Awesome
Clean Architecture Manifest (v. 0.9.5)
Here you will find description of the main principles and rules, that are worth following in developing Android apps using Clean Architecture approach.
Translations:
If you want to translate this document to your language, please visit this page.
Table of contents
- Introduction
- Layers and Inversion of Control
- Additional entities used in practice
- Errors handling
- Testing
- Start a new application development using Clean Architecture
- Migration project to Clean Architecture
- Clean Architecture FAQ
Introduction
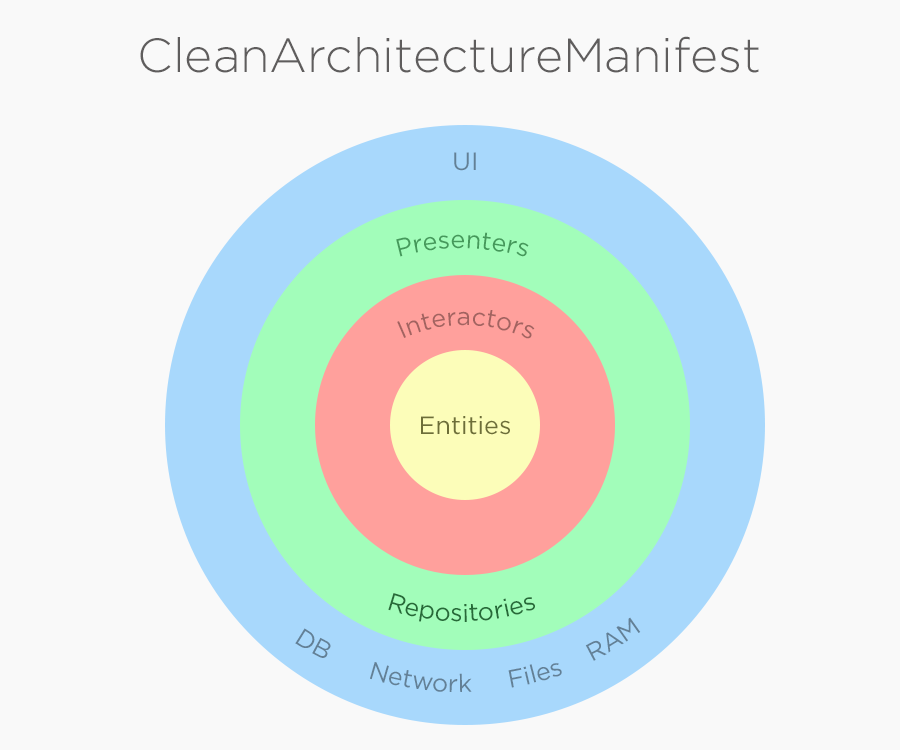
Clean Architecture is an approach suggested by Robert Martin in 2012.
Clean Architecture includes two main principles:
- Separation into layers
- Inversion of Control
Let's take a closer look at them.
1. Separating into layers
The main idea of this principle is separating whole app into layers. In general we have three layers:
- Presentation layer
- Domain layer (business logic)
- Data layer
2.Inversion of Control
According to this principle, domain layer must not depends on outer ones. That is, classes from outer layers must not be used in the domain layer. Interaction with outer layers is implemented through interfaces. Declaration of the interfaces contains in domain layer and their implementation contains in outer ones.
Thanks to separation of concerns between classes we can easily change an application code and add new functional with modifying minimal number of classes. In addition we get testable code. Please note that building the right app architecture depends entirely on a developer experience.
Advantages of Clean Architecture:
- independent of UI, DB or frameworks
- allows you to add new features faster
- a higher percentage of test coverage
- easy packages structure navigation
Disadvantages:
- large number of classes
- hard for beginners to understand
Attention: this article assumes knowledge on the following topics:
- Dagger 2
- RxJava 2
P. S. I developed an application to demonstrate the use of Clean Architecture in practice. You can find the source code here - Bubbble.
Find this article useful? ❤️
- Support it by clicking the ⭐️ button on the upper right of this page. ✌️