Awesome
fastv
fastv is an ultra-fast tool for identification of SARS-CoV-2 and other microbes from sequencing data. It detects microbial sequences from FASTQ data, generates JSON reports and visualizes the result in HTML reports. This tool can be used to detect viral infectious diseases, like COVID-19. This tool supports both short reads (Illumina, BGI, etc.) and long reads (ONT, PacBio, etc.)
- Examples
- How it works?
- Understand the input
- Understand the output
- Download or build fastv
- Screenshot
- Options
- Citation
- Tutorials
- ---- mNGS data analysis
- ---- SARS-CoV-2 identification
- ---- influenza A virus subtyping
take a quick glance of the informative report
- Sample HTML report (Illumina): http://opengene.org/fastv/fastv.html
- Sample HTML report (ONT): http://opengene.org/fastv/ont.html
- Sample JSON report: http://opengene.org/fastv/fastv.json
quick example for SARS-CoV-2 identification
- download FASTQ file for testing: http://opengene.org/fastv/testdata.fq.gz
- get fastv and use following command for testing:
# make sure that SARS-CoV-2.kmer.fa and SARS-CoV-2.genomes.fa are in the ./data folder
./fastv -i testdata.fq.gz
how it works?
fastv accepts FASTQ files as input, and then:
- performs data QC and quality filtering as
fastpdoes (cut adapters, remove low quality reads, correct wrong bases). - scans the clean data to collect the sequences that containing any unique k-mer, or can be mapped to any reference microbial genomes.
- makes statistics, visualizes the result in HTML format, and output the results in JSON format.
- outputs the on-target sequencing reads so that they can be analyzed by downstream tools.
understand the input
fastv accepts following files as input:
FASTQfile (required) to be scanned, can be single-end (-i) or paired-end (-iand-I), can be short reads (Illumina, MGI, etc.) or long reads (PacBio, ONT, etc.)genomesfile (optional): a FASTA file containing one or many reference genomes of the target microorganism (-g).k-merfile (optional): a FASTA file containing the UNIQUE k-mer of the target microbial genomes (-k).k-mer collectionfile (optional): a FASTA containing the unique k-mers of many microorganisms (-c). See an example: http://opengene.org/kmer_collection.fasta
If none of (k-mer, k-mer collection, genomes) files is specified, fastv will try to load the SARS-CoV-2 Genomes/k-mer files in the data folder to detect SARS-CoV-2 sequences.
Besides the HTML/JSON reports, fastv also can output the sequence reads that contains any unique k-mer or can be mapped to any of the target reference genomes. The output data:
- is in FASTQ format
- is clean data after quality filtering
- the file names can be specified by
-ofor SE data, or-oand-Ofor PE data.
get the pre-built k-mer file, genomes file or k-mer collection file for viruses
- You can download
k-merfiles andgenomesfiles of viruses from http://opengene.org/uniquekmer/viral/index.html. This is generated by extracting unique k-mers for all genomes in a big FASTA (http://opengene.org/viral.genomic.fasta), which contains all NCBI complete RefSeq release of viral sequences that can be found from https://ftp.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/refseq/release/viral/. The k-mers that can be mapped to human reference genome (GRCh38) withedit_distance <= 3have already been filtered out. - You can download the
k-mer collectionfile for viral genomes from: http://opengene.org/viral.kc.fasta.gz
get the pre-built k-mer file, genomes file or k-mer collection file for viruses and human microorganisms
- You can download
k-merfiles andgenomesfiles of viruses from http://opengene.org/uniquekmer/microbial/index.html. This is generated by extracting unique k-mers for all genomes in a big FASTA (http://opengene.org/microbial.genomic.fasta), which contains genomes for the viruses above and common human microorganisms. The k-mers that can be mapped to human reference genome (GRCh38) withedit_distance <= 3have already been filtered out. - You can download the
k-mer collectionfile for viral and microbial genomes from: http://opengene.org/microbial.kc.fasta.gz - you can get the
k-merfile andgenomesfile for SARS-CoV-2 bygit clone https://github.com/OpenGene/fastv.git. If you don't use git, you can also download these two files from http://opengene.org/fastv/SARS-CoV-2.kmer.fa and http://opengene.org/fastv/SARS-CoV-2.genomes.fa
If you want to generate your own unique k-mer files and k-mer collection files, please use UniqueKMER: https://github.com/OpenGene/UniqueKMER
understand the output
fastv outputs reports in HTML and JSON formats.
- Sample HTML report (Illumina): http://opengene.org/fastv/fastv.html
- Sample JSON report: http://opengene.org/fastv/fastv.json
- If the
k-merfile is specified, there will be aPOSITIVEorNEGATIVEresult, which is determined by comparing the mean depth of the k-mer keys to the threshold (--positive_threshold).
Besides the HTML/JSON reports, fastv also can output the sequence reads that contains any unique k-mer or can be mapped to any of the target reference genomes. The output data:
- is in FASTQ format
- is clean data after quality filtering
- the file names can be specified by
-ofor SE data, or-oand-Ofor PE data.
get fastv
download binary
This binary is only for Linux systems: http://opengene.org/fastv/fastv
# this binary was compiled on CentOS, and tested on CentOS/Ubuntu
wget http://opengene.org/fastv/fastv
chmod a+x ./fastv
or compile from source
# step 1: get the code
git clone https://github.com/OpenGene/fastv.git
# step 2: build
cd fastv
make
# step 3: install it to system if you have a sudo permission
make install
screenshot
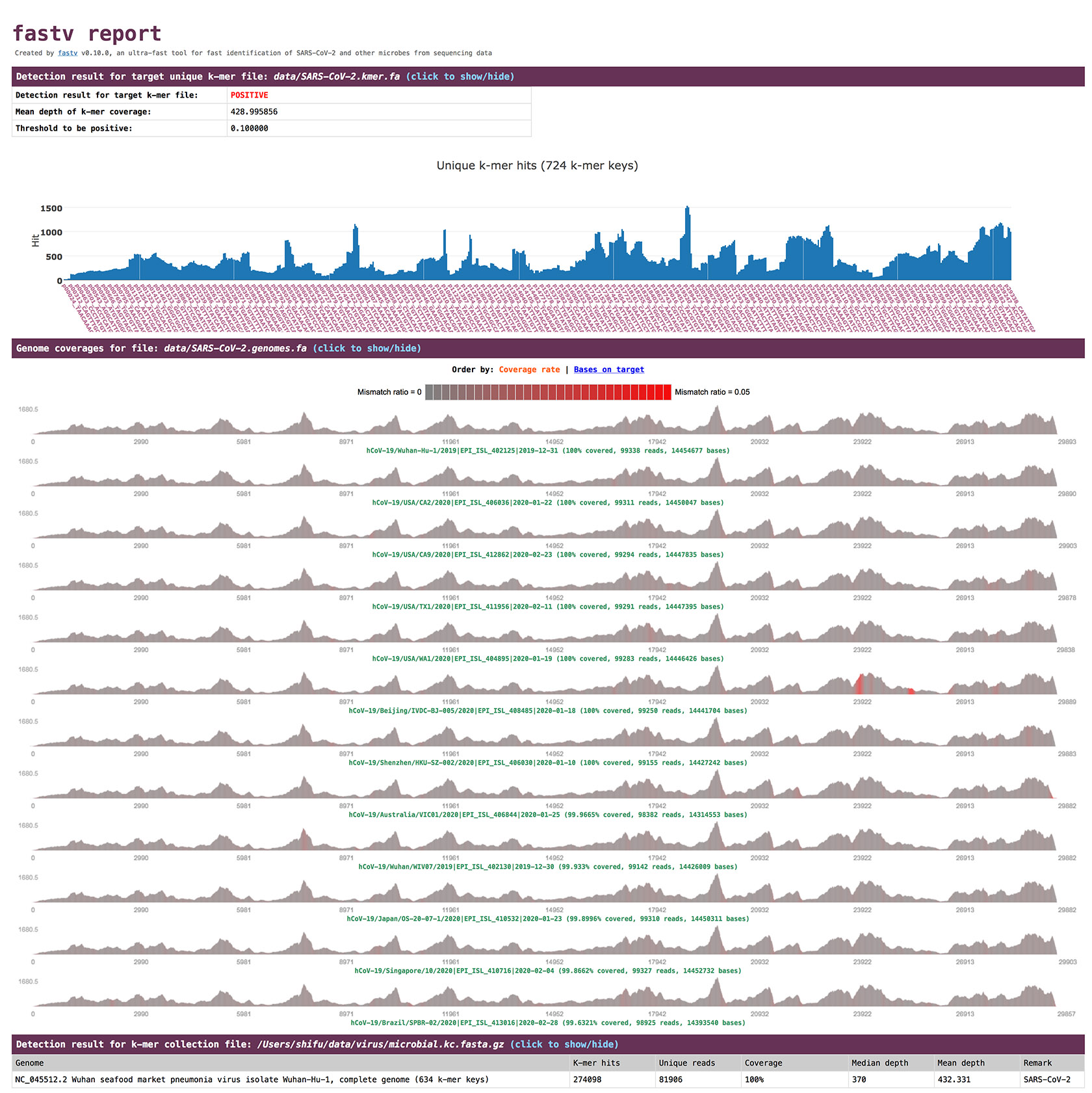
options
Key options:
-i, --in1 read1 input file name (string [=])
-I, --in2 read2 input file name (string [=])
-o, --out1 file name to store read1 with on-target sequences (string [=])
-O, --out2 file name to store read2 with on-target sequences (string [=])
-c, --kmer_collection the unique k-mer collection file in fasta format, see an example: http://opengene.org/kmer_collection.fasta (string [=])
-k, --kmer the unique k-mer file of the detection target in fasta format. data/SARS-CoV-2.kmer.fa will be used if none of k-mer/Genomes/k-mer_Collection file is specified (string [=])
-g, --genomes the genomes file of the detection target in fasta format. data/SARS-CoV-2.genomes.fa will be used if none of k-mer/Genomes/k-mer_Collection file is specified (string [=])
-p, --positive_threshold the data is considered as POSITIVE, when its mean coverage of unique kmer >= positive_threshold (0.001 ~ 100). 0.1 by default. (float [=0.1])
-d, --depth_threshold For coverage calculation. A region is considered covered when its mean depth >= depth_threshold (0.001 ~ 1000). 1.0 by default. (float [=1])
-E, --ed_threshold If the edit distance of a sequence and a genome region is <=ed_threshold, then consider it a match (0 ~ 50). 8 by default. (int [=8])
--long_read_threshold A read will be considered as long read if its length >= long_read_threshold (100 ~ 10000). 200 by default. (int [=200])
--read_segment_len A long read will be splitted to read segments, with each <= read_segment_len (50 ~ 5000, should be < long_read_threshold). 100 by default. (int [=100])
--bin_size For coverage calculation. The genome is splitted to many bins, with each bin has a length of bin_size (1 ~ 100000), default 0 means adaptive. (int [=0])
--kc_coverage_threshold For each genome in the k-mer collection FASTA, report it when its coverage > kc_coverage_threshold. Default is 0.01. (double [=0.01])
--kc_high_confidence_coverage_threshold For each genome in the k-mer collection FASTA, report it as high confidence when its coverage > kc_high_confidence_coverage_threshold. Default is 0.9. (double [=0.9])
--kc_high_confidence_median_hit_threshold For each genome in the k-mer collection FASTA, report it as high confidence when its median hits > kc_high_confidence_median_hit_threshold. Default is 5. (int [=5])
-j, --json the json format report file name (string [=fastv.json])
-h, --html the html format report file name (string [=fastv.html])
-R, --report_title should be quoted with ' or ", default is "fastv report" (string [=fastv report])
-w, --thread worker thread number, default is 4 (int [=4])
Other I/O options:
-6, --phred64 indicate the input is using phred64 scoring (it'll be converted to phred33, so the output will still be phred33)
-z, --compression compression level for gzip output (1 ~ 9). 1 is fastest, 9 is smallest, default is 4. (int [=4])
--stdin input from STDIN. If the STDIN is interleaved paired-end FASTQ, please also add --interleaved_in.
--stdout stream passing-filters reads to STDOUT. This option will result in interleaved FASTQ output for paired-end output. Disabled by default.
--interleaved_in indicate that <in1> is an interleaved FASTQ which contains both read1 and read2. Disabled by default.
--reads_to_process specify how many reads/pairs to be processed. Default 0 means process all reads. (int [=0])
--dont_overwrite don't overwrite existing files. Overwritting is allowed by default.
-V, --verbose output verbose log information (i.e. when every 1M reads are processed).
QC and quality pruning options (inherited from fastp: https://github.com/OpenGene/fastp)
-A, --disable_adapter_trimming adapter trimming is enabled by default. If this option is specified, adapter trimming is disabled
-a, --adapter_sequence the adapter for read1. For SE data, if not specified, the adapter will be auto-detected. For PE data, this is used if R1/R2 are found not overlapped. (string [=auto])
--adapter_sequence_r2 the adapter for read2 (PE data only). This is used if R1/R2 are found not overlapped. If not specified, it will be the same as <adapter_sequence> (string [=auto])
--adapter_fasta specify a FASTA file to trim both read1 and read2 (if PE) by all the sequences in this FASTA file (string [=])
--detect_adapter_for_pe by default, the auto-detection for adapter is for SE data input only, turn on this option to enable it for PE data.
-f, --trim_front1 trimming how many bases in front for read1, default is 0 (int [=0])
-t, --trim_tail1 trimming how many bases in tail for read1, default is 0 (int [=0])
-b, --max_len1 if read1 is longer than max_len1, then trim read1 at its tail to make it as long as max_len1. Default 0 means no limitation (int [=0])
-F, --trim_front2 trimming how many bases in front for read2. If it's not specified, it will follow read1's settings (int [=0])
-T, --trim_tail2 trimming how many bases in tail for read2. If it's not specified, it will follow read1's settings (int [=0])
-B, --max_len2 if read2 is longer than max_len2, then trim read2 at its tail to make it as long as max_len2. Default 0 means no limitation. If it's not specified, it will follow read1's settings (int [=0])
--poly_g_min_len the minimum length to detect polyG in the read tail. 10 by default. (int [=10])
-G, --disable_trim_poly_g disable polyG tail trimming, by default trimming is automatically enabled for Illumina NextSeq/NovaSeq data
-x, --trim_poly_x enable polyX trimming in 3' ends.
--poly_x_min_len the minimum length to detect polyX in the read tail. 10 by default. (int [=10])
-5, --cut_front move a sliding window from front (5') to tail, drop the bases in the window if its mean quality < threshold, stop otherwise.
-3, --cut_tail move a sliding window from tail (3') to front, drop the bases in the window if its mean quality < threshold, stop otherwise.
-r, --cut_right move a sliding window from front to tail, if meet one window with mean quality < threshold, drop the bases in the window and the right part, and then stop.
-W, --cut_window_size the window size option shared by cut_front, cut_tail or cut_sliding. Range: 1~1000, default: 4 (int [=4])
-M, --cut_mean_quality the mean quality requirement option shared by cut_front, cut_tail or cut_sliding. Range: 1~36 default: 20 (Q20) (int [=20])
--cut_front_window_size the window size option of cut_front, default to cut_window_size if not specified (int [=4])
--cut_front_mean_quality the mean quality requirement option for cut_front, default to cut_mean_quality if not specified (int [=20])
--cut_tail_window_size the window size option of cut_tail, default to cut_window_size if not specified (int [=4])
--cut_tail_mean_quality the mean quality requirement option for cut_tail, default to cut_mean_quality if not specified (int [=20])
--cut_right_window_size the window size option of cut_right, default to cut_window_size if not specified (int [=4])
--cut_right_mean_quality the mean quality requirement option for cut_right, default to cut_mean_quality if not specified (int [=20])
-Q, --disable_quality_filtering quality filtering is enabled by default. If this option is specified, quality filtering is disabled
-q, --qualified_quality_phred the quality value that a base is qualified. Default 15 means phred quality >=Q15 is qualified. (int [=15])
-u, --unqualified_percent_limit how many percents of bases are allowed to be unqualified (0~100). Default 40 means 40% (int [=40])
-n, --n_base_limit if one read's number of N base is >n_base_limit, then this read/pair is discarded. Default is 5 (int [=5])
-e, --average_qual if one read's average quality score <avg_qual, then this read/pair is discarded. Default 0 means no requirement (int [=0])
-L, --disable_length_filtering length filtering is enabled by default. If this option is specified, length filtering is disabled
-l, --length_required reads shorter than length_required will be discarded, default is 15. (int [=15])
--length_limit reads longer than length_limit will be discarded, default 0 means no limitation. (int [=0])
-y, --low_complexity_filter enable low complexity filter. The complexity is defined as the percentage of base that is different from its next base (base[i] != base[i+1]).
-Y, --complexity_threshold the threshold for low complexity filter (0~100). Default is 30, which means 30% complexity is required. (int [=30])
--filter_by_index1 specify a file contains a list of barcodes of index1 to be filtered out, one barcode per line (string [=])
--filter_by_index2 specify a file contains a list of barcodes of index2 to be filtered out, one barcode per line (string [=])
--filter_by_index_threshold the allowed difference of index barcode for index filtering, default 0 means completely identical. (int [=0])
-C, --correction enable base correction in overlapped regions (only for PE data), default is disabled
--overlap_len_require the minimum length to detect overlapped region of PE reads. This will affect overlap analysis based PE merge, adapter trimming and correction. 30 by default. (int [=30])
--overlap_diff_limit the maximum number of mismatched bases to detect overlapped region of PE reads. This will affect overlap analysis based PE merge, adapter trimming and correction. 5 by default. (int [=5])
--overlap_diff_percent_limit the maximum percentage of mismatched bases to detect overlapped region of PE reads. This will affect overlap analysis based PE merge, adapter trimming and correction. Default 20 means 20%. (int [=20])
-U, --umi enable unique molecular identifier (UMI) preprocessing
--umi_loc specify the location of UMI, can be (index1/index2/read1/read2/per_index/per_read, default is none (string [=])
--umi_len if the UMI is in read1/read2, its length should be provided (int [=0])
--umi_prefix if specified, an underline will be used to connect prefix and UMI (i.e. prefix=UMI, UMI=AATTCG, final=UMI_AATTCG). No prefix by default (string [=])
--umi_skip if the UMI is in read1/read2, fastv can skip several bases following UMI, default is 0 (int [=0])
citation
If you use fastv, UniqueKMER or the pre-generated resources provided by this repository, please cite our work as:
Shifu Chen, Changshou He, Yingqiang Li, Zhicheng Li, Charles E Melancon III. A Computational Toolset for Rapid Identification of SARS-CoV-2, other Viruses, and Microorganisms from Sequencing Data. bioRxiv 2020.05.12.092163; doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.05.12.092163
tutorials
analyze metagenomics sequencing (mNGS) data
- download or build fastv
- download the k-mer collection for all viruses and microorganisms that have reference genomes in NCBI RefSeq:
wget http://opengene.org/microbial.kc.fasta.gz
- run fastv:
./fastv -i filename.fastq.gz -c microbial.kc.fasta.gz
-
check the result in HTML report
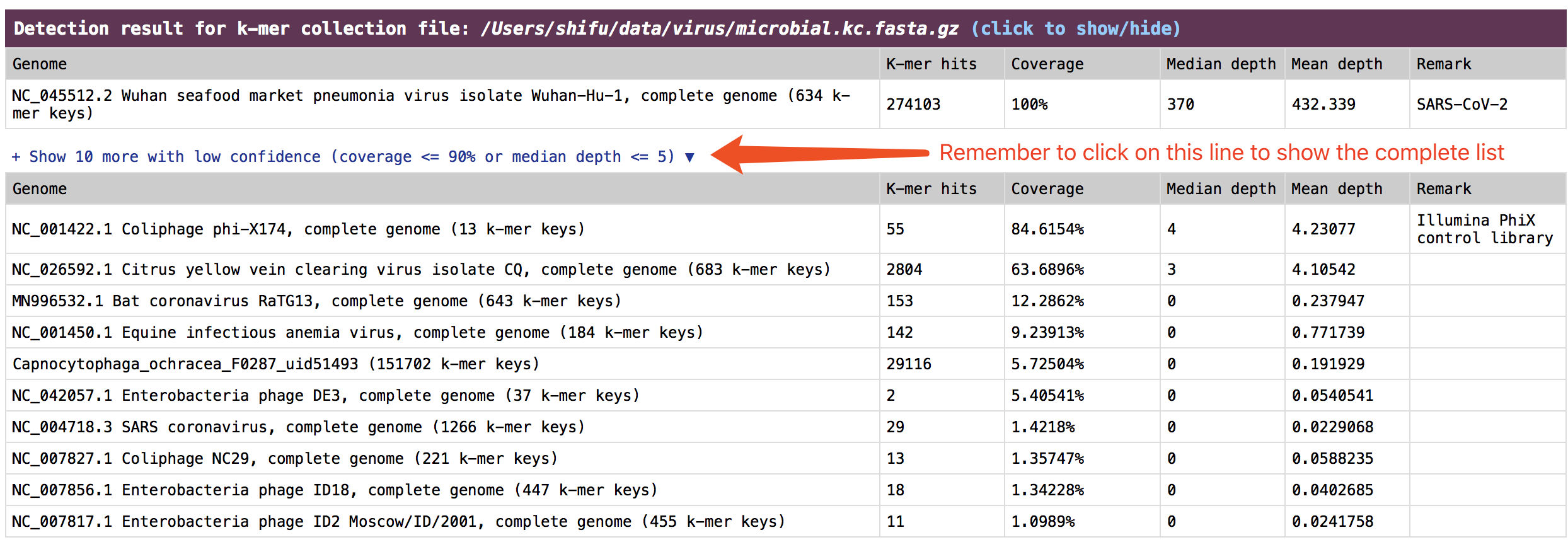 The result is presented in the section:
The result is presented in the section: Detection result for k-mer collection file.
See an example: http://opengene.org/fastv/mngs.html -
check the result in JSON report
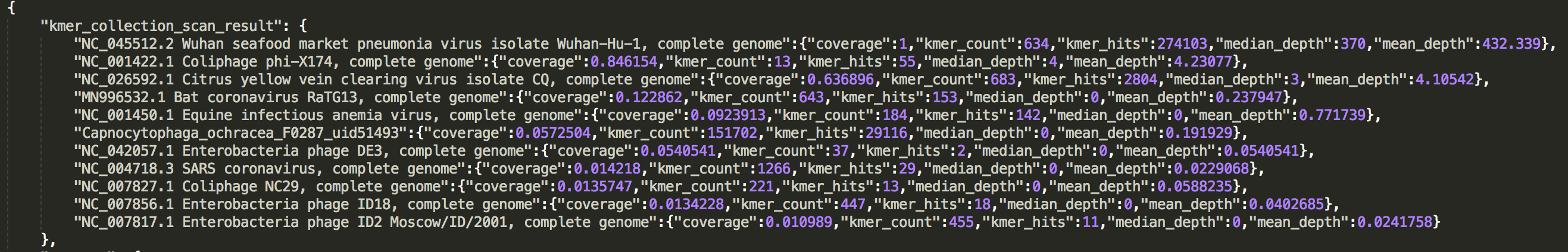
The result is presented in a list:kmer_collection_scan_result.
See an example: http://opengene.org/fastv/mngs.json
identify SARS-CoV-2
- download or build fastv
- download the
k-merfile andgenomesfile for SARS-CoV-2
wget http://opengene.org/fastv/data/SARS-CoV-2.kmer.fa
wget http://opengene.org/fastv/data/SARS-CoV-2.genomes.fa
- run fastv:
./fastv -i filename.fastq.gz -k SARS-CoV-2.kmer.fa -g SARS-CoV-2.genomes.fa
-
check the result in SHELL
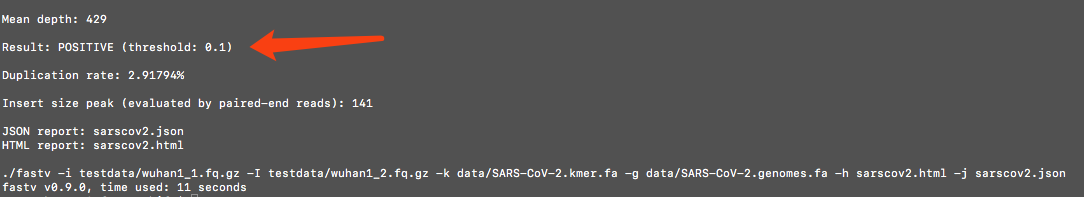 The detection result will be
The detection result will be POSITIVEif the SARS-CoV-2 coverage is higher than the threshold. -
check the result in HTML report
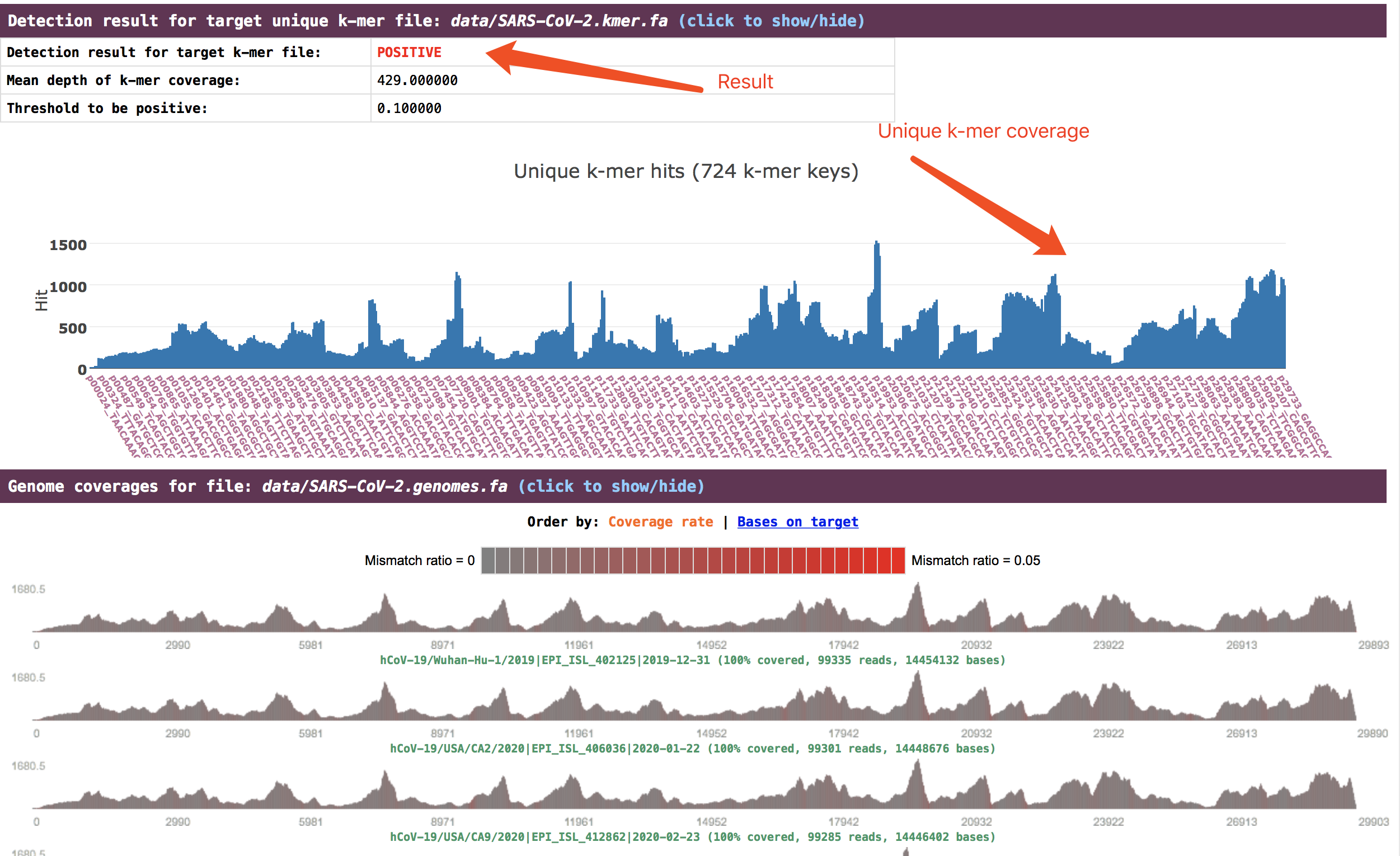 The detection result is presented in the section
The detection result is presented in the section Detection result for target unique k-mer file. The genome coverage result is presented in the sectionGenome coverages for file.
See an example: http://opengene.org/fastv/sarscov2.html -
check the result in JSON report
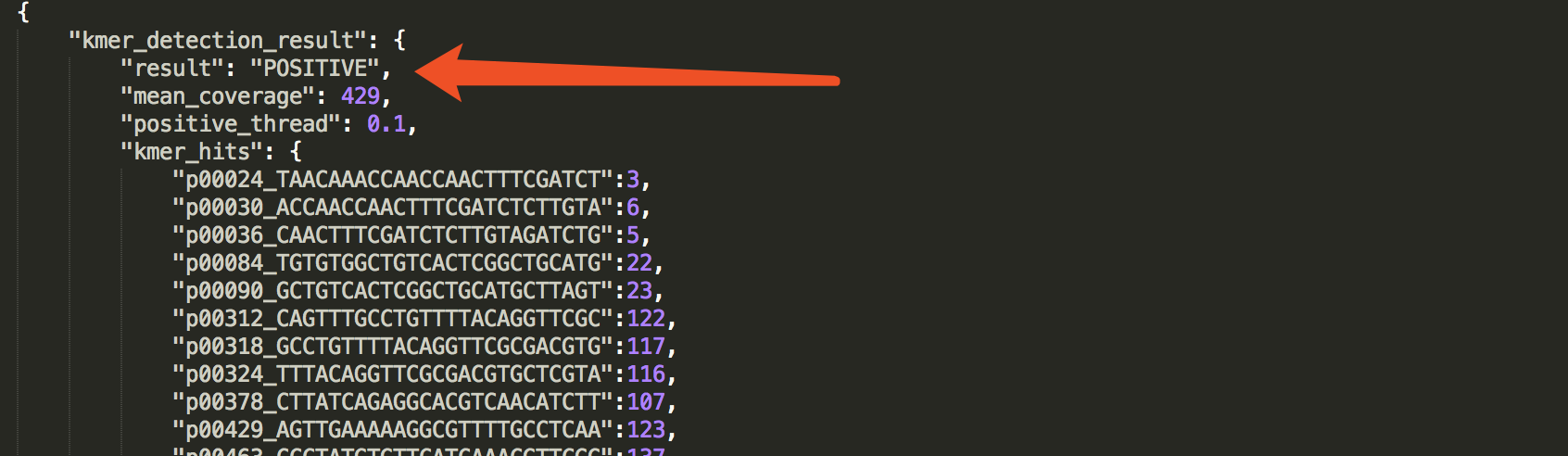
The result is presented in:kmer_detection_result.
See an example: http://opengene.org/fastv/sarscov2.json
influenza A virus subtyping
Influenza A viruses are divided into subtypes on the basis of two proteins on the surface of the virus: hemagglutinin (HA) and neuraminidase (NA). For example, “H5N1” virus has an hemagglutinin type 5 protein and an neuraminidase type 1 protein. fastv can be used to identify the hemagglutinin type and neuraminidase type for influenza A virus from sequencing data.
- download or build fastv
- download the k-mer collection for all viruses and microorganisms that have reference genomes in NCBI RefSeq:
wget http://opengene.org/influenzaA.kc.fasta.gz
- run fastv:
./fastv -i filename.fastq.gz -c influenzaA.kc.fasta.gz
- check the result in HTML report
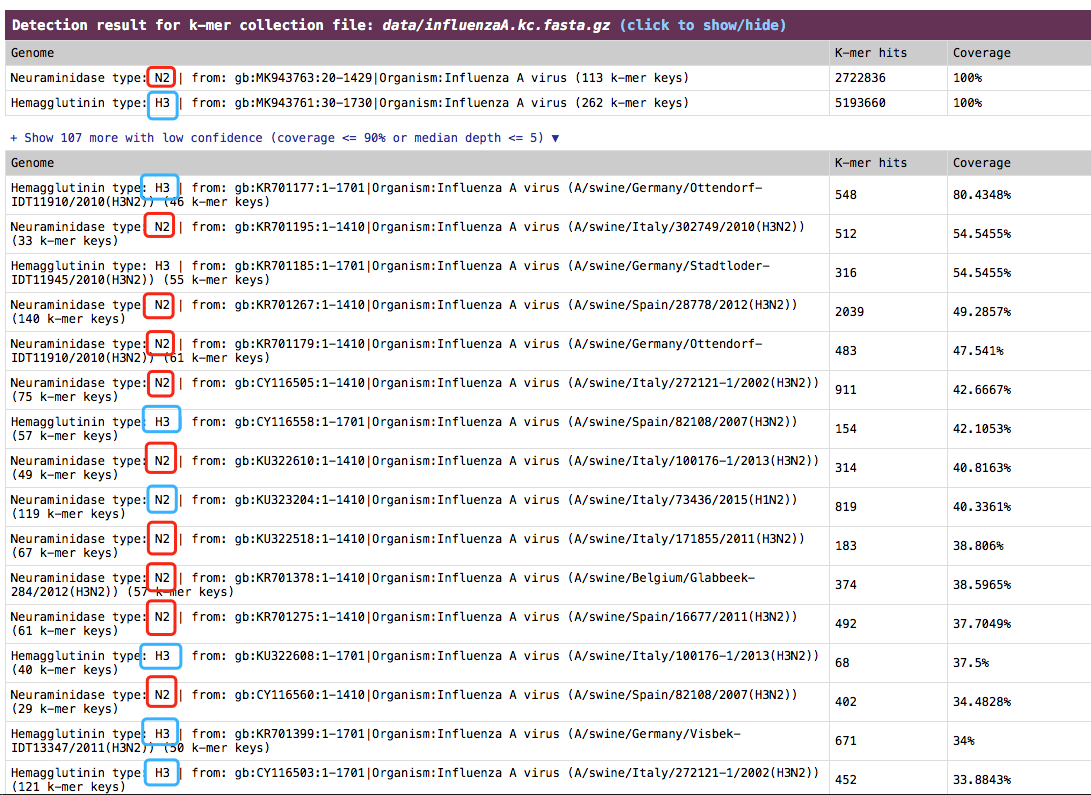 The result is presented in the section:
The result is presented in the section: Detection result for k-mer collection file.
See an example (influenza A H3N2): http://opengene.org/fastv/H3N2.html