Awesome
Table of Contents
<!-- TOC depthFrom:2 -->Kuiper
Digital Investigation Platform
What is Kuiper?
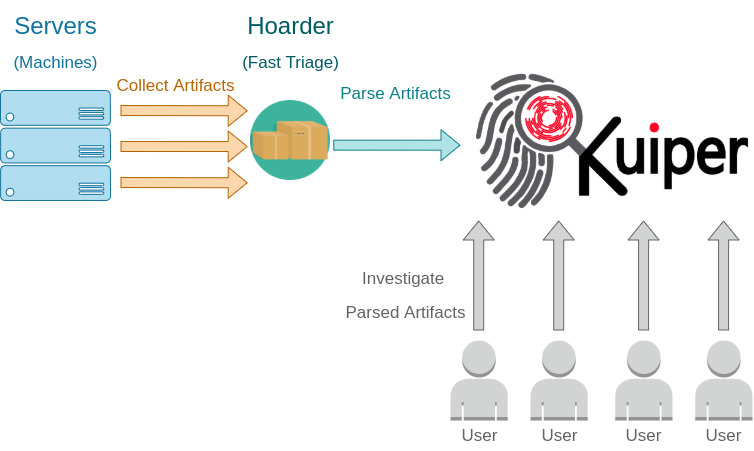
Kuiper is a digital investigation platform that provides a capabilities for the investigation team and individuals to parse, search, visualize collected evidences (evidences could be collected by fast triage script like Hoarder). In additional, collaborate with other team members on the same platform by tagging artifacts and present it as a timeline, as well as setting rules for automating the detection. The main purpose of this project is to aid in streamlining digital investigation activities and allow advanced analytics capabilities with the ability to handle a large amounts of data.
Why Kuiper?
Today there are many tools used during the digital investigation process, though these tools help to identify the malicious activities and findings, as digital analysts there are some shortages that needs to be optimized:
- Speeding the work flow.
- Increase the accuracy.
- Reduce resources exhaustion.
With a large number of cases and a large number of team members, it becomes hard for team members collaboration, as well as events correlation and building rules to detect malicious activities. Kuiper solve these shortages.
How Kuiper Will Help Optimize the Investigation?
- Centralized server: Using a single centralized server (Kuiper) that do all the processing on the server-side reduce the needed hardware resources (CPU, RAM, Hard-disk) for the analysts team, no need for powerful laptop any more. In addition, all evidences stored in single server instead of copying it on different machines during the investigation.
- Consistency: Depending on different parsers by team members to parse same artifacts might provide inconsistency on the generated results, using tested and trusted parsers increases the accuracy.
- Predefined rules: Define rules on Kuiper will save a lot of time by triggering alerts on past, current, and future cases, for example, creating rule to trigger suspicious encoded PowerShell commands on all parsed artifacts, or suspicious binary executed from temp folder, within Kuiper you can defined these rules and more.
- Collaboration: Browsing the parsed artifacts on same web interface by team members boost the collaboration among them using tagging and timeline feature instead of every analyst working on his/her own machine.
Use Cases
- Case creation: Create cases for the investigation and each case contain the list of machines scoped.
- Bulk evidences upload: Upload multiple files (artifacts) collected from scoped machines via Hoarder, KAPE, or files collected by any other channel.
- Evidence processing: Start parsing these artifact files concurrently for selected machines or all.
- Holistic view of evidences: Browse and search within the parsed artifacts for all machines on the opened case.
- Rules creation: Save search query as rules, these rules could be used to trigger alerts for future cases.
- Tagging and timeline: Tag suspicious/malicious records, and display the tagged records in a timeline. For records or information without records (information collected from other external sources such as FW, proxy, WAF, etc. logs) you can add a message on timeline with the specific time.
- Parsers management: Collected files without predefined parser is not an issue anymore, you can write your own parser and add it to Kuiper and will parse these files. read more how to add parser from Add Custom Parser
Examples
Create cases and upload artifacts

Investigate parsed artifacts in Kuiper

Kuiper Components
Components Overview
Kuiper use the following components:
-
Flask: A web framework written in Python, used as the primary web application component.
-
Elasticsearch: A distributed, open source search and analytics engine, used as the primary database to store parser results.
-
MongoDB: A database that stores data in JSON-like documents that can vary in structure, offering a dynamic, flexible schema, used to store Kuiper web application configurations and information about parsed files.
-
Redis: A in-memory data structure store, used as a database, cache and message broker, used as a message broker to relay tasks to celery workers.
-
Celery: A asynchronous task queue/job queue based on distributed message passing, used as the main processing engine to process relayed tasks from redis.
-
Gunicorn: Handle multiple clients HTTPs requests
Getting Started
Requirements
- OS: 64-bit Ubuntu 18.04.1 LTS (Xenial) (preferred)
- RAM: 4GB (minimum), 64GB (preferred)
- Cores: 4 (minimum)
- Disk: 25GB for testing purposes and more disk space depends on the amount of data collected.
- Docker: Docker version 20.10.17
- Docker-Compose: docker-compose version 1.29.2
Notes
- If you want to use RAM more than 64GB to increase Elasticsearch performence, it is recommended to use multiple nodes for Elasticsearch cluster instead in different machines
- For parsing, Celery generate workers based on CPU cores (worker per core), each core parse one machine at a time and when the machine finished, the other queued machines will start parsing, if you have large number of machines to process in the same time you have to increase the cores number
- To install docker and docker-compose on Ubuntu run the following
# Install Docker
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install ca-certificates curl gnupg lsb-release
sudo mkdir -p /etc/apt/keyrings
curl -fsSL https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu/gpg | sudo gpg --dearmor -o /etc/apt/keyrings/docker.gpg
echo "deb [arch=$(dpkg --print-architecture) signed-by=/etc/apt/keyrings/docker.gpg] https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu $(lsb_release -cs) stable" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/docker.list > /dev/null
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io docker-compose-plugin
sudo docker -v
# Install Docker Compose
sudo curl -L "https://github.com/docker/compose/releases/download/1.29.2/docker-compose-$(uname -s)-$(uname -m)" -o /usr/local/bin/docker-compose
sudo chmod +x /usr/local/bin/docker-compose
sudo docker-compose -v
Installation
Starting from version 2.2.0, Kuiper run over dockers, there are 7 docker images:
- Flask: the main docker which host the web application (check docker image).
- Mongodb: stores the cases and machines metadata.
- Elasticsearch (es01): stores the parsed artifacts data.
- Nginx: reverse proxy for the flask container.
- Celery: artifacts parser component check docker image.
- Redis: queue for celery workers
- NFS (Network File System): container that stores the shared files between Flask and Celery containers.
To run the docker use the following command:
sysctl -w vm.max_map_count=262144
git clone https://github.com/DFIRKuiper/Kuiper.git
cd Kuiper
docker-compose pull
docker-compose up -d
Issues
1 - Note: when you first run the dockers, Elasticsearch will fail to run and give the following error
ERROR: [1] bootstrap checks failed
[1]: max virtual memory areas vm.max_map_count [65530] is too low, increase to at least [262144]
To solve the issue run the command
sysctl -w vm.max_map_count=262144
2- Note: if you faced the following issue
Creating network "kuiper_kuiper" with driver "bridge"
Creating kuiper_es01 ... done
Creating kuiper_mongodb ... done
Creating kuiper_redis ... done
Creating kuiper_flask ... error
Creating kuiper_nfs ... done
Creating kuiper_celery ...
ERROR: for kuiper_flask Cannot start service flask: error while mounting volume '/var/lib/docker/volumes/kuiper_kuiper_nfs/_data': failed to mount local volume: mount :/:/var/lib/docker/vCreating kuiper_celery ... done
ERROR: for flask Cannot start service flask: error while mounting volume '/var/lib/docker/volumes/kuiper_kuiper_nfs/_data': failed to mount local volume: mount :/:/var/lib/docker/volumes/kuiper_kuiper_nfs/_data, data: addr=172.30.250.10: permission denied
ERROR: Encountered errors while bringing up the project.
To solve the issue, run the command again
docker-compose up -d
Troubleshooting
To check the dockers, run the command
docker-compose ps -a
It should show the results
Name Command State Ports
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
kuiper_celery /bin/sh -c cron && python ... Up
kuiper_es01 /bin/tini -- /usr/local/bi ... Up 0.0.0.0:9200->9200/tcp,:::9200->9200/tcp, 9300/tcp
kuiper_flask /bin/sh -c cron && gunicor ... Up 0.0.0.0:5000->5000/tcp,:::5000->5000/tcp
kuiper_mongodb docker-entrypoint.sh /bin/ ... Up 0.0.0.0:27017->27017/tcp,:::27017->27017/tcp
kuiper_nfs /usr/bin/nfsd.sh Up 0.0.0.0:2049->2049/tcp,:::2049->2049/tcp
kuiper_nginx /docker-entrypoint.sh ngin ... Up 0.0.0.0:443->443/tcp,:::443->443/tcp, 80/tcp
kuiper_redis docker-entrypoint.sh /bin/ ... Up 0.0.0.0:6379->6379/tcp,:::6379->6379/tcp
if anyone failed, check the logs for the service that failed
docker-compose logs -f --tail=100 <service>
Kuiper API
Kuiper has a limited feature API, check the repo DFIRKuiperAPI.
- GetFieldsScript: Retrieves parsed data from Kuiper.
- UploadMachines: Upload new machine (.zip file) to specific case.
Issues Tracking and Contribution
We are happy to receive any issues, contribution, and ideas.
we appreciate sharing any parsers you develop, please send a pull request to be able to add it to the parsers list.
Licenses
-
Each parser has its own license, all parsers placed in the following folder
/kuiper/parsers/. -
All files in this project under GPL-3.0 license, unless mentioned otherwise.
Creators
Saleh Muhaysin, Twitter (@saleh_muhaysin),
Muteb Alqahtani, Twitter(@muteb_alqahtani)
Abdullah Alrasheed, Twitter(@abdullah_rush)