Awesome
colab-convert
Converts ipython/Google Colab Notebooks into runable Python code and vice versa
Features
- converts files: .ipynb to .py and .py to .ipynb.
- converts ipython/colab magic % and ! to regular python code
- Supported magic commands (%)
- %pwd, %ls, %cd, %cp, %mv, %mkdir, %rm, %rmdir, %cat, %pip, %conda, %env, %setenv
- comments out unsupported ipython magic
- creates new import blocks for converted code
- logs all changes to a log file for review
- converted magic commands are appended with
#<cc-cm> - commented magic commands are prefixed with
#<cc-ac> - multi-lingual support to detect system language and let users choose
- Arabic, Dutch, English, German,
- consider helping expand translations by adding your langauge in the
/langfolder
- consider helping expand translations by adding your langauge in the
- Arabic, Dutch, English, German,
Atom/Hydrogen or VSCode/Python allows creating a python file split into cells with # %% separators having the ability to run cells via the backend of a Jupyter session and interactively show results back.
VSCode
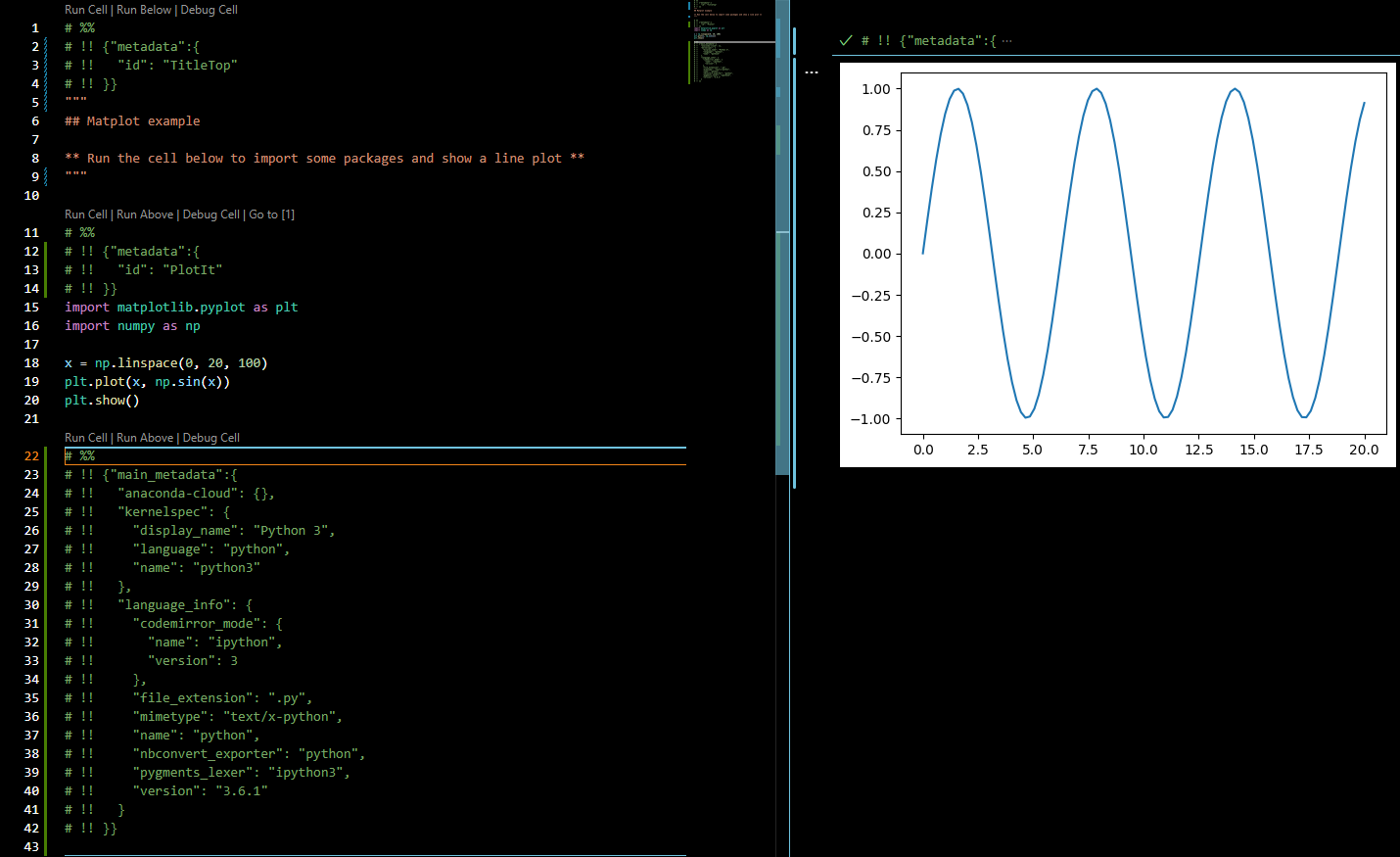
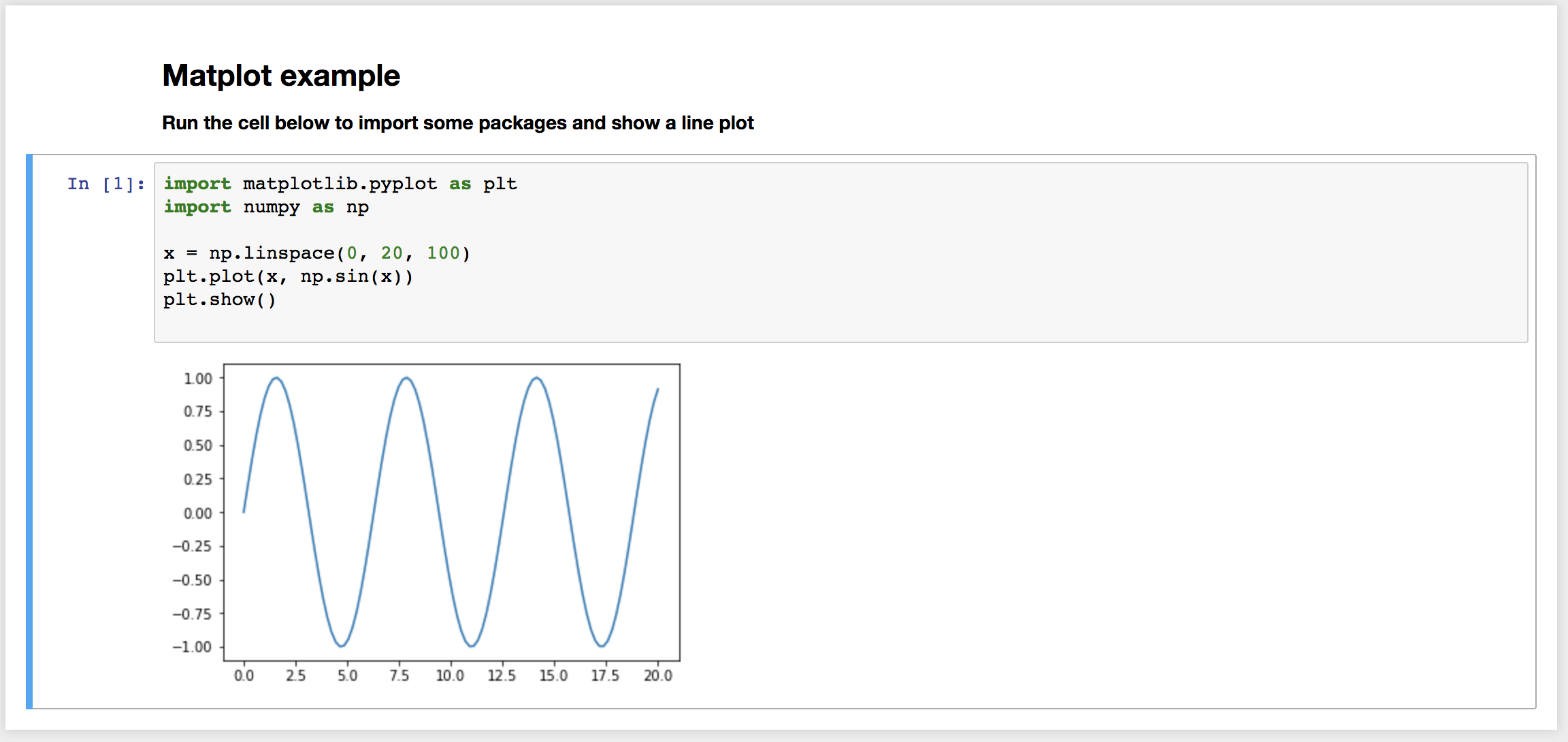
Jupyter ipynb notebook
Install & Basic Usage
pip install colab-convert
Usage: colab-convert <input_file> <output_file> <flags>
<input_file>: input file to convert
<output_file>: output file to write to
<flags>: extra flags to pass to the converter
all flags are optional and have set defaults for best results
use flags to enable or disable certain functions on/off by default
colab-convert in.ipynb out.py -nc -rm -o
Default options and Flags
Default Flags Set (defaults are determined by input file)
ipynb input file:
[YES] convert magic , [YES] auto comment , [YES] imports , [NO] Outputs
py input file:
[NO] convert magic , [NO] auto comment , [NO] imports , [NO] Outputs
Available Flags
toggle certain items on or off
--retain-magic (-rm) : Keep magic commands in the output
.py default [ON]
.ipynb default [OFF]
--convert-magic (-cm) : Convert magic commands to python code
.py default [OFF]
.ipynb default [ON]
--auto-comment (-ac) : Convert unsupported magic commands to comments
.py default [OFF]
.ipynb default [ON]
--no-comment (-nc) : Keep unsupported magic commands
.py default [ON]
.ipynb default [OFF]
--no-imports (-ni) : Do not add imports from converted magic commands
.py default [OFF]
.ipynb default [OFF]
--outputs (-o) : Outputs to console of conversions and commented lines.
.py default [OFF]
.ipynb default [OFF]
--lang= (-l=) : Language to change output messages to
default [English]
--lang=en_US
en_US, en, english, eng, nl_NL, nl, dutch, dut, nlt, nederlands
Conversion Code used
<details> <summary>>click me to see code<</summary>Magic commands using bang (!)
for this particular magic we send the command to the subprocess system and print the results
# !git clone https://test.com/test/test.git
sub_p_res = subprocess.run(['git', 'clone' ,'https://test.com/test/test.git'], stdout=subprocess.PIPE).stdout.decode('utf-8')
print(sub_p_res)
Magic commands using percent (%)
%pwd - get current working directory
# %pwd
os.getcwd()
%ls - list items in directory
# %ls
os.listdir()
# %ls folderName/subFolder
os.listdir('folderName/subFolder')
%cd - change directory
# %cd test-directory
os.chdir('test-directory')
%mkdir - make a new directory
# %mkdir test/newFolder
os.makedirs('test/newFolder')
%mv - move file from one location to another
# %mv testFile.txt testFolder/
shutil.move('testFile.txt', 'testFolder/testFile.txt')
%cp - copy file from one location to another
# %cp testFolder/testFile.txt newFolder/newTestFile.txt
shutil.copy('testFolder/testFile.txt', 'newFolder/newTestFile.txt')
%cat - show the output of a file in standard format
# %cat testFolder/testFile.txt
cat_read_file = open('testFolder/testFile.txt', 'r')
cat_read_text = cat_read_file.read()
print(cat_read_text)
cat_read_file.close()
%env & %set_env - get, set or list environmental variables
this command actually has 5 ways to be used
%env
lists all environment variables/values
%env var
get value for var
[%env or %set_env] var val
set value for var
[%env or %set_env] var=val
set value for var
[%env or %set_env] var=$val
set value for var, using python expansion if possible
# %env
for k, v in os.environ.items():
print(f'{k}={v}')
# %env var
os.environ['var']
# %env var value
# %set_env var value
os.environ['var'] = 'value'
# %env var=value
# %set_env var=value
os.environ['var'] = 'value'
# %env var=$value
# %set_env var=$value
os.environ['var'] = '$value'
%pip - install a pip package or other pip functions
# %pip install colab-convert
pip_sub_p_res = subprocess.run(['pip', 'install', 'colab-convert'], stdout=subprocess.PIPE).stdout.decode('utf-8')
print(pip_sub_p_res)
%conda - install a conda package or other conda functions
# %conda install colab-convert
conda_sub_p_res = subprocess.run(['conda', 'install', 'colab-convert'], stdout=subprocess.PIPE).stdout.decode('utf-8')
print(conda_sub_p_res)
Unsupported Magic Commands
these will be commented out
# %quickref
#<cc-cm> %quickref
Example
colab-convert examples/plot.py examples/plot.ipynb
or
colab-convert examples/plot.ipynb examples/plot.py
Markdown cells are converted to python multiline strings '''. Code cells are left as is.
eg. will render header section
"""
## Matplot example
** Run the cell below to import some packages and show a line plot **
"""
# %% is used by vscode as the cell marker on which 'Run Cell' action is available.
eg. will render a code cell
# %%
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
Metadata is converted from notebooks into .py and vise versa using # !! to denote the meta data lines in the .py files
eg.
# %%
# !! {"metadata":{
# !! "id": "PlotIt"
# !! }}
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
eg. final code block must include atleast this
# %%
# !! {"main_metadata":{
# !! "anaconda-cloud": {},
# !! "kernelspec": {
# !! "display_name": "Python 3",
# !! "language": "python",
# !! "name": "python3"
# !! },
# !! "language_info": {
# !! "codemirror_mode": {
# !! "name": "ipython",
# !! "version": 3
# !! },
# !! "file_extension": ".py",
# !! "mimetype": "text/x-python",
# !! "name": "python",
# !! "nbconvert_exporter": "python",
# !! "pygments_lexer": "ipython3",
# !! "version": "3.6.1"
# !! }
# !! }}
Troubleshooting
- If encoding problems on Windows try using
python>=3.7, settingset PYTHONUTF8=1in Windows console and usecolab-convertfor UTF-8 files only. If using Git-Bash on Windows setting:
export LANG=C.UTF-8
export PYTHONIOENCODING=utf-8
export PYTHONUTF8=1
should be enough. Also try setting default Bash settings to UTF-8: [Options] - [Text] - [Locale / Character set] - [C / UTF-8]. It might affect all Bash runs so there would be no need to setting encoding every time.
Credits
colab-convert is a fork of the ipynb-py-convert.