Awesome
Rubix Server
Rubix Server is a library for deploying your Rubix ML models to production. Our server wraps your trained estimator in an API that can be queried using standard protocols. Included is a real-time dashboard for monitoring the health and throughput of your models.
- Optimized for low latency predictions
- Scale by adding more instances
- Monitoring with real-time analytics dashboard
- Robust to common threats and failure modes
Installation
Install Rubix Server using Composer:
$ composer require rubix/server
Docker Image
A Docker Image is available for a quick start or deployment.
Requirements
- PHP 7.4 or above
Documentation
The latest documentation can be found in this README.
Table of Contents
Servers
Rubix model servers are stand-alone processes that wrap an estimator in an API that can be queried over a network connection. Since servers implement their own networking stack, they can be run directly from the PHP command line interface (CLI) without the need for an intermediary server such as Nginx or Apache.
To boot up a server, pass a trained estimator instance to the serve() method:
public function serve(Estimator $estimator) : void
use Rubix\Server\HTTPServer;
use Rubix\ML\Classifiers\KNearestNeighbors;
$server = new HTTPServer('127.0.0.1', 8000);
$estimator = new KNearestNeighbors(5);
// Import a dataset
$estimator->train($dataset);
$server->serve($estimator);
Or, you can load a previously trained estimator from storage and serve it like in the example below.
use Rubix\ML\PersistentModel;
use Rubix\ML\Persisters\Filesystem;
$estimator = PersistentModel::load(new Filesystem('example.model'));
$server->serve($estimator);
Note: The server will stay running until the process is terminated. It is a good practice to use a process monitor such as Supervisor to start and autorestart the server in case of a failure.
Shutting Down The Server
To gracefully shut down the server, send a quit signal (SIGQUIT) to the process. To shut down immediately, without waiting for current connections to close, you can either send a terminate (SIGTERM) or interrupt (SIGINT) signal.
Note: Signal handling does not work in Windows environments.
For example, to shut down gracefully, first identify the server's process ID (PID) and then send the QUIT signal to it.
$ kill -s QUIT 1234
Verbose Interface
Servers that implement the Verbose interface accept any PSR-3 compatible logger instance and begin logging critical information such as errors and start/stop events. To set a logger pass the PSR-3 logger instance to the setLogger() method on the server instance.
use Rubix\Server\Loggers\File;
$server->setLogger(new File('example.log'));
HTTP Server
A JSON over HTTP server exposing Representational State Transfer (REST) and GraphQL APIs. The HTTP Server operates using ubiquitous standards making it compatible with a wide range of systems. In addition, it provides its own web-based user interface for real-time server monitoring.
Parameters
| # | Param | Default | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | host | '127.0.0.1' | string | The host address to bind the server to. Use '0.0.0.0' to bind to all interfaces. |
| 2 | port | 8000 | int | The network port to run the HTTP services on. |
| 3 | cert | null | string | The path to the certificate used to authenticate and encrypt the HTTP channel. |
| 4 | middlewares | [] | array | The stack of server middleware to run on each request/response. |
| 5 | max concurrent requests | 10 | int | The maximum number of requests that can be handled concurrently. |
| 6 | static assets cache | InMemoryCache | Cache | The cache used to serve static asset requests. |
| 7 | sse reconnect buffer | 50 | int | The maximum number of events to store in the server-sent events (SSE) reconnect buffer. |
PHP INI Configuration
| Name | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| memory_limit | 128M | The maximum amount of memory the server is allowed to consume. |
| post_max_size | 8M | The maximum size of a request body the server can buffer. |
Example
use Rubix\Server\HTTPServer;
use Rubix\Server\HTTP\Middleware\\AccessLogGenerator;
use Rubix\Server\Loggers\File;
use Rubix\Server\HTTP\Middleware\\BasicAuthenticator;
use Rubix\Server\Services\Caches\InMemoryCache;
$server = new HTTPServer('127.0.0.1', 443, '/cert.pem', [
new AccessLogGenerator(new File('access.log')),
new BasicAuthenticator([
'morgan' => 'secret',
'taylor' => 'secret',
]),
], 50, new InMemoryCache(86400), 100);
Routes
The HTTP server exposes the following resources and their methods.
| Method | URI | Description |
|---|---|---|
| GET | /ui | The web user interface. |
| GET | /ui/dashboard | The server dashboard interface. |
| GET | /model | Return the properties of the model. |
| POST | /model/predictions | Make a set of predictions on a dataset. |
| POST | /model/probabilities | Return the joint probabilities of each sample in a dataset. |
| POST | /model/anomaly-scores | Return the anomaly scores of each sample in a dataset. |
| GET | /server | Return the properties of the server. |
| GET | /dashboard/events | Subscribe to the dashboard events stream. |
| POST | /graphql | Query the server using GraphQL. |
Server Analytics
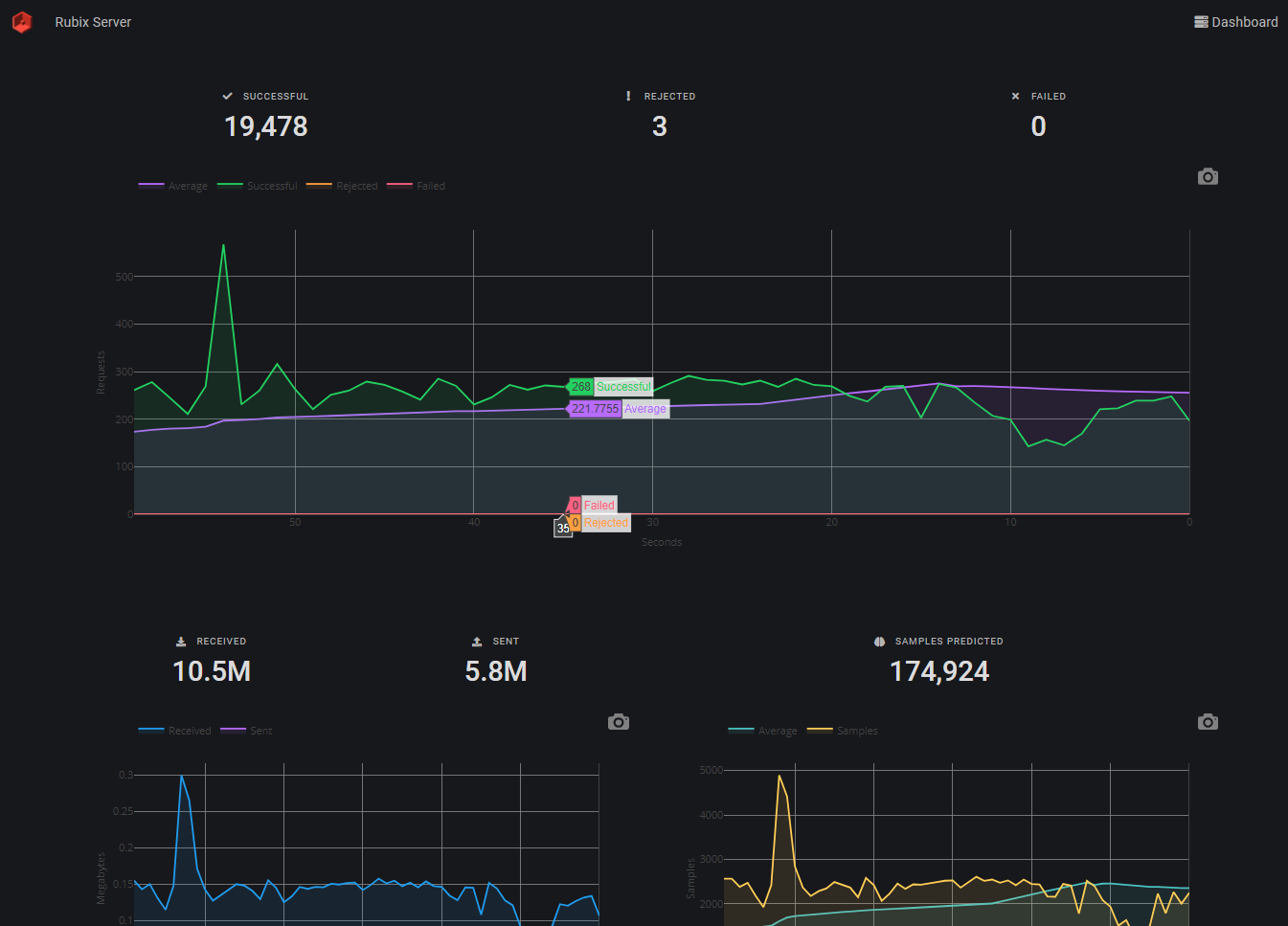
The HTTP server provides its own high-level user interface (UI) to the GraphQL API it exposes under the hood offering features such as server monitoring and traffic visualization. To access the web interface, navigate to http://hostname:port/ui (or https://hostname:port/ui if using a secure socket connection) using your favorite modern web browser.
The example below is a screen capture of the server dashboard in dark mode.
References
- R. Fielding et al. (2014). Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP/1.1): Semantics and Content.
Server Middleware
HTTP middleware are processors of the incoming HTTP requests and outgoing responses produced by the request handler (or Controller). They allow the user to hook into the HTTP request/response cycle by inserting additional logic into the pipeline.
Access Log Generator
Generates an HTTP access log using a format similar to the Apache log format.
Parameters
| # | Param | Default | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | logger | LoggerInterface | A PSR-3 logger instance. |
Example
use Rubix\Server\HTTP\Middleware\\AccessLog;
use Rubix\Server\Loggers\File;
$middleware = new AccessLog(new File('access.log'));
[2020-11-04 23:10:57] INFO: 127.0.0.1 "POST /predictions HTTP/1.1" 200 140 - "Rubix ML REST Client/0.2.3"
[2020-11-04 23:11:54] INFO: 127.0.0.1 "POST /predictions/sample HTTP/1.1" 200 96 - "Rubix ML REST Client/0.2.3"
Basic Authenticator
An implementation of HTTP Basic Auth as described in RFC7617.
Note: This authorization strategy is only secure to man-in-the-middle attacks over HTTPS.
Parameters
| # | Param | Default | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | passwords | array | An associative map from usernames to their passwords. | |
| 2 | realm | 'auth' | string | The unique name given to the scope of permissions required for this server. |
Example
use Rubix\Server\HTTP\Middleware\\BasicAuthenticator;
$middleware = new BasicAuthenticator([
'morgan' => 'secret',
'taylor' => 'secret',
], 'ml models');
Shared Token Authenticator
Authenticates incoming requests using a shared key that is kept secret between the client and server. It uses the Authorization header with the Bearer prefix to indicate the shared key.
Note: This authorization strategy is only secure to man-in-the-middle attacks over HTTPS.
Parameters
| # | Param | Default | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | tokens | array | The shared secret keys (bearer tokens) used to authorize requests. | |
| 2 | realm | 'auth' | string | The unique name given to the scope of permissions required for this server. |
Example
use Rubix\Server\HTTP\Middleware\\SharedTokenAuthenticator;
$middleware = new SharedTokenAuthenticator([
'secret', 'another-secret',
], 'ml models');
Trusted Clients
A whitelist of clients that can access the server - all other connections will be dropped.
Parameters
| # | Param | Default | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ips | ['127.0.0.1'] | array | An array of trusted client ip addresses. |
Example
use Rubix\Server\HTTP\Middleware\\TrustedClients;
$middleware = new TrustedClients([
'127.0.0.1', '192.168.4.1', '45.63.67.15',
]);
Loggers
PSR-3 compatible loggers for capturing important server events.
File
A simple append-only file logger.
Parameters
| # | Name | Default | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | path | string | The path to the append-only log file. A new file will be created if it doesn't exist yet. | |
| 2 | channel | '' | string | The channel name that appears on each line. |
| 3 | timestampFormat | 'Y-m-d H:i:s' | string | The format of the timestamp. |
Example
use Rubix\Server\Loggers\File;
$logger = new File('server.log', 'example', 'Y-m-d H:i:s');
FAQs
Here you will find answers to the most frequently asked questions.
How do I run the server?
All model servers are designed to be run from the PHP command line interface (CLI). Model servers are long-running asynchronous processes that handle concurrent requests and implement their own networking stack avoiding the need for a third-party web server such as Nginx or Apache.
To run the server, you can execute your script containing the server code by entering the following on the command line.
$ php server.php
Can I run the model server on the same host as a regular web server?
Yes, model server are designed to coexist with other web servers (including other model servers) seamlessly. Just make sure that each server runs on its own unique port.
How do I scale inference throughput?
Since model servers are inference-only (i.e. they only support queries), they scale horizontally by adding more instances behind a load balancer such as Nginx.
Do servers support compression?
Yes, the HTTP Server supports both Gzip and Deflate compression schemes applied to the request bodies and to the response bodies of requests for static assets.
License
The code is licensed MIT and the documentation is licensed CC BY-NC 4.0.