Awesome

The Mackey-Glass Anomaly Benchmark
This repository contains the Mackey-Glass anomaly benchmark (MGAB), which is composed of synthetic Mackey-Glass time series with non-trivial anomalies. Mackey-Glass time series are known to exhibit chaotic behavior under certain conditions. MGAB contains 10 MG time series of length 10<sup>5</sup>. Into each time series 10 anomalies are inserted with a procedure as described below. In contrast to other synthetic benchmarks, it is very hard for the human eye to distinguish the introduced anomalies from the normal (chaotic) behavior. An excerpt of a time series containing 3 anomalies is shown in the graph above. The location of the anomalies are revealed in the last plot of this page.
Authors/Contributors
Citing this Repository
This repository can be cited using the following identifier:
The benchmark is also used in the following paper: Thill, M., Konen, W., & Bäck, T. (2020, November). Time series encodings with temporal convolutional networks. In International Conference on Bioinspired Methods and Their Applications (pp. 161-173). Springer, Cham.
If you use the MGAB for your work as well, just let us know and we can add a reference to your publication here.
Download
The easiest way to download this repository is to clone it with Git:
git clone https://github.com/MarkusThill/MGAB.git
The Benchmark Files
The labeled data for the time series 1-10 can be found in the CSV files [1-10].csv. Each file contains a table with 4 columns:
time: Time in seconds in the range 0 to 10<sup>5</sup> -1.value: Value of x(t) in the range [0.26, 1.66].is_anomaly: Binary values (0/1) indicate which data points are considered as normal (0) or anomalous (1). For each anomaly, a range of 400 points, the so called anomaly window, is flagged. Detections within the anomaly window are to be considered as correct.is_ignored: Since some algorithms might require a "warm-up" phase when processing the time series, the is_ignored column indicates for the initial 256 time steps that false detections can be ignored. It was ensured that no anomalies were placed at the beginning of any time series.
Time Series Generation
We use the following Mackey-Glass equation (a non-linear time delay differential equation, DDE) to generate our time series:
The parameters are real numbers which we set to τ=18, n=10, β=0.25, γ=0.1. Additionally, a constant history parameter is required which is set to h=0.9. A sufficiently long time series is generated using the JiTCDDE solver ( with an integration stepsize of one) which is then divided into 10 new time series. The time delay embedding of such a time series is illustrated in Fig. 1.
 <br>Figure 1: Time delay embedding of the Mackey-Glass attractor.
<br>Figure 1: Time delay embedding of the Mackey-Glass attractor.
Anomaly Insertion Process
The main idea of the anomaly insertion process is to randomly remove segments from each time series in a way that this will be hardly visible later. To do so, we try to find two points (with a minimal and maximal distance) in a random segment of the time series so that the values of these two points as well as their derivatives closely match. Then, we remove the segment between those two points and "stich" the remaining parts together again. The exact procedure is as follows:
- For the time series sequence
estimate the first 3 derivatives
,
and
by numerical differentiation of
. Then, stack the original time series
and the three derivatives in a four-dimensional time series
.
- Randomly select a position
in
. This will be the first split point
- Starting at
, with
, for all
, compare
to
and compute the euclidean norm
.
- The index
which minimizes the distance
will give us the second split point
, where
- Construct a new manipulated time series
, which is
, for
and
for
.
The procedure is also summarized in Algorithm 1 below.

An example of how such an anomaly, which was generated using the described procedure, could look like is illustrated in Fig. 2. For the human eye it would be almost impossible to spot the anomaly.

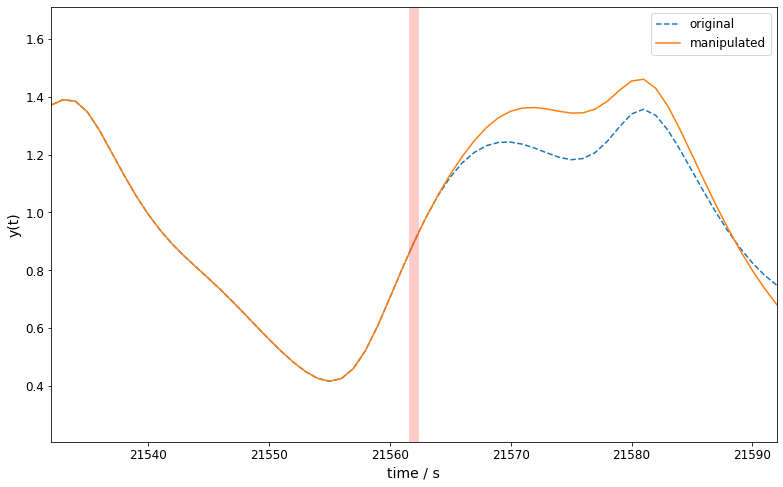 <br>
Figure 2: Top: Example for the creation of a Mackey-Glass time series with a temporal anomaly. The original time series (dashed line) is manipulated in such a way, that a segment is removed and the two remaining ends are joined together. In this example, the interval [21562,21703] is removed from the original curve. The resulting manipulated time series (solid line) has a smooth point of connection, but significantly differs from the original. Bottom: Zoomed-In. The red shaded area indicates the position where the anomaly was inserted.
<br>
Figure 2: Top: Example for the creation of a Mackey-Glass time series with a temporal anomaly. The original time series (dashed line) is manipulated in such a way, that a segment is removed and the two remaining ends are joined together. In this example, the interval [21562,21703] is removed from the original curve. The resulting manipulated time series (solid line) has a smooth point of connection, but significantly differs from the original. Bottom: Zoomed-In. The red shaded area indicates the position where the anomaly was inserted.
Adding Noise
For the 10 time series of this benchmark, in total 100 anomalies were inserted (10 anomalies per time series). In the last step, in order to increase the complexity of the anomaly detection task slightly, we add noise drawn from a random uniform distribution with the range [-0.01, 0.01] to each point of all time series.
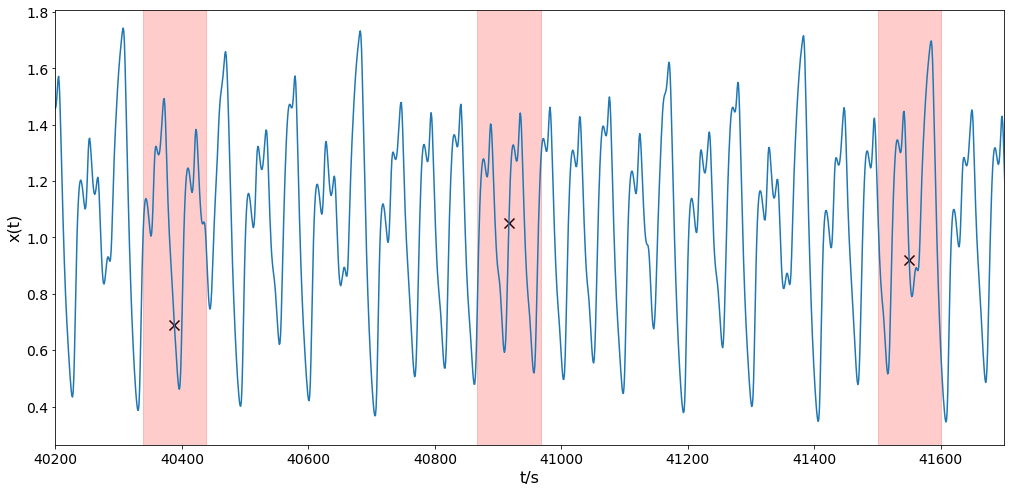 Figure 3: This graph shows the same section of a Mackey-Glass time series as the first graph on this page, but now reveals the location of the anomalies in the time series. The anomalies are at t<sub>1</sub> = 40388, t<sub>2</sub>=40917 and t<sub>3</sub>=41550. The positions are indicated by the black crosses in the plot.
Figure 3: This graph shows the same section of a Mackey-Glass time series as the first graph on this page, but now reveals the location of the anomalies in the time series. The anomalies are at t<sub>1</sub> = 40388, t<sub>2</sub>=40917 and t<sub>3</sub>=41550. The positions are indicated by the black crosses in the plot.
Generating your own MGAB Benchmark
Based on the procedure described in the previous section, it is also possible to adjust different parameters and generate an own MGAB with steerable size and difficulty.
Dependencies
The following dependencies are required for running the code on all operating systems. In the parentheses we add the version, which we used for our experiments.
- Python 3 (3.6.9)
- jitcdde (1.5.0)
pip3 install jitcdde - numpy (1.14.5)
pip3 install numpy - scipy (1.4.1)
pip3 install scipy - matplotlib (3.1.1)
pip3 install matplotlib - pandas (0.23.3)
pip3 install pandas
Usage
The main function of this module is generate_benchmark(args). All parameters are passed to this function through a Python dictionary. It is possible to pass an empty dictionary or no argument at all. Typically, one would specify a subset of the required parameters in the dictionary; the function would then use the default values for the remaining parameters.
Usage:
import mgab
benchmark_list = mgab.generate_benchmark(args)
generate_benchmark(args:dict={'reproduce_original_mgab':'use_precomputed_mg'})
Generates a MGAB according to the specifications of the user. A list of MG time series with a certain number of anomalies is created. The created time series can be directly written to CSV-files and/or returned by this function and processed further.
- Parameters
args: Dictionary, containing all user-specified parameters for generating a MGAB benchmark. It is not necessary to pass any argument togenerate_benchmark(). In this case, the original MGAB data is created which was also uploaded to this repository. The function will use the pre-computed MG time series from the file./data/mgts_len=5000000tau=18n=10.0bet=0.25gam=0.1h=0.9T=1.npyto generate the 10 original time series. It is also possible to create the whole benchmark from scratch, by adjusting the dictionary entry of'reproduce_original_mgab', as described below. Currently, the following options are supported:'verbosity'(int): Integer, describing the level of verbosity.- 0: No outputs to stdout
- 1: Print standard Info-messages
- Larger than 1: Debug Messages
- default: 1
'output_dir'(str): Directory, in which the resulting files containing the individual time series will be written. The optionNoneallows to turn off the saving. Per default, the files are named 1.csv, 2.csv, ... and have the same format as the original files described above.- default: './mgab/',
'output_force_override'(bool): If a file with the same name already exists in the output directory, then this will not be overwritten per default. This can be changed by setting this option to True. So with this option you can force the generator to override benchmark files in the output directory, if a file with that name already exists.- default: False
'output_format'(str): Currently, only 'csv' is supported. All output files, saved as 1.csv, 2.csv, ..., are comma-seperated-value (CSV) files.- default: 'csv'
'num_series'(int): The number of individual anomalous time series, which should be generated. Creating many time series might take a lot of time, since the DDE solver has to pre-compute (and if no already pre-computed MG time series is available, see'mg_ts_path_load') one long MG time series which is then split into the specified number.- default: 10
'series_length'(int): The length of one anomalous time series. Similarly to'num_series', it might be computationally expensive, if too large values are chosen.- default: 100000
'num_anomalies'(int) : The number of anomalies which are placed into each time series. E.g., if 10 time series are generated and this option is set to 10, then the overall benchmark will contain 100 anomalies.- default: 10,
'noise'(str) : In order to further increase the complexity of the benchmark and to be more similar to real-world problems, there is a possibility to add random noise to the individual anomalous MG time series. It is also possible to turn off the noise component. The amount of noise is controlled by'noise_param'. There are 4 options:- 'rnd_uniform': Adds random uniform noise to the time series.
- 'rnd_walk': Samples from a random uniform distribution and computes a random walk (cumulative sum) over these values.
- 'rnd_normal': Sample from a Gaussian normal distribution.
- None: Do not add any noise to the time series
- default: 'rnd_uniform'
'noise_param'(tuple,float) : For 'rnd_uniform' and 'rnd_walk', specifies the lower and upper bound for the random uniform distribution, respectively. For 'rnd_normal', the first element describes the mean (loc) and the second element the standard deviation (scale).- default: (-0.01, 0.01) for 'rnd_uniform', (-0.001, 0.001) for 'rnd_walk' and (0, 0.01) for 'rnd_normal'.
'min_anomaly_distance'(int) : The minimum distance between 2 anomalies. The difficulty of the benchmark usually increases, if this distance is reduced.- default: 2000,
'mg_ts_path_load'(str): Full path to a pre-computed MG time series, which can be used to produce the anomalous time series. The file must contain a numpy array ('.npy'-file). Usually, a lot of time can be saved, if a pre-computed MG time series is available, since the DDE solver does not have to be called in this case. However, this time series has to be long enough, to be split into'num_series'new series of length'series_length'. The length should be roughly 1.5 x'num_series'x'series_length', since also segments of the time series are removed in order to create the anomalies. If this pre-computed time series is too short, an exception will be thrown. In this case, one could reduce'num_series'or'series_length'or set this parameter to None. If this option is set to None, no pre-computed MG time series will be loaded from disk. Instead, the DDE solver will generate a time series which is suffiently long.- default: None
'mg_tau'(float) : Parameter τ in the MG equation.- default: 18.0
'mg_n'(float): Parameter n in the MG equation.- default: 10.0
'mg_beta'(float) : Parameter β in the MG equation.- default: 0.25
'mg_gamma'(float) : Parameter γ in the MG equation.- default: 0.1
'mg_history'(float) : Value for the constant history h, which is required by the DDE solver as initial condition.- default: 0.9
'mg_T'(float): Step-size parameter T for the DDE solver. Usually, 'mg_T=1' is sufficient. Smaller step-sizes will reduce the "gaps" between the evaluated points of the MG equation and increase the number of data points which are generated.- default: 1.0
'mg_ts_dir_save'(str): In order to possibly save time in the future, this option can be used to specify a file (only the directory) where the pre-computed MG time series shall be saved. The filename will contain all necessary parameters, which allow the user to later find a certain setting. Since the filename is unique (according to the setting), no check is performed to ensure that no duplicate file is present in the folder. If a file with the same filename should already be present, then this file should contain exactly the same data as the generated one.- default: None,
'seed'(int): In order to allow to reproduce certain settings, the user may specify a seed. If no seed is provided (None) then the algorithm will take the value i for the i-th time series as seed (0,1,...). So, if a completly random result is necessary, the user should set a sufficiently random seed (e.g., a timestamp in ms, etc.)- default: None
'min_length_cut'(int): This option specifies the minimum size of the segments which are removed from the time series in order to create an anomaly. It does not make sense to make trivial cuts (e.g. cut segment of length 1, which might happen if adjacent points have the largest similarity in a certain range). Usually, the default value is a good choice.- default: 100,
'max_sgmt'(int): Maximum segment length in which we want to find the most similar values. In order to create an anomaly we compare the values (and the derivatives) of the time series in two windows with each other. Then, the segment between the 2 most similar values is removed and the 2 remaining ends are "stiched" together again:# xxxxxxxxxxx [window1] xxxxx [window2] xxxxxxxxxxx. 'max_sgmt' basically describes the size of window1 and window2 (which both have the same size).- default: 100
'anomaly_window'(int): Window size of anomaly window which is put around each anomaly. Smaller windows increase the difficulty, since algorithms have to locate the anomalies more accurately.- default: 400
'order_derivative'(int): Until which (numerical) derivative do we want to compare the similarity of the points? (0->only value, 1-> value and 1st derivative, ...)- default: 3
'reproduce_original_mgab': This option is used to generate the original MGAB, which is described in the beginning of this page and for which the data has been added to this repository. If this option is set to a value which is not None, then most of the previous options will be ignored and the default settings will be taken, so that the original results can be re-produced. Currently, it is only possible to adjust the other options'output_dir','output_force_override'and'output_format'(which currently also only has one possibility). There are 3 options:- 'generate_new_mg': With this option, the whole benchmark is re-computed from scratch. This can take a long time, since the DDE solver has to be run again.
- 'use_precomputed_mg': Using this option, the pre-computed MG time series in
./data/mgts_len=5000000tau=18n=10.0bet=0.25gam=0.1h=0.9T=1.npywill be used to generate the benchmark. The compuation time should be limited in this case. - None: This value is usually chosen, since in most cases we do not want to re-produce the old time series, but rather create our own new benchmark.
- default: None
- Returns
- A list of Pandas DataFrames containing the anomalous time series including the anomaly labels. Each DataFrame has an index column, the column "value", "is_anomaly" and "is_ignored". These columns are described above.
Examples
# Generate the original MGAB. This will create a directory "mgab" (if not existant yet),
# and write the 10 CSV-files containing the 10 time series into this folder. These CSV-
# files should be exactly the same as the original ones in this repository.
import mgab
original_mgab = mgab.generate_benchmark()
# Generate some customized new benchmark. We can change a few of the default parameters.
import mgab
my_new_benchmark = mgab.generate_benchmark({ # we choose a few parameters ourselves
'output_dir' : 'my_new_benchmark', # specify new directory for the output files
'output_force_override': True, # Override files, if necessary
'num_series': 3, # Create only 3 time series for this benchmark
'series_length': 10000, # Only create time series of lenth 10k
'num_anomalies' : 5, # Each time series contains 5 anomalies
'noise' : 'rnd_uniform',# Add random uniform noise
'noise_param' : (-0.01, 0.01), # range for random uniform noise
'min_anomaly_distance' : 200, # Anomalies have to have a distance of at least 200
'mg_tau' : 30, # use a larger value for tau
'mg_ts_path_load' : None, # We do not have any pre-computed MG time series. So generate it with the DDE solver
'mg_ts_dir_save' : "./data/" # Save the generated MG time series of the DDE solver in the data directory. This
# allows us, to reuse it again (e.g., if we want to change the number of anomalies)
})