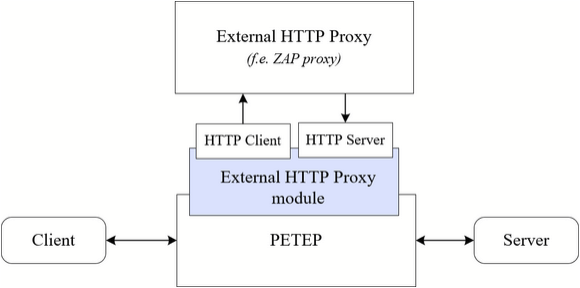
For more information, see User Guide - External HTTP Proxy.
Note: If you only want to use PETEP as the tunnel for sending the TCP through HTTP proxies,
I would recommend setting it up in GUI mode and then running it in NO-GUI mode (PETEP [project_path] --nogui).
SSL/TLS, STARTTLS proxy support
PETEP supports TCP proxy with SSL/TLS and STARTTLS. In order to use these, you have to provide certificate,
since the application does not generate it itself. For certificate generation, there are many tools that can be used,
but one of them is part of Java binaries (%JAVA_HOME%/bin/keytool).
To generate a certificate in JKS keystore, you can use the following command:
keytool -genkey -alias petep -keyalg RSA -validity 3650 -keysize 4096 -keystore server.jks
Note: It is recommended to store these certificates alongside the project (project_dir/conf/server.jks)
Guides/Tutorials
There are three different guides that will help you use PETEP to its full potential:
- User Guide - explanation of PETEP components for basic users
- Methodology - methodology with example usage (with video example)
- Development Guide - guide for extending PETEP using own Java extensions (to support custom protocols or create custom modules for traffic interception)
Extensibility
It is possible to develop extensions using Java to implement support for new protocols and/or to implement new functionality for intercepting the communication (including graphical user interface).
For more information about extension development, please see Dev Guide.
Screenshots
Repeater
Tagger
Modifier
Proxy Settings
License
PETEP is licensed under GNU GPL 3.0.




