Awesome
CHEAT
CHEAT stands for C Header Embedded Automated Testing or something like that. It is a convenient unit testing framework for the C programming language. It has no dependencies and requires no installation or configuration. Only a header file and a test case is needed.
#include <cheat.h>
CHEAT_TEST(mathematics_still_work,
cheat_assert(2 + 2 == 4);
cheat_assert_not(2 + 2 == 5);
)
The following section presents the basic use case; you can skip to section 2 if you are only looking for an overview.
1 Getting Started
In this introduction it is assumed that you are running a Linux system with the GNU Core Utilities and the GNU Compiler Collection installed. None of that is necessary, but it makes the introduction easier to follow. Compatibility with other tools and operating systems is addressed in section 4.
1.1 Preparing
First you need to download the main header
[user@computer:~]$ wget http://github.com/Tuplanolla/cheat/raw/1.0.4/cheat.h
and move it to a suitable location like the global search path
[user@computer:~]$ sudo mv -i cheat.h /usr/include
or the working directory of your project.
[user@computer:~]$ mv -i cheat.h project
Then you are ready to write tests.
1.2 Writing Tests
Tests go into their own source file.
[user@computer:~/project]$ cat > tests.c
#include <cheat.h>
It is an ordinary file with the exception that it is processed more than once. Therefore you must wrap all top level declarations and definitions with the appropriate preprocessor directives. The reason for that is found in section 2.3.
Including the main header is enough to get an empty test suite, but
such a thing is not very useful beyond making sure everything is set up right.
The next step is to define tests.
You can define tests with CHEAT_TEST(name, statements) and
their success conditions called assertions with cheat_assert(bool expected).
Doing so is demonstrated in the example file.
[user@computer:~/project]$ wget http://github.com/Tuplanolla/cheat/raw/1.0.4/example.c
[user@computer:~/project]$ mv -i example.c tests.c
The example also shows how you can declare global variables with
CHEAT_DECLARE(declarations) and manage them with
CHEAT_SET_UP(statements) and CHEAT_TEAR_DOWN(statements), which
are executed before and after each test respectively.
A detailed explanation of the entire interface is in section 3.2. However it is important to note that the state of all global variables that are mutable (as in modified by any execution path) is undefined when the set up or, in case there is no set up, a test begins.
It is time to run your new tests.
1.3 Running Tests
Tests compile into an executable
[user@computer:~/project]$ gcc -I . -o tests tests.c
that takes care of running the tests and reporting their outcomes.
There are two things that need to be taken care of when compiling a test suite.
First you have to add the directory of the test suite to the search path, as
is done here with -I ..
Then you have to make __BASE_FILE__ point to the test suite, by
using -D __BASE_FILE__=\"tests.c\" or such, if the compiler does not.
The reason is related to the previous oddity and again found in section 2.3.
The resulting executable runs tests in a security harness if possible, so the suite does not crash or hang if one of its tests does.
[user@computer:~/project]$ ./tests
..:..??..!..
---
tests.c:81: assertion in 'philosophy_never_worked' failed: 'heap == stack'
tests.c:104: assertion in 'important' failed: 'THIS_TEST == IMPORTANT_TEST'
---
8 successful and 2 failed of 12 run
FAILURE
The results are reported in five parts.
The first part is the progress bar, where
- a success is a green dot,
- a failure is a red colon,
- a crash is a red exclamation mark,
- a time out is a yellow exclamation mark and
- an ignored outcome is signaled with a yellow question mark.
The second part contains diagnostic messages in a format similar to what many popular C compilers produce.
The third and fourth parts, which are omitted here, hold the contents of the captured standard output and error streams.
The fifth and last part, which is always shown, briefly summarizes what the outcome of the test suite is. A test suite is considered successful if and only if every single one of its tests completes without failing a single assertion. The outcome is also reflected by the exit code of the process.
[user@computer:~/project]$ echo returned $?
returned 1
You can change the behavior of the test suite with command line options or force running individual tests by giving their names as arguments.
[user@computer:~/project]$ ./tests --list --minimal | xargs ./tests
..:..:.:..!..
---
example.c:81: assertion in 'philosophy_never_worked' failed: 'heap == stack'
example.c:104: assertion in 'important' failed: 'THIS_TEST == IMPORTANT_TEST'
example.c:112: assertion in 'pointless' failed: '(0 | ~0) == 0'
---
9 successful and 4 failed of 13 run
FAILURE
The option syntax is specified in section 3.3.
1.4 Using Extensions
There is an extension header in addition to the main header.
[user@computer:~/project]$ wget http://github.com/Tuplanolla/cheat/raw/1.0.4/cheats.h
It is supposed to be used as a supplement and expects the main header to be included first.
[user@computer:~/project]$ cat > tests.c
#include <cheat.h>
#include <cheats.h>
It provides specialized assertions like
cheat_assert_double(double actual, double expected, double tolerance) and
cheat_assert_string(char const* actual, char const* expected) for
they require less typing and provide more detailed diagnostic messages.
Its features are demonstrated in the additional example file.
[user@computer:~/project]$ wget http://github.com/Tuplanolla/cheat/raw/1.0.4/examples.c
[user@computer:~/project]$ mv -i examples.c tests.c
You can read more about the extensions in section 3.4.
Hopefully you have now gotten started by now.
2 Overview
2.1 License
CHEAT is free software and
as such licensed under the simplified BSD license with two clauses.
The full license can be found in the LICENSE file that
resides in the same directory as this file.
In short, copies and derivative works are permitted as long as
they use the same license.
It would be licensed under the GNU GPL, but
the authors felt that such a decision would hinder its adoption.
2.2 History
The project was started on 2012-08-07 and first released on 2014-08-07. It was originally written by Guillermo "Tordek" Freschi for the entertainment and education of everyone in the ISO/IEC 9899 community on Freenode. The prototype was later picked up by Sampsa "Tuplanolla" Kiiskinen who grew tired of unit testing frameworks that suck and wondered what happened to the one that did not. It was rewritten, stuffed with new features and finally audited in a small scale.
2.3 Implementation
The working principle is best explained by a thought experiment.
Imagine a source file including a header file. Then imagine the header file including the source file that included it. Now imagine doing that three times in a row within the same header file. Proceed to imagine redefining all of the identifiers each time. Finally imagine doing all of that with preprocessor directives. What you ended up with is CHEAT.
It sounds strange, but it works.
2.4 Correctness
Everything in the project is built with extreme care and attention to detail. While the authors are quite confident the project is free of serious bugs, they are mere mortals and not well versed in certified programming.
2.5 Contributing
The support for Windows and other more exotic operating systems is not complete. For example stream capturing is currently very limited without POSIX interfaces.
Contributions in the forms of feedback and pull requests are all very welcome!
3 Usage
3.1 Files
The project contains other useful files in addition to the main header. You can acquire them by cloning the repository
[user@computer:~]$ git clone git@github.com:Tuplanolla/cheat.git
[user@computer:~]$ cd cheat
or downloading the clone directly.
[user@computer:~]$ wget http://github.com/Tuplanolla/cheat/archive/1.0.4.zip
[user@computer:~]$ unzip 1.0.4.zip
[user@computer:~]$ mv -i cheat-1.0.4 cheat
[user@computer:~]$ cd cheat
In addition to the main header there is an extension header and examples of how to use them with various compilers.
[user@computer:~/cheat]$ less example.c examples.c
[user@computer:~/cheat]$ make -f makefile.gcc
The extensions are introduced in section 3.4.
There are also tests for corner cases,
[user@computer:~/cheat]$ ls tests
[user@computer:~/cheat]$ ./test
supplementary reading material
[user@computer:~/cheat]$ man ./cheat.7
[user@computer:~/cheat]$ sudo cp -i cheat.7 /usr/man/man7
[user@computer:~/cheat]$ sudo gzip /usr/man/man7/cheat.7
and things used during development.
[user@computer:~/cheat]$ xdot streams.dot
[user@computer:~/cheat]$ tcc -run meta.c 4
[user@computer:~/cheat]$ rm -i windowed.h
3.2 Interface
Tests can be defined with CHEAT_TEST(name, statements), where
name must be a valid identifier and statements a list of statements.
The identifier must not conflict with an existing preprocessor directive.
For example putc is not a valid identifier, because
it is reserved by the standard library and
exit and write may not be valid unless CHEAT_NO_WRAP is defined, because
procedures that resemble continuations or effects are wrapped by default.
The list of statements must not be empty or ambiguous.
For example int x, y; may be interpreted as an invalid parameter list if
the compiler does not support __VA_ARGS__.
Solutions to that are presented in section 5.5.
Tests can also be defined with
CHEAT_IGNORE(name, statements) and CHEAT_SKIP(name, statements).
They work like CHEAT_TEST(name, statements) with the exception that
the outcome of the former is ignored and the latter is not executed at all, but
only when they are not explicitly requested to be run.
That feature is explained in section 3.3.
Repeated tests can be defined with CHEAT_REPEAT(name, statements), which
is otherwise identical with CHEAT_TEST(name, statements), but
the statement list is repeated until a failure or
CHEAT_REPETITIONS is reached.
Its purpose is to make working with stochastic tests less of a hassle.
Manually interrupting tests that have already failed can be achieved by
calling cheat_yield(void) in the appropriate place.
It must not be used outside test cases or compatible procedures, because
it can only alter the control flow of the procedure it is called from.
Here compatible procedures mean procedures that have the same type as
CHEAT_GET(name) for any valid name.
Tests need success conditions called assertions and
those can be checked with cheat_assert(bool expected) or
its logical complement cheat_assert_not(bool unexpected).
The condition is satisfied if expected is true or, in other words, not zero.
In addition to tests it is possible to write global declarations by
putting them inside CHEAT_DECLARE(declarations), where
declarations must be a valid list of top level declarations or definitions.
Preprocessor directives do not need it since
an #ifndef condition works similarly.
Global definitions can also contain assertions and be called from within tests.
Running code before and after each test can be done with
CHEAT_SET_UP(statements) and CHEAT_TEAR_DOWN(statements), where
statements is a list of statements with the same restrictions as before.
There can be only one set up and one tear down in a test suite.
The names given to tests are not directly used identifiers, but
the identifier of a test can be retrieved with CHEAT_GET(name), where
name must match the name of the test.
Pointers to test procedures have the type cheat_procedure or
equivalently void (*)(void).
The convenient CHEAT_CALL(name) is equivalent to CHEAT_GET(name)().
The behavior of the test suite is primarly controlled with command line options. However some of the options are compiled into the test suite and their default values can be overridden by defining them before including the main header.
The size_t CHEAT_REPETITIONS option controls the amount of
repetitions done by CHEAT_REPEAT(name, statements).
Its default value is 256.
The size_t CHEAT_LIMIT option determines how long string literals in
diagnostic messages can be.
Its valid values go from 3 to SIZE_MAX - 1 and
the default is the maximum length of a string literal required by the standard.
The CHEAT_TIME option sets the maximum time after which
unresponsive tests are terminated if such a thing is possible.
It is always stored in milliseconds, but its type is implementation defined.
The default value is two thousand and therefore equal to two seconds.
The int CHEAT_OFFSET option changes the range of
exit codes used for internal interprocess communication.
The only reason it exists is to stop serious crashes that
use reserved error numbers from showing up with the wrong outcome.
The CHEAT_NO_MAIN option removes the main procedure from the test suite,
making it possible to link it with other object files.
It is not very useful.
The CHEAT_NO_WRAP option prevents wrapping procedures that
resemble continuations or effects.
Such procedures include exit, printf, fwrite, fflush and perror.
It is only useful if the tests rely on
the exact way they call standard library and system procedures or
their names clash with existing preprocessor directives.
Wrapping can be undone with CHEAT_UNWRAP(name) instead of turning it off or
repeated with CHEAT_WRAP(name) if it is already turned off.
The expansion of commas can be delayed with CHEAT_COMMAS(...) or,
in case __VA_ARGS__ is not available, with CHEAT_COMMA or
the matching CHEAT_COMMAS_ n (x1, x2, ... ), where
n is the amount of commas in the argument list.
For example CHEAT_COMMAS(int x, y;), int x CHEAT_COMMA y; and
CHEAT_COMMAS_1(int x, y;) all expand to int x, y;.
3.3 Options
Test suites obey a basic set of command line options so that they do not need to be recompiled after every change. There are options and names with slightly different semantics.
Options begin with a dash.
They are parameterless, essentially orderless and case insensitive.
Each of them has a long and a short form that work identically.
Everything else is considered a name.
Since names might start with a dash, there is a special -- option that
disables parsing and so turns the arguments that come after it into names.
For example the command ./tests -e x --plain -- -ed would
treat x and -ed as a names and the rest as options.
It is safe to use wrong or conflicting options, because they are checked before anything else is done.
The -h for --help option briefly summarizes all of the options.
The -v for --version option prints the name of the project and its version.
The -l for --list option lists the names of all of the tests.
The -s for --safe option enables a security harness that
runs tests in isolated processes if fork() or CreateProcess() is supported.
The -d for --dangerous option provides an alternative harness that
runs everything in the same process, but provides some stability by
attempting to recover from fatal signals like SIGFPE and SIGSEGV.
It most likely leads to undefined behavior, but
luckily undefined behavior is often defined enough behavior.
The -u for --unsafe option disables all security measures.
The -t for --timed option enables terminating unresponsive processes and
the -e for --eternal option disables doing so.
The -n for --noisy option enables capturing and displaying the contents of
the standard streams and the -q for --quiet option enables them.
As an added bonus the -c for --colorful option makes everything colorful if
the output terminal has ISO/IEC 6429 escape sequence support,
the -m for --minimal option makes those things machine readable and
the -x for --xml option does nothing for good measure.
The default options depend on the target platform.
3.4 Extensions
Specialized assertions can be checked with
the matching cheat_assert_ i ( t actual, t expected), where
t is its type and i is an identifier built from the type.
The CHEAT_NO_MATH option disables floating point extensions that
use a few mathematical functions and
therefore may require compiling the test suite with -lm to link libm.
3.5 Design Decisions
Empty tests and test suites are both have successful outcomes, because every predicate is true for the empty set, so why not choose favorably?
4 Portability
4.1 Standards Compliance
CHEAT follows the original language specification, ANSI X3.159-1989 or ISO/IEC 9899:1990, and the first POSIX specification, IEEE Std 1003.1-1988, to the letter. It also takes the newer revisions, both ISO/IEC 9899:1999 and IEEE Std 1003.1-2001, into account whenever possible.
The project does not require a POSIX system to work, but it helps, because only the most critical features are universal and just a few of the rest are compatible with Windows.
While the project does not rely on a particular compiler, it is easier to use with some of them. Specialized build automation scripts are provided to help hammer out common problems and save you from needless frustration.
[user@computer:~/cheat]$ make -f makefile.gcc
computer# make -f makefile.tcc
E:\CHEAT> makefile.bat
You can see screenshots of them in section 6.
4.2 Language Compatibility
The project is designed for C, but also works with C++. It abides by ISO/IEC 14882:1998 as far as is reasonable.
Hopefully it is not an issue to wade through a million warnings.
[user@computer:~/cheat]$ make -e CC=g++ -f makefile.gcc
5 Bugs and Limitations
CHEAT is naturally fickle, because it is built with heavy preprocessor abuse. Some problems are impossible to fix, so they are collected into this section.
5.1 Identifiers
Identifiers starting with CHEAT_ and cheat_ are reserved for
internal use as C does not have namespaces.
Extensions reserve identifiers starting with CHEATS_ and cheats_ as well.
5.2 Base File
If the compiler does not define __BASE_FILE__, then
the test suite will fail to compile.
Luckily it can be to set to __FILE__ at the beginning of the test suite
#ifndef __BASE_FILE__
#define __BASE_FILE__ __FILE__
#endif
or defined manually.
5.3 Commas
Using commas directly inside preprocessor directives like
CHEAT_TEST(name, statements) without support for __VA_ARGS__ causes
everything that comes after them to be interpreted as extra arguments.
The solution is to delay the expansion of the commas as described in section 3.2.
5.4 Expressions
The expressions given to cheat_assert(bool expected) and friends should be
at most 509 characters long since they are converted into string literals and
the limit of their length may be that low.
5.5 Broken Compiler
If the compiler works like Microsoft C/C++ (commonly known as cl.exe) and
defines both __BASE_FILE__ and __FILE__ wrong, then
the test suite will be empty.
The definition should be fed to the compiler manually.
5.6 Debugging
It is not possible to attach a breakpoint to any of the identifiers that are part of the public interface, because they are all preprocessor directives.
Attaching one to CHEAT_GET(name) or cheat_check() should work instead.
5.7 Printing
Streams are captured by default, so it is not possible to print things on the screen while the tests are running.
However using the CHEAT_NO_WRAP option with
the --dangerous option allows bypassing stream capturing.
6 Screenshots
Everyone likes pretty pictures.
Here is a picture of CHEAT being compiled with the GNU Compiler Collection and run in the Xfce terminal emulator that is provided by a Linux distribution.
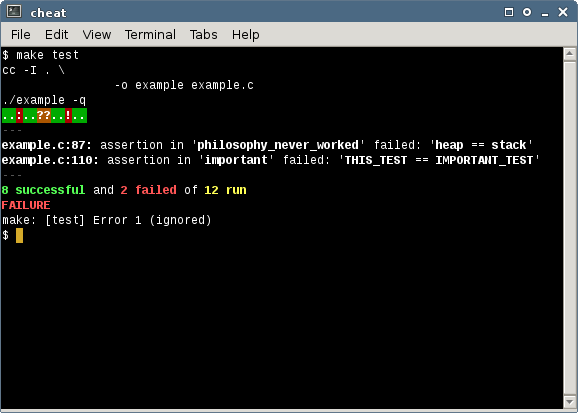
Here is a picture of CHEAT being compiled with Microsoft C/C++ and run in the command prompt of Windows XP.
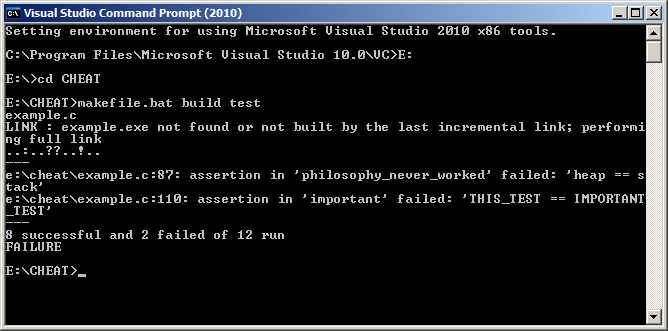
Here is a picture of CHEAT being compiled with Borland Turbo C and run in the default shell of FreeDOS.
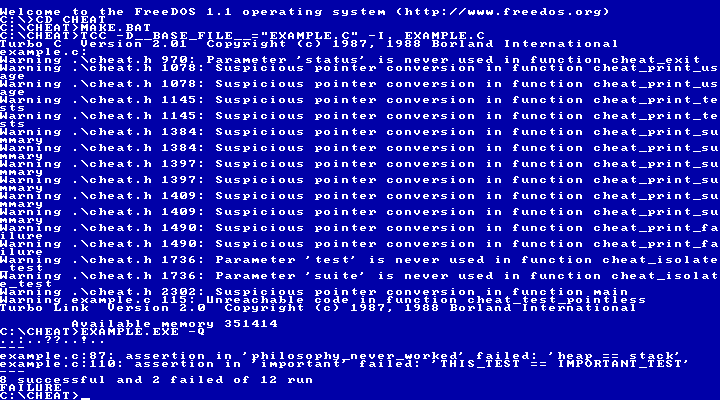
7 Reference
7.1 Main Header
CHEAT_TEST(name, statements)defines a testCHEAT_IGNORE(name, statements)defines a test that does not matterCHEAT_SKIP(name, statements)defines a test that is not runCHEAT_REPEAT(name, statements)defines a test that is repeated several times
cheat_yield(void)interrupts a test if it has already failed
cheat_assert(bool expected)checks a success conditioncheat_assert_not(bool unexpected)checks the opposite of a success condition
CHEAT_DECLARE(declarations)creates global declarations and definitions
CHEAT_SET_UP(statements)defines what to do before every testCHEAT_TEAR_DOWN(statements)defines what to do after every test
CHEAT_GET(name)returns a test procedureCHEAT_CALL(name)calls a test procedure
size_t CHEAT_REPETITIONScontrols the amount of repetitionssize_t CHEAT_LIMITdetermines the maximum length of string literalsCHEAT_TIMEsets the time after which unresponsive tests are terminatedint CHEAT_OFFSETchanges the range of internal exit codesCHEAT_NO_MAINdoes not compilemain()CHEAT_NO_WRAPdisables wrapping certain proceduresCHEAT_UNWRAP(name)returns an unwrapped procedureCHEAT_WRAP(name)returns a wrapped procedureCHEAT_COMMAexpands to a commaCHEAT_COMMAS(...)separates its arguments with commasCHEAT_COMMAS_1(x1, x2)separates its arguments with commas
CHEAT_BEGINandCHEAT_ENDturn a preprocessor directive into a statementtype CHEAT_CAST(type, expression)casts pointer types when using C++size_t CHEAT_INTEGER_LENGTH(type)returns the string length of an integer
size_t CHEAT_PASSdetermines the internal state of preprocessing
CHEAT_Hguards the main header
7.2 Command Line
-hor--helpshows this help-vor--versionprints version information-lor--listlists test cases
-sor--saferuns tests in isolated subprocesses-dor--dangerouspretends that crashing tests do nothing harmful-uor--unsafelets crashing tests bring down the test suite
-tor--timedterminates isolated tests that take too long-eor--eternalallows isolated tests to take their time
-nor--noisycaptures and displays standard streams-qor--quietdoes not capture standard streams
-cor--colorfuluses ISO/IEC 6429 escape codes to color text-mor--minimalreports things in a machine readable format-por--plainpresents everything in plain text
7.3 Extension Header
cheat_assert_char(char actual, char expected)checks a specialized success conditioncheat_assert_not_char(char actual, char unexpected)checks the opposite of a specialized success condition
cheat_assert_short_int(short int actual, short int expected)cheat_assert_not_short_int(short int actual, short int unexpected)cheat_assert_short_unsigned_int(short unsigned int actual, short unsigned int expected)cheat_assert_not_short_unsigned_int(short unsigned int actual, short unsigned int unexpected)cheat_assert_int(int actual, int expected)cheat_assert_not_int(int actual, int unexpected)cheat_assert_unsigned_int(unsigned int actual, unsigned int expected)cheat_assert_not_unsigned_int(unsigned int actual, unsigned int unexpected)cheat_assert_long_int(long int actual, long int expected)cheat_assert_not_long_int(long int actual, long int unexpected)cheat_assert_long_unsigned_int(long unsigned int actual, long unsigned int expected)cheat_assert_not_long_unsigned_int(long unsigned int actual, long unsigned int unexpected)
cheat_assert_double(double actual, double expected, double tolerance)cheat_assert_not_double(double actual, double unexpected, double tolerance)
cheat_assert_size(size_t actual, size_t expected)cheat_assert_not_size(size_t actual, size_t unexpected)cheat_assert_ptrdiff(ptrdiff_t actual, ptrdiff_t expected)cheat_assert_not_ptrdiff(ptrdiff_t actual, ptrdiff_t unexpected)
cheat_assert_long_long_int(long long int actual, long long int expected)cheat_assert_not_long_long_int(long long int actual, long long int unexpected)cheat_assert_long_long_unsigned_int(long long unsigned int actual, long long unsigned int expected)cheat_assert_not_long_long_unsigned_int(long long unsigned int actual, long long unsigned int unexpected)
cheat_assert_float(float actual, float expected, float tolerance)cheat_assert_not_float(float actual, float unexpected, float tolerance)
cheat_assert_long_double(long double actual, long double expected, long double tolerance)cheat_assert_not_long_double(long double actual, long double unexpected, long double tolerance)
cheat_assert_int8(int8_t actual, int8_t expected)cheat_assert_not_int8(int8_t actual, int8_t unexpected)cheat_assert_uint8(uint8_t actual, uint8_t expected)cheat_assert_not_uint8(uint8_t actual, uint8_t unexpected)cheat_assert_int16(int16_t actual, int16_t expected)cheat_assert_not_int16(int16_t actual, int16_t unexpected)cheat_assert_uint16(uint16_t actual, uint16_t expected)cheat_assert_not_uint16(uint16_t actual, uint16_t unexpected)cheat_assert_int32(int32_t actual, int32_t expected)cheat_assert_not_int32(int32_t actual, int32_t unexpected)cheat_assert_uint32(uint32_t actual, uint32_t expected)cheat_assert_not_uint32(uint32_t actual, uint32_t unexpected)cheat_assert_int64(int64_t actual, int64_t expected)cheat_assert_not_int64(int64_t actual, int64_t unexpected)cheat_assert_uint64(uint64_t actual, uint64_t expected)cheat_assert_not_uint64(uint64_t actual, uint64_t unexpected)cheat_assert_int_fast8(int_fast8_t actual, int_fast8_t expected)cheat_assert_not_int_fast8(int_fast8_t actual, int_fast8_t unexpected)cheat_assert_uint_fast8(uint_fast8_t actual, uint_fast8_t expected)cheat_assert_not_uint_fast8(uint_fast8_t actual, uint_fast8_t unexpected)cheat_assert_int_fast16(int_fast16_t actual, int_fast16_t expected)cheat_assert_not_int_fast16(int_fast16_t actual, int_fast16_t unexpected)cheat_assert_uint_fast16(uint_fast16_t actual, uint_fast16_t expected)cheat_assert_not_uint_fast16(uint_fast16_t actual, uint_fast16_t unexpected)cheat_assert_int_fast32(int_fast32_t actual, int_fast32_t expected)cheat_assert_not_int_fast32(int_fast32_t actual, int_fast32_t unexpected)cheat_assert_uint_fast32(uint_fast32_t actual, uint_fast32_t expected)cheat_assert_not_uint_fast32(uint_fast32_t actual, uint_fast32_t unexpected)cheat_assert_int_fast64(int_fast64_t actual, int_fast64_t expected)cheat_assert_not_int_fast64(int_fast64_t actual, int_fast64_t unexpected)cheat_assert_uint_fast64(uint_fast64_t actual, uint_fast64_t expected)cheat_assert_not_uint_fast64(uint_fast64_t actual, uint_fast64_t unexpected)cheat_assert_int_least8(int_least8_t actual, int_least8_t expected)cheat_assert_not_int_least8(int_least8_t actual, int_least8_t unexpected)cheat_assert_uint_least8(uint_least8_t actual, uint_least8_t expected)cheat_assert_not_uint_least8(uint_least8_t actual, uint_least8_t unexpected)cheat_assert_int_least16(int_least16_t actual, int_least16_t expected)cheat_assert_not_int_least16(int_least16_t actual, int_least16_t unexpected)cheat_assert_uint_least16(uint_least16_t actual, uint_least16_t expected)cheat_assert_not_uint_least16(uint_least16_t actual, uint_least16_t unexpected)cheat_assert_int_least32(int_least32_t actual, int_least32_t expected)cheat_assert_not_int_least32(int_least32_t actual, int_least32_t unexpected)cheat_assert_uint_least32(uint_least32_t actual, uint_least32_t expected)cheat_assert_not_uint_least32(uint_least32_t actual, uint_least32_t unexpected)cheat_assert_int_least64(int_least64_t actual, int_least64_t expected)cheat_assert_not_int_least64(int_least64_t actual, int_least64_t unexpected)cheat_assert_uint_least64(uint_least64_t actual, uint_least64_t expected)cheat_assert_not_uint_least64(uint_least64_t actual, uint_least64_t unexpected)cheat_assert_intmax(intmax_t actual, intmax_t expected)cheat_assert_not_intmax(intmax_t actual, intmax_t unexpected)cheat_assert_uintmax(uintmax_t actual, uintmax_t expected)cheat_assert_not_uintmax(uintmax_t actual, uintmax_t unexpected)cheat_assert_intptr(intptr_t actual, intptr_t expected)cheat_assert_not_intptr(intptr_t actual, intptr_t unexpected)cheat_assert_uintptr(uintptr_t actual, uintptr_t expected)cheat_assert_not_uintptr(uintptr_t actual, uintptr_t unexpected)
cheat_assert_float_complex(float complex actual, float complex expected, float tolerance)cheat_assert_not_float_complex(float complex actual, float complex unexpected, float tolerance)cheat_assert_double_complex(double complex actual, double complex expected, double tolerance)cheat_assert_not_double_complex(double complex actual, double complex unexpected, double tolerance)cheat_assert_long_double_complex(long double complex actual, long double complex expected, long double tolerance)cheat_assert_not_long_double_complex(long double complex actual, long double complex unexpected, long double tolerance)
cheat_assert_signed_char(signed char actual, signed char expected)cheat_assert_not_signed_char(signed char actual, signed char unexpected)cheat_assert_unsigned_char(unsigned char actual, unsigned char expected)cheat_assert_not_unsigned_char(unsigned char actual, unsigned char unexpected)
cheat_assert_pointer(void const* actual, void const* expected)cheat_assert_not_pointer(void const* actual, void const* unexpected)
cheat_assert_string(char const* actual, char const* expected)cheat_assert_not_string(char const* actual, char const* expected)
CHEAT_NO_MATHdisables mathematical assertions
CHEATS_Hguards the extension header