Awesome
Modmobjam
A smart jamming proof of concept for mobile equipments that could be powered with Modmobmap
For more information, this little tool has been presented during SSTIC rump 2018:
- english slides: https://penthertz.com/resources/sstic_rump_2018_modmobjam.pdf
- french presentation: https://static.sstic.org/rumps2018/SSTIC_2018-06-14_P10_RUMPS_22.mp4
Warning
You should be warned that Jamming is illegal and you're responsible for any damages when using it on your own.
Prerequisites
- a radio devices that is enabled to transmit signal (HackRF, USRP, bladeRF, and so on.)
- GNU Radio installed
- Modmobmap to perform automatic smartjamming: https://github.com/PentHertz/Modmobmap
Usage
Manual jamming
If you have a HackRF or any device compatible with osmocom drivers, you can directly run the code provided in GRC/jammer_gen.py as follows:
$ python GRC/jammer_gen.py
Note that compatible devices with gr-osmosdr are the following:
- FunCube Dongle through libgnuradio-fcd
- FUNcube Dongle Pro+ through gr-fcdproplus
- sysmocom OsmoSDR Devices through libosmosdr
- Nuand LLC bladeRF through libbladeRF library
- Great Scott Gadgets HackRF through libhackrf
- Ettus USRP Devices through Ettus UHD library
- Fairwaves UmTRX through Fairwaves' fork of Ettus' UHD library
- RFSPACE SDR-IQ, SDR-IP, NetSDR (incl. X2 option)
- RTL2832U based DVB-T dongles through librtlsdr
- RTL-TCP spectrum server (see librtlsdr project)
- MSi2500 based DVB-T dongles through libmirisdr
- SDRplay RSP through SDRplay API library
- AirSpy R820t dongles through libairspy
For those who want to use another device, edit the GNU Radio block schema GRC/jammer_gen.grc:
$ gnuradio-companion GRC/jammer_gen.grc
Then you can configure the central frequency with the QT GUI to target a frequency. But this tool has also a feature to do it automatically.
Automatic smartjamming
To automate jamming, you can first get a list of we the Modmobmap that saves a JSON file after monitoring surrounding cells in a precise location. This JSON file looks as follows:
$ cat cells_<generated timestamp>.json
{
"****-***50": {
"PCI": "****",
"PLMN": "208-01",
"TAC": "50****",
"band": 3,
"bandwidth": "20MHz",
"eARFCN": 1850,
"type": "4G"
},
"7-***": {
"PLMN": "208-20",
"arfcn": 1018,
"cid": "***",
"type": "2G"
},
"****:-****12": {
"PLMN": "208-1",
"RX": 10712,
"TX": 9762,
"band": 1,
"type": "3G"
},
[...]
}
After generating this file containing cells to jam, you can launch the RPC client that communicate with GRC/jammer_gen.py as follows:
$ python smartjam_rpcclient.py -f cells_<generated timestamp>.json
Then leverage the gain for transmission and you should observe that a lot of noise is overflowing the targeted cells with gaussian noise.
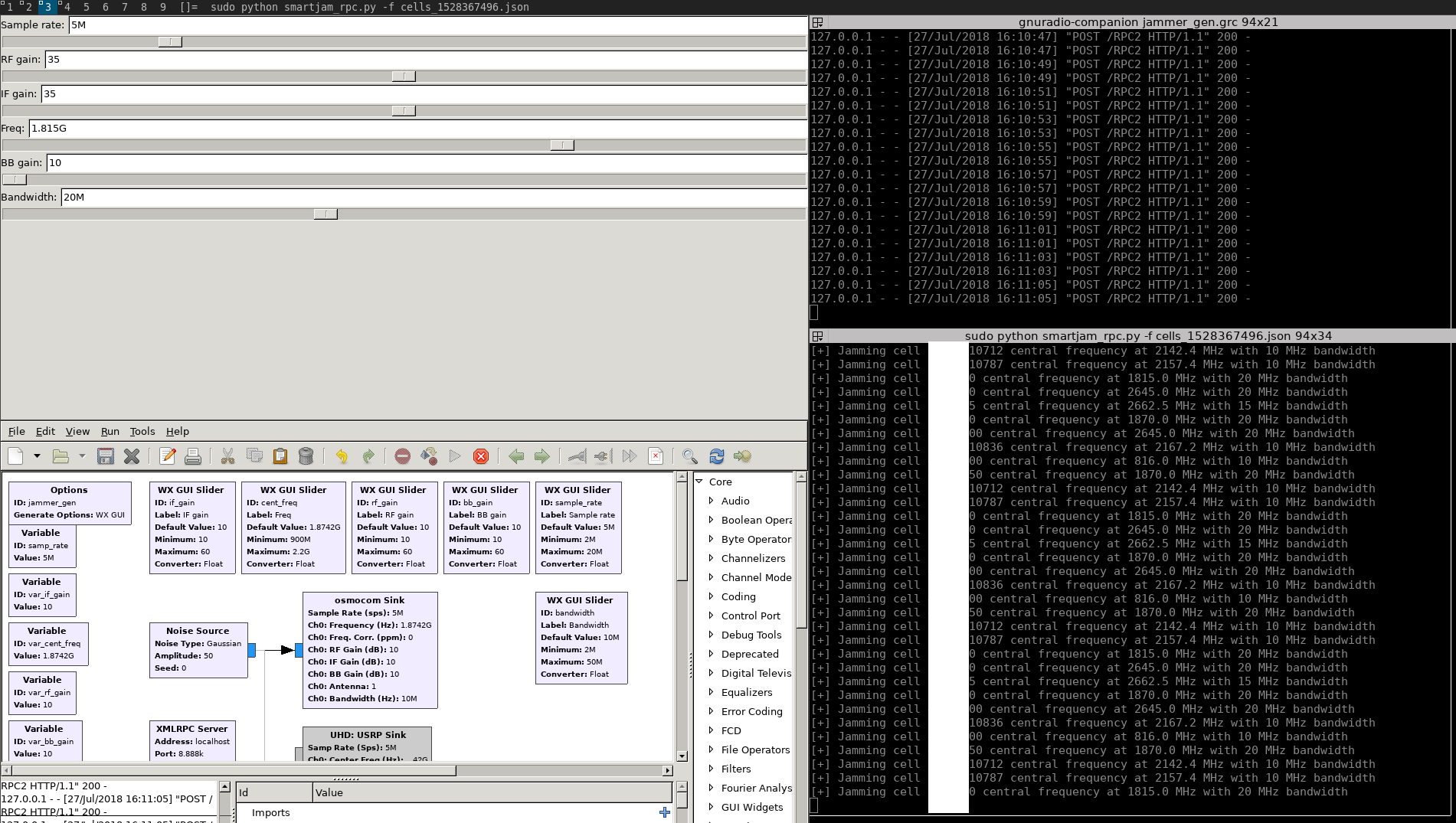
Please note that the delay between each targeted cell can be set with a provided arguments '-d' (see arguments helper).