Awesome
The JavaScript API to consume openrouteservice(s) painlessly!
This library lets you consume the openrouteservice API in JavaScript applications. It allows you to painlessly consume the following services:
- Directions (routing)
- Geocoding | Reverse Geocoding | Structured Geocoding (powered by Pelias)
- Isochrones (accessibility)
- Time-distance matrix
- Snap (Get the closest point on road network)
- POIs (points of interest)
- Elevation (linestring or point)
- Optimization
See the examples in the examples folder
Note: In order to use this client, you have to register for a token at openrouteservice. To understand the features of openrouteservice, please don't forget to read the docs. For visualization purposes on the map please use openrouteservice maps.
Documentation
This library uses the ORS API for request validation. To understand the input of each API specifically, please check API Playground that provides an interactive documentation.
Installation and Usage
Requirements
- git
- nodeJS
- if not included in nodeJS: npm
Install the library with npm:
npm install openrouteservice-js --save
Use es module import
import Openrouteservice from 'openrouteservice-js'
let orsDirections = new Openrouteservice.Directions({ api_key: "XYZ"});
// ...
Use requirejs
const Openrouteservice = require("openrouteservice-js");
let orsDirections = new Openrouteservice.Directions({ api_key: "XYZ"});
// ...
Use the distribution file directly in html
<script type="module" src="../openrouteservice-js/dist/ors-js-client.js"></script>
<script>
let orsDirections = new Openrouteservice.Directions({ api_key: "XYZ"});
// ...
</script>
Pair with local openrouteservice instance
// Note: The API key is currently still passed as a parameter but not needed by the local instance
import Openrouteservice from 'openrouteservice-js'
let orsDirections = new Openrouteservice.Directions(
{ host: "http://localhost:8082/ors" }
);
// ...
Integrate the APIs in your application
Isochrones Example
// Add your api_key here
const Isochrones = new Openrouteservice.Isochrones({ api_key: "XYZ"})
try {
let response = await Isochrones.calculate({
locations: [[8.690958, 49.404662], [8.687868, 49.390139]],
profile: 'driving-car',
range: [600],
units: 'km',
range_type: 'distance',
attributes: ['area'],
smoothing: 0.9,
avoidables: ['highways'],
avoid_polygons: {
type: 'Polygon',
coordinates: [
[
[8.683533668518066, 49.41987949639816],
[8.680272102355957, 49.41812070066643],
[8.683919906616211, 49.4132348262363],
[8.689756393432617, 49.41806486484901],
[8.683533668518066, 49.41987949639816]
]
]
},
area_units: 'km'
})
// Add your own result handling here
console.log("response: ", response)
} catch (err) {
console.log("An error occurred: " + err.status)
console.error(await err.response.json())
}
Directions HGV example (browser)
Note: Nested parameters from the options object are easier accessible like
restrictions,avoidablesandavoid_polygons(cf. API docs)
<script>
window.onload = async function() {
// Add your api_key here
let orsDirections = new Openrouteservice.Directions({ api_key: "XYZ"});
try {
let response = await orsDirections.calculate({
coordinates: [[8.690958, 49.404662], [8.687868, 49.390139]],
profile: 'driving-hgv',
restrictions: {
height: 10,
weight: 5
},
extra_info: ['waytype', 'steepness'],
avoidables: ['highways', 'tollways', 'ferries', 'fords'],
avoid_polygons: {
type: 'Polygon',
coordinates: [
[
[8.683533668518066, 49.41987949639816],
[8.680272102355957, 49.41812070066643],
[8.683919906616211, 49.4132348262363],
[8.689756393432617, 49.41806486484901],
[8.683533668518066, 49.41987949639816]
]
]
},
format: 'json'
})
// Add your own result handling here
console.log("response: ", response)
} catch (err) {
console.log("An error occurred: " + err.status)
console.error(await err.response.json())
}
};
</script>
Geocode examples
// Add your api_key here
const Geocode = new Openrouteservice.Geocode({ api_key: "XYZ"})
try {
let response = await Geocode.geocode({
text: "Heidelberg",
boundary_circle: { lat_lng: [49.412388, 8.681247], radius: 50 },
boundary_bbox: [[49.260929, 8.40063], [49.504102, 8.941707]],
boundary_country: ["DE"]
})
// Add your own result handling here
console.log("response: ", response)
} catch (err) {
console.log("An error occurred: " + err.status)
console.error(await err.response.json())
}
try {
let response_reverse = await Geocode.reverseGeocode({
point: { lat_lng: [49.412388, 8.681247], radius: 50 },
boundary_country: ["DE"]
})
// Add your own result handling here
console.log("response: ", response_reverse)
} catch (err) {
console.log("An error occurred: " + err.status)
console.error(await err.response.json())
}
try {
let response_structured = await Geocode.structuredGeocode({
locality: "Heidelberg"
})
// Add your own result handling here
console.log("response: ", response_structured)
} catch (err) {
console.log("An error occurred: " + err.status)
console.error(await err.response.json())
}
Matrix example
// Add your api_key here
const Matrix = new Openrouteservice.Matrix({ api_key: "XYZ"})
try {
let response = await Matrix.calculate({
locations: [[8.690958, 49.404662], [8.687868, 49.390139], [8.687868, 49.390133]],
profile: "driving-car",
sources: ['all'],
destinations: ['all']
})
// Add your own result handling here
console.log("response: ", response)
} catch (err) {
console.log("An error occurred: " + err.status)
console.error(await err.response.json())
}
Elevation example
// Add your api_key here
const Elevation = new Openrouteservice.Elevation({api_key: "XYZ"})
try {
let response = await Elevation.lineElevation({
format_in: 'geojson',
format_out: 'geojson',
geometry: {
coordinates: [[13.349762, 38.11295], [12.638397, 37.645772]],
type: 'LineString'
}
})
// Add your own result handling here
console.log("response: ", response)
} catch (err) {
console.log("An error occurred: " + err.status)
console.error(await err.response.json())
}
Snap example
// Add your api_key here
const Snap = new Openrouteservice.Snap({api_key: "XYZ"})
try {
let response = await Snap.calculate({
locations: [[8.681495,49.51461],[8.686507,49.41943]],
radius: 300,
profile: 'driving-car',
format: 'json'
})
// Add your own result handling here
console.log("response: ", response)
} catch (err) {
console.log("An error occurred: " + err.status)
console.error(await err.response.json())
}
Optimization example
Or consume Optimization API to solve vehicle routing problems
// Add your api_key here
let Optimization = new openrouteservice.Optimization({api_key: "XYZ"});
try {
let response = await Optimization.optimize({
jobs: [
{
id: 1,
service: 300,
amount: [1],
location: [2.03655, 48.61128],
skills: [1]
},
{
id: 2,
service: 300,
amount: [1],
location: [2.03655, 48.61128],
skills: [2]
},
],
vehicles: [
{
id: 1,
profile: 'driving-car',
start: [2.35044, 48.71764],
end: [2.35044, 48.71764],
capacity: [3],
skills: [1, 2],
}
],
})
// Add your own result handling here
console.log("response: ", response)
} catch (err) {
console.log("An error occurred: " + err.status)
console.error(await err.response.json())
}
Development Setup
Clone the openrouteservice-js repository from GitHub into a development environment of your choice.
git clone https://github.com/GIScience/openrouteservice-js.git
cd openrouteservice-js
# Install the dependencies
npm install
# Make your openrouteservice API key available for tests, examples and dev_app
sh setup.sh <your-api-key>
Start the dev_app for debugging when working with source files:
# runs the app at http://localhost:5173
vite
Now you can either use the devtools of your browser to set breakpoints (e.g. in OrsGeocode)
or create a JavaScript Debug configuration to debug with WebStorm:
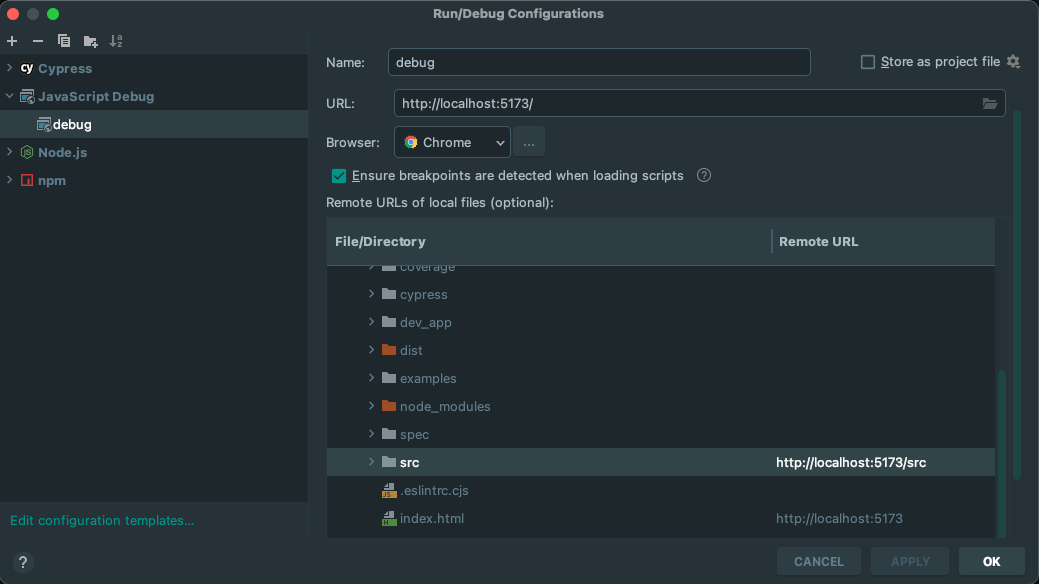
Run the config in debug mode to open the Chrome browser and reload the page after changes for them to take effect immediately.
Running Tests
To run specific unit test files in src/__tests__ on demand during development, run
npm run test:e2e
Choose one of your installed browsers in the cypress UI you want to test in and select the test file you want to run.
Component tests for the web app can be run by switching to component testing.
To run tests without ui use the npm scripts ending with :ci e.g. for unit, component and e2e tests:
npm run test:ci
Commits and versioning
- This app uses the
commitizenplugin to generate standardized commit types/messages. After applying any change in a feature branch, usegit add .and thennpm run commit(instead ofgit commit ...) - The plugin
standard-versionis used to generate changelog entries, version tag and to bump the app version in package.json.
Deployment flow:
- Apply the changes in a feature branch and test it locally
- Once the feature is ready, merge it to
develop, deploy it to the testing environment - Checkout in
main, merge from develop and usenpm run releaseto generate a release. This will generate a new release commit as well as a git tag and an entry in CHANGELOG.md.
For more details about commitizen and standard-version see this article