Awesome
ROS-Mobile
ROS-Mobile is an Android application designed for dynamic control and visualization of mobile robotic system operated by the Robot Operating System (ROS). The application uses ROS nodes initializing publisher and subscriber with standard ROS messages. The overall code architecture pattern is Model View ViewModel (MVVM), which stabilizes the application and makes it highly customizable. For a detailed overview of the functionality, we refer to our wiki.
- Current stable Version: 2.0.0
Cite
If you use ROS-Mobile for your research, please cite
<details> <summary>Citation Formats@article{rottmann2020ros,
title={ROS-Mobile: An Android application for the Robot Operating System},
author={Rottmann, Nils and Studt, Nico and Ernst, Floris and Rueckert, Elmar},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2011.02781},
year={2020}
}
Markdown: Rottmann et al., 2020
Plain text: N. Rottmann, N. Studt, F. Ernst, and E. Rueckert. 2020. ROS-Mobile: An Android application for the Robot Operating System. arXiv preprint arXiv:2011.02781.(2020).
Requirements
- Mobile Android Device with Android Version 5.0 (Lollipop) or higher
- Android Studio Version 3.6.1 or higher (if built from source)
Installing Instructions
There are three different ways for installing ROS-Mobile onto your mobile device: Built from source, install current apk, download from Google Playstore. We highly recommend to use the download function from the Google Playstore.
Built from Source:
- Install Android Studio Version 3.6.1 or higher
- Download the complete repository (Master Branch) and open it via Android Studio
- Built the Code (Make Project Button), connect your mobile device to your PC and install the Software (Run 'app'). Make sure you activated the developer options and adb debugging on your mobile device and installed all required drivers for usb and adb.
Install current APK:
- Download the current ROS-Mobile version as apk file and store it in an easy-to-find location onto your mobile device
- Allow third-party apps on your device. Therefore go to Menu > Settings > Security and check Unknown Sources
- Go now to the apk file, tap it, then hit install
Download from Google Playstore:
- Simply go to the Google Playstore Website of the ROS-Mobile app and download it. It will be installed automatically
Introduction Video
Currently available ROS Nodes
The following Nodes are currently supported by ROS-Mobile. For a comprehensive overview over the functionality of each node have a look into Nodes Description in the wiki. Additional Nodes will be available in upcoming Versions or can be easily added independently. See the How to add your own Nodes section in the wiki.
-
Debug (similar to rostopic echo)
-
Joystick (geometry_msgs/Twist)
-
GridMap (nav_msgs/OccupancyGrid)
-
Camera (sensor_msgs/Image, sensor_msgs/CompressedImage)
-
GPS (sensor_msgs/NavSatFix)
-
Button (std_msgs/Bool)
-
Logger (std_msgs/String)
Short Example Usage
 |  |
|---|---|
 |  |
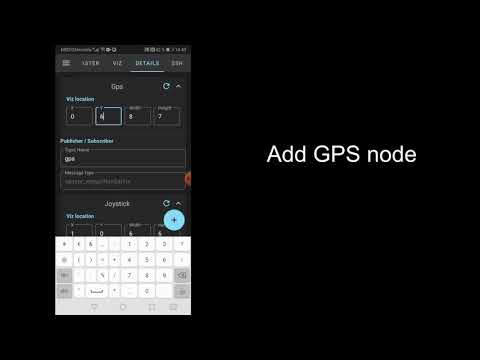
Manually map an apartment environment using a differential drive robot. Therefore, we connected the application with the ROS master running the differential drive robot over wireless LAN by inserting the correct IP address in the MASTER configuration tab, first figure. Adding ROS nodes in the DETAILS tab, second figure and third figure, enables the control of the differential drive robot via a joystick method sending geometry_msgs/Twist to a cmd_vel topic and the visualization of the generated occupancy grid map by subscribing to the map topic via a gridmap method. In the VIZ tab, most right figure, the recorded occupancy grid map is displayed as well as the joystick. The joystick can be used via touch for sending control inputs over the cmd_vel topic to the differential drive robot. For a more detailed examples, we refer to our wiki.
License
The MIT License (MIT) Copyright (c) 2020 Nils Rottmann, Nico Studt
Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all copies or substantial portions of the Software.
THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM, OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE SOFTWARE.
Contributor / Maintainer
Main-Developer:
Contributor: