Awesome
<div id="header" align="center"> </div>Debugger for Mainframe
Debugger for Mainframe provides a debugging interface for InterTest™ for CICS and InterTest™ Batch. This extension provides a modern debugging experience for CICS and Batch programs written in COBOL and High-Level Assembler Language (HLASM).
How can we improve Debugger for Mainframe? Let us know on our Git repository
Debugger for Mainframe is part of Code4z, an all-round VS Code extension package that offers a modern experience for mainframe application developers, including tools for language support, data editing, testing, and source code management. For an interactive overview of Code4z, see the Code4z Developer Cockpit.
Compatibility
Debugger for Mainframe is supported on Visual Studio Code and Github Codespaces.
<a href="https://www.openmainframeproject.org/all-projects/zowe/conformance"><img alt="This extension is Zowe v2 conformant" src="https://artwork.openmainframeproject.org/other/zowe-conformant/zowev2/explorer/color/zowe-conformant-zowev2-explorer-color.png" width=20% height=20% /></a>
Prerequisites
Server
- InterTest for CICS and/or InterTest Batch, incremental release 11.0.07 or higher.
- Acquire and install PTFs LU08488, LU08046, LU06771, LU08177, LU08307, LU11016, LU13684, LU14009 and LU14606.
- To connect to Debugger for Mainframe via the Zowe API Mediation Layer, acquire and install PTF LU11400 in addition to the PTFs above.
- Testing Tools Server
- To use Debugger for Mainframe to debug CICS programs, ensure that you complete the tasks in the sections "Activation of the IP CICS Sockets" and "Set Up an IRC Connection" on the linked page when you configure your Testing Tools Server instance.
- To connect to Debugger for Mainframe via the Zowe API Mediation Layer, integrate your Testing Tools Server instance with the API Mediation Layer
For information on the Testing Tools server and API Mediation Layer, see the InterTest documentation.
Client
- Java version 8.0 or higher with the PATH variable correctly configured. For more information see the Java documentation.
Secure Connection
- Follow the instructions in the Set Up a Secure Connection section below.
IDE
Debugger for Mainframe is supported on Visual Studio Code version 1.67.0 and above.
Integrate with Zowe Explorer
You can integrate Debugger for Mainframe with Zowe Explorer and set up a Zowe profile to access mainframe data sets and track the status of JCL jobs in connection with your debugging sessions. You can also use Zowe Explorer to submit JCL or to edit your converted JCL before running batch debugging sessions.
To enable job status messages, a Zowe profile name must be specified in your configuration file (see the Add Configuration section below).
Zowe Explorer is available as part of the Code4z package.
Getting Started
Debugger for Mainframe includes two walkthroughs to help you become acquainted with key features of the extension. To access the walkthroughs, select Welcome from the Help menu, and select from the options under Walkthroughs - More...
The buttons in these walkthroughs run commands which can otherwise be found in the F1 menu.
Get Started with CICS Debugging
The Get Started with CICS Debugging walkthrough guides you through the steps required to set up and run a basic CICS debugging session. If you do not have a CICS program to run, you can use the Basic COBOL Demo Session which comes shipped with InterTest for CICS.
For more information about the Basic COBOL Demo Session, see the InterTest and SymDump documentation.
See this video for a step-by-step walkthrough of CICS debugging using Debugger for Mainframe.
Basic Batch Demo Session
The Basic Batch Demo Session walkthrough guides you through the Basic Batch Link Demo which comes shipped with InterTest Batch. For more information about the Basic Batch Link Demo, see the InterTest and SymDump documentation.
The demo program, CAMRCOBB, is in the data set CAI.CAVHSAMP. Note that CAI is the default high-level qualifier, and it can be changed during installation, so on your instance of InterTest the HLQ might be different.
Before you run the Basic Batch Demo Session on Debugger for Mainframe, complete the following tasks:
- Allocate a PROTSYM.
- Allocate a LOADLIB.
- Compile CAMRCOBB and link it to the PROTSYM and LOADLIB.
- Locate the step in the demo JCL that runs CAMRCOBB and change the STEPLIB to refer to your LOADLIB. The demo JCL can be found in CAVHJCL(DEMOJCL).
Basic Batch Demo Configuration
During the demo session, you are instructed to fill in a launch.json file with details of your Testing Tools Server and the program that you want to run. Ensure that you add the following parameter, which is not included by default, between "interTestSecure" and "convertedJCL":
"originalJCL": {
"inDSN": "",
"stepName": ""
},
If you connect to InterTest through an Zowe API Mediation Layer gateway, add the line "APIMLServiceID": "", below the "port" parameter.
After you add these optional parameters, the full empty configuration displays as follows:
{
"name": "Debugger for Mainframe: INTERTEST™ FOR BATCH",
"type": "intertest-batch",
"request": "launch",
"programName": [
"PROGNAME"
],
"protsym": [
"PROTSYM"
],
"host": "HOST",
"port": 0,
"APIMLServiceID": "",
"interTestUserName": "USER",
"interTestSecure": true,
"originalJCL": {
"inDSN": "",
"stepName": ""
},
"convertedJCL": ""
}
Populate the fields as follows:
- "programName":
- Replace PROGNAME with CAMRCOBB.
- "protsym":
- Replace PROTSYM with the DSN of the PROTSYM that you linked to CAMRCOBB.
- "host":
- Replace HOST with the address of your Testing Tools Server or Zowe API Mediation Layer Gateway.
- "port":
- Specify the port of your Testing Tools Server or Zowe API Mediation Layer Gateway.
- "APIMLServiceID":
- (API Mediation Layer only) Specify your Zowe API Mediation Layer Service ID. Do not include this field if you connect through a Testing Tools Server instance.
- "interTestUser":
- Replace USER with your mainframe username.
- "interTestSecure":
- Change this to false unless you are using a secure connection. Using a secure connection requires extra configuration steps on both the client and the server side. For more information, see Set Up a Secure Connection.
- "inDSN":
- Specify the data set and member name of your demo JCL, e.g. yourHLQ.CAVHJCL(DEMOJCL).
- stepName":
- Specify the name of the step which launches CAMRCOBB, e.g. STEP1.
- "convertedJCL":
- Specify the full name of a partitioned data set and a member in the format DSN(MEMBER). Debugger for Mainframe creates or overwrites this member when you convert the JCL. For this demo session, we recommend that you create a new member in the same data set where your demo JCL is stored, e.g. yourHLQ.CAVHJCL(CONVJCL).
Using Debugger for Mainframe
To debug CICS and Batch programs with Debugger for Mainframe you open the workspace in your IDE and configure your connection to InterTest using the file launch.json.
Debugged files are temporarily saved in the workspace within the /.c4z/.extsrcs folder.
To debug Batch programs, you also convert the JCL of your program into a new file which is used for debugging.
Create a Configuration File
To start debugging programs in your IDE, you first create a launch.json file within your workspace.
Follow these steps:
-
Select the Explorer icon in your IDE and open a folder.
- The workspace opens.
-
Select the Bug icon to open Debug view.
-
In the sidebar, click create a launch.json file.
A list of configurations displays. -
Select either Debugger for Mainframe: INTERTEST™ FOR CICS or Debugger for Mainframe: INTERTEST™ BATCH
-
Fill in the necessary fields as described in the Add Configuration section below.
Add Configuration
The launch.json file contains configurations for debugging different types of programs. The configurations supported by Debugger for Mainframe are:
- Debugger for Mainframe: INTERTEST™ FOR CICS
Basic configuration for CICS programs. - Debugger for Mainframe: INTERTEST™ BATCH
Basic configuration for Batch programs. - Debugger for Mainframe: INTERTEST™ BATCH - Attach
Configuration to attach Batch programs to the Batch Link Queue.
When you create a launch.json file for the first time, a configuration is added. Click the Add configuration button in the configuration drop-down list to add further configurations.
Basic CICS Configuration
To add a basic CICS configuration, do the following:
- Open your
launch.jsonfile. - Click the Add configuration... button in the bottom-right corner of the tab.
- Select Debugger for Mainframe: INTERTEST™ FOR CICS.
- Populate the following fields:
- "type": (string)
- Specify "intertest-cics".
- "request": (string)
- Specify "launch".
- "name": (string)
- Specifies the name of the debugging session.
- "programName": (array)
- Specifies the name of the program that you want to debug using this configuration. To debug a program along with other programs called within it, specify all program names you want to debug in this field.
- To debug a program that is part of a composite module, use the format MODULE_PROGRAM. To debug all programs in a composite module, specify MODULE_.
- Tip: To see the list of all programs in a composite module, add the module to this field, and run the pallet command List Composites. The list of programs displays in the Output Panel.
- Specify an array with either one value or up to 30 values separated by commas.
- "host": (string)
- Specifies the host address of your Testing Tools Server instance or Zowe API Mediation Layer Gateway.
- "port": (integer)
- Specifies the port number of your Testing Tools Server instance or Zowe API Mediation Layer Gateway.
- "APIMLServiceID": (string)
- (API Mediation Layer only) Specifies your Zowe API Mediation Layer Service ID. Do not include this field if you connect through a Testing Tools Server instance.
- "interTestUserName": (string)
- Specifies your mainframe username.
- "interTestSecure": (boolean)
- Specify "true" to use a secure connection to the InterTest server or "false" to use a non-secure connection.
Ensure that you complete the steps in the Set Up a Secure Connection section if you want to use a secure connection.
- Specify "true" to use a secure connection to the InterTest server or "false" to use a non-secure connection.
- "cicsApplId": (string)
- Specifies the CICS Application ID (cicsApplID) of your CICS region.
- "cicsUserId": (string)
- (Optional) Specify a CICS user logon ID to debug a CICS program or transaction as it executes for that specific ID. You cannot modify this value during an active debugging session.
- "interTestCharset": (string)
- (Optional) Specifies the Testing Tools Server Charset for Listings. Specify this field only if your Testing Tools Server instance is configured to use a client code page other than UTF-8.
- "paragraphBreakpoints": (boolean)
- (Optional) Specify "true" to have the debugging session stop automatically at each new paragraph or label. For more information, see Paragraph Breakpoints.
- "callTrace": (boolean)
- (Optional) Specify "false" to disable the call trace feature. The feature is enabled by default. For more information, see Call Trace and Statement Trace.
- "statementTrace": (boolean)
- (Optional) Specify "false" to disable the statement trace feature. The feature is enabled by default. For more information, see Call Trace and Statement Trace.
- Note: If you disable this parameter, the "step out" and "step over" functions of the debug toolbar are also disabled.
- "variableOrder": (string)
- (Optional) Specify "alphabetical" to sort the variables that are defined in your program in alphabetical order in the variables view. Specify "definition" to sort the variables in the order of their definition in the program. The default setting is "definition".
- Follow the steps in Run a Debug Session to start your debug session.
Basic Batch Configuration
To add a basic configuration to debug a batch application, do the following:
- Open your
launch.jsonfile. - Click the Add configuration... button in the bottom-right corner of the tab.
- Select Debugger for Mainframe: INTERTEST™ FOR BATCH.
- Populate the following fields:
- "type": (string)
- Specify "intertest-batch".
- "request": (string)
- Specify "launch".
- "name": (string)
- Specifies the name of the debugging session.
- "programName": (array)
- Specifies the name of the program that you want to debug using this configuration. To debug a program along with other programs called within it, specify all program names you want to debug in this field.
- Specify an array with either one value or up to 30 values separated by commas.
- "protsym": (array)
- Specify an array with up to 8 PROTSYM DSNs separated by commas. The newest PROTSYM which matches your executable is used for the debug session.
- DSS: (string)
- (Optional) Specify the PROTSYM which is designated to receive dynamic symbolic data from Endevor. For more information, see Dynamic Symbolic Support.
- Note: The DSS PROTSYM counts towards the maximum of 8 PROTSYMs per configuration. If you specify this parameter, the maximum allowed number of PROTSYMs in the "protsym" array is reduced to 7.
- "host": (string)
- Specifies the host address of your Testing Tools Server instance or Zowe API Mediation Layer Gateway.
- "port": (integer)
- Specifies the port number of your Testing Tools Server instance or Zowe API Mediation Layer Gateway.
- "APIMLServiceID": (string)
- (API Mediation Layer only) Specifies your Zowe API Mediation Layer Service ID. Do not include this field if you connect through a Testing Tools Server instance.
- "interTestUserName": (string)
- Specifies your mainframe username.
- "interTestSecure": (boolean)
- Specify "true" to use a secure connection to the InterTest server or "false" to use a non-secure connection.
Ensure that you complete the steps in the Set Up a Secure Connection section if you want to use a secure connection.
- Specify "true" to use a secure connection to the InterTest server or "false" to use a non-secure connection.
- "originalJCL": (JSON)
- (Optional) Specify this parameter if you want Debugger for Mainframe to convert the JCL of your program for debugging.
This is a JSON element containing the following fields:
- "inDSN": (string)
- Specifies the DSN and member name of the JCL containing the program that you want to debug.
- "stepName": (string)
- Specifies the step name of the program that you want to debug.
- "procLibs": (array)
- (Optional) Specify an array with any number of DSNs containing procedure libraries. Specify this field if your JCL requires a procedure library to be converted.
- "inDSN": (string)
- (Optional) Specify this parameter if you want Debugger for Mainframe to convert the JCL of your program for debugging.
This is a JSON element containing the following fields:
- "convertedJCL": (string)
- Specifies the DSN and member name where you want to store your converted JCL. Specify the full name of a partitioned data set and a member in the format DSN(MEMBER). Debugger for Mainframe creates or overwrites this member when you convert the JCL.
- "symbols": (JSON)
- (Optional) Specify values for any number of variables in the converted JCL. Use the format
"PARAM": "VALUE"and separate each entry by commas within this JSON element. - The value on the right side of each entry can use input variables. For more information, see the VS Code documentation.
- (Optional) Specify values for any number of variables in the converted JCL. Use the format
- "interTestCharset": (string)
- (Optional) Specifies the Testing Tools Server Charset for Listings. Specify this field only if your Testing Tools Server instance is configured to use a client code page other than UTF-8.
- "paragraphBreakpoints": (boolean)
- (Optional) Specify "true" to have the debugging session stop automatically at each new paragraph or label. For more information, see Paragraph Breakpoints.
- "statementTrace": (boolean)
- (Optional) Specify "false" to disable the statement trace feature. The feature is enabled by default. For more information, see Call Trace and Statement Trace.
- "executionCounts": (boolean)
- (Optional) Specify "true" to enable the execution counts feature. The feature is disabled by default. For more information, see Execution Counts.
- "variableOrder": (string)
- (Optional) Specify "alphabetical" to sort the variables that are defined in your program in alphabetical order in the variables view. Specify "definition" to sort the variables in the order of their definition in the program. The default setting is "definition".
- "zoweProfileName": (string)
- (Optional) Specify the name of a Zowe profile to enable job status messages when you run your debugging session.
- Follow the steps in Run a Debug Session to start your debug session.
Enable the Batch Link Queue
Enable the Batch Link Queue to add the Suspend and Attach functionalities to your Batch debugging experience. These functionalities allow you to suspend and later resume a debugging session, for example:
- If you need to run two debugging sessions simultaneously and switch between them.
- If you want to start a debugging session on InterTest Batch or the InterTest Batch Eclipse User Interface, and resume it on Debugger for Mainframe.
To enable the Batch Link Queue you add a new configuration to your existing launch.json file, which must already contain at least one intertest-batch configuration.
- Open your
launch.jsonfile. - Click the Add configuration... button in the bottom-right corner of the tab.
- Select Debugger for Mainframe: INTERTEST™ FOR BATCH - Attach.
- Populate the following fields:
- "type": (string)
- Specify "intertest-batch".
- "request": (string)
- Specify "attach".
- "name": (string)
- Specifies the name of the debugging session.
- "programName": (array)
- (Optional) Specifies the name of the program that you want to debug using this configuration. To debug a program along with other programs called within it, specify all program names you want to debug in this field.
- Specify an array with either one value or up to 30 values separated by commas.
- "protsym": (array)
- (Optional) Specify an array with up to 8 PROTSYM DSNs separated by commas. The newest PROTSYM which matches your executable is used for the debug session.
- DSS: (string)
- (Optional) Specify the PROTSYM which is designated to receive dynamic symbolic data from Endevor. For more information, see Dynamic Symbolic Support.
- Note: The DSS PROTSYM counts towards the maximum of 8 PROTSYMs per configuration. If you specify this parameter, the maximum allowed number of PROTSYMs in the "protsym" array is reduced to 7.
- "host": (string)
- Specifies the host address of your Testing Tools Server instance or Zowe API Mediation Layer Gateway.
- "port": (integer)
- Specifies the port number of your Testing Tools Server instance or Zowe API Mediation Layer Gateway.
- "APIMLServiceID": (string)
- (API Mediation Layer only) Specifies your Zowe API Mediation Layer Service ID. Do not include this field if you connect through a Testing Tools Server instance.
- "interTestUserName": (string)
- Specifies your mainframe username.
- "interTestSecure": (boolean)
- Specify "true" to use a secure connection to the InterTest server or "false" to use a non-secure connection.
Ensure that you complete the steps in the Set Up a Secure Connection section if you want to use a secure connection.
- Specify "true" to use a secure connection to the InterTest server or "false" to use a non-secure connection.
- "interTestCharset": (string)
- (Optional) Specifies the Testing Tools Server Charset for Listings. Specify this field only if your Testing Tools Server instance is configured to use a client code page other than UTF-8.
- "paragraphBreakpoints": (boolean)
- (Optional) Specify "true" to have the debugging session stop automatically at each new paragraph or label. For more information, see Paragraph Breakpoints.
- "statementTrace": (boolean)
- (Optional) Specify "false" to disable the statement trace feature. The feature is enabled by default. For more information, see Call Trace and Statement Trace.
- "executionCounts": (boolean)
- (Optional) Specify "true" to enable the execution counts feature. The feature is disabled by default. For more information, see Execution Counts.
- "variableOrder": (string)
- (Optional) Specify "alphabetical" to sort the variables that are defined in your program in alphabetical order in the variables view. Specify "definition" to sort the variables in the order of their definition in the program. The default setting is "definition".
Dynamic Symbolic Support
If you have integrated InterTest with Endevor on the backend, you can activate the dynamic symbolic support feature to dynamically load symbolic data into a PROTSYM. To enable dynamic symbolic support, specify a PROTSYM in the "DSS" parameter of a batch launch or attach configuration. This PROTSYM is searched along with the other PROTSYMs that you specify in the "protsym" array.
For more information about dynamic symbolic support, see the InterTest and SymDump documentation.
Run a Debug Session
After you define your configuration in launch.json, you can run your debug session in the debugging interface.
-
Open the Run and Debug panel.
-
(Batch only, optional) To convert your JCL, press F1 to open the command pallet and run the command Batch: Convert JCL. Complete this step when debugging a program for the first time, or if your program changed since the last debug session.
-
Press F1 to open the command pallet and run the command Fetch Extended Sources.
-
If you have more than one Debugger for Mainframe configuration defined in
launch.json, a list of available configurations displays. Select the name of the configuration that you want to use to fetch your source. -
Enter your mainframe password.
- The expanded source is displayed.
-
Set breakpoints as required. You can set breakpoints before you start the debugging process or as the process is running.
- For more information, see Conditional and Unconditional Breakpoints
-
Set logpoints as required. Logpoints can be used to highlight an issue within the program while it is running, however logpoints do not cause the program to terminate.
- For more information, see Logpoints
-
Click the play icon in the top left of the interface to start the debugging process.
-
(CICS only) Run your program in your CICS region.

You have successfully initiated a debugging session.
- Once the session is running, the debugging session stops at each breakpoint, or if an abend occurs.
- You can use the Continue, Step over, Step into and Step out functions of the IDE Debug Toolbar. The Restart function is not supported.
- To use the Step over and Step out functions during a CICS session, ensure that you enable statement trace in your
launch.jsonfile. - Use the Stop button to terminate the debugging session. If you have a Batch Link Queue (
attach) configuration in yourlaunch.jsonfile, you can use the drop-down arrow to switch between the Stop and the Suspend buttons. Use the Suspend button to temporarily terminate a debug session and add it to the Batch Link Queue, from which you can resume it later. - If you specified a Zowe profile name in the
zoweProfileNamefield oflaunch.json, a message with a batch job ID appears when the session completes. Click the job ID to open information about the job in Zowe Explorer.
Run a Debug Session From the Batch Link Queue
To run a debug session from the Batch Link Queue, ensure that you have an attach configuration in your launch.json file (see Enable the Batch Link Queue for more information.)
- Select an
attachconfiguration from the list of configurations on the Run and Debug panel. - Enter your mainframe password
- Select the session that you want to resume from the drop-down list The listing is downloaded and the debugging session starts.
When you run a debug session using an attach configuration, the Suspend button is shown by default in the Debug Toolbar. Use the drop-down arrow to switch to the Stop button.
When you suspend a debug session, breakpoints that you define in Visual Studio Code are saved with the session. If you load a debug session from the Batch Link Queue that has breakpoints saved, these breakpoints override ones that are defined locally on the same lines.
Manage the Batch Link Schedule Table
You can use Debugger for Mainframe to manage the Batch Link Schedule Table, which enables you to debug DB2 Stored Procedures and IMS DC applications.
To manage your Batch Link Schedule Table, ensure that you have a batch launch or attach configuration containing your Testing Tools Server host and port and your mainframe username. You can leave the programName and protsym fields in this configuration at their default values.
Schedule a DB2 Stored Procedure or IMS DC Application
To debug a DB2 stored procedure or an IMS DC application, you add the appropriate criteria to the Batch Link Schedule Table, from which you can later run it from the Batch Link Queue using an attach configuration.
- Open the F1 menu and select Batch: Show Schedule Table
- Select your batch configuration.
- Enter your mainframe password and press enter.
The Batch Link Schedule Table displays. - Select Add New Schedule Entry.
- Select either DB2 or IMS.
- (Optional) Specify a name for your job and press enter.
- Specify your program name and press enter.
- (IMS only, optional) Specify an IMS transaction ID for the schedule entry and press enter. If you leave this prompt blank, all transactions are processed. This field can be wildcarded and cannot contain more than eight characters.
- (IMS only, optional) Specify an IMS user ID for the schedule entry and press enter. This field can be wildcarded and cannot contain more than eight characters.
The Is this a one-time entry? prompt displays. - Select Yes or No. If you select Yes, the session is deleted from the Batch Link Schedule Table after it is attached to the Batch Link Queue.
The stored procedure is scheduled. To view it in the Batch Link Schedule Table, repeat steps 1 to 3 above.
Delete a Batch Link Schedule Table Entry
- Open the F1 menu and select Batch: Show Schedule Table
- Select your batch configuration.
- Enter your mainframe password and press enter.
The Batch Link Schedule Table displays. - Select the delete icon next to the procedure that you want to delete.
- When prompted select Yes to confirm the deletion. The entry is deleted.
Variables Tree View
Use the VS Code variables tree view to view and edit the value of variables during your debugging session. As well as the regular VS Code functionality, Debugger for Mainframe also enables you to edit the hexadecimal value of a variable.
Variables in the tree view are sorted under the following categories:
- Global
- Shows the last known value of all variables in the program.
- Local
- (COBOL only) Shows the value of all variables on the currently selected line when the debugging session is paused.
- CICS Defined Variables
- (COBOL only, CICS only) Shows the value of all variables defined in the CICS region where your debug session is running.
- General Purpose Registers
- (Assembler only) Shows the content of all 16 General Purpose Registers.
Filter Variables
To find a variable in the variables tree view, click the Filter icon and type a search string in the text box at the top of the interface. The search returns all variables which contain the provided string. To clear an active filter, click the Filter icon.
The filter searches variable names under the Global and CICS Defined Variables headings only.
Edit the Hexadecimal Value of a Variable
To edit the hexadecimal value of a variable, do the following:
- Locate the variable in the variables view.
- Right-click the variable and select Set Value.
- Enter the hexadecimal value in the format <b>0x<i>value</i></b> and press enter.
You can hover over a variable with an invalid format in the edit window to view the hexadecimal value.
Inline Variables View
Enable inline variables view to see the values of all variables on the highlighted line of code inline.
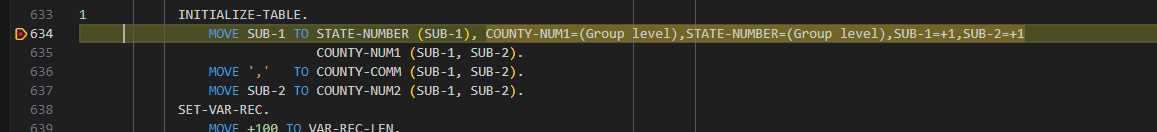
To enable and disable inline variables view, use the following commands in the debug console:
/inline on,/inline off- Enables and disables inline variables view.
Call Trace and Statement Trace
Debugger for Mainframe includes tracing features which send information about statements and programs to the left-hand sidebar of your IDE. There are two tracing features, call trace (for CICS programs only) and statement trace (for CICS and Batch programs).
Call trace displays information about calls from program to program, displaying the logical flow between listings. You can view this information in the Call Stack View in the left-hand sidebar of your IDE.
Statement trace displays information about the statements that you pass during your debug session. You can view this information in the Statement Trace View in the left-hand sidebar of your IDE.
You can click on an entry in the Call Stack or Statement Trace View to move the cursor to the relevant line of the source code file.
Records displayed in both views contain the following information:
- Name of the program
- Number of the last statement processed
- Text of the last statement processed
The call trace and statement trace features are enabled by default. They can be disabled in launch.json before you begin your debug session. For more information, see Add Configuration.
To disable or enable the tracing features during your debug session, use the following commands in the debug console:
/trace on,/trace off- Enables and disables statement trace.
/calltrace on,/calltrace off- Enables and disables call trace.
Conditional and Unconditional Breakpoints
Breakpoints can be unconditional or conditional. Unconditional breakpoints always stop the process at the specified point until they are removed.
Conditional breakpoints contain specified scenarios which trigger the breakpoint, and are formatted as follows:
leftvalue operator rightvalue
Important: Include a space before and after the operator value.
Where:
- leftvalue
- Specifies either a variable or a keyword.
- A variable is any PICTURE value that is contained within the program.
- A keyword is one of the following values: R0, R1, R2, R3, R4, R5, R6, R7, R8, R9, R10, R11, R12, R13, R14, R15, CMAR, CSA, CURR, CWA, CWK, DSA, ITBE, LCL, MXR, MXS, OPFL, PREV, TAL, TGT, TIOA, TWA
- Specifies either a variable or a keyword.
- operator
- Specifies one of the following values: =, <, >, <=, >=, !=
- rightvalue
- Specifies a variable, a keyword, a constant, or a literal.
- A constant is one of the following values: LOW-VALUES, HIGH-VALUES, ZEROES, SPACES
- A literal is a string inside single quotation marks (' ') with a leading value of C, P, H, F or X, which specifies the string format:
- C specifies a string of any type of character. Example: C'ASDF'
- P specifies a positive or negative number. Example: P'-1548'
- H specifies a hexadecimal value which is four characters long. Example: H'A2DF'
- F specifies a hexadecimal value which is eight characters long. Example: F'A86FE567'
- X specifies a hexadecimal value of any length. Example: X'A0DF27'
- Specifies a variable, a keyword, a constant, or a literal.
Correctly defined breakpoints are marked by a red dot.
Incorrectly defined breakpoints are marked by a grey dot or circle, with a summary error message indicating the cause of the error.
You can only use one conditional breakpoint per line.
Data Breakpoints
Data breakpoints are attached to variables and cause the program to stop when the value of the attached variable changes. To set a data breakpoint, right-click a variable in the Variable Tree View and select Break on Value Change.
When you set a data breakpoint in Debugger for Mainframe, a variable-change breakpoint is set on the same variable on the server side. When you set a variable-change breakpoint in InterTest, a data breakpoint is set in Debugger for Mainframe when you load the program listing.
- Note: Due to a known issue, data breakpoints that are set as variable-change breakpoints on InterTest do not show up in the Variables Tree View.
Data breakpoints are valid for one debug session only and must be reset after each use.
Paragraph Breakpoints
Set the launch.json parameter paragraphBreakpoints to "true" to trigger a breakpoint at the beginning of every new paragraph in COBOL code, and every label in Assembler code. For more information, see Add Configuration.
You can also turn this feature on and off in the debugger console by submitting the commands /AT LABEL and /LABEL OFF.
Logpoints
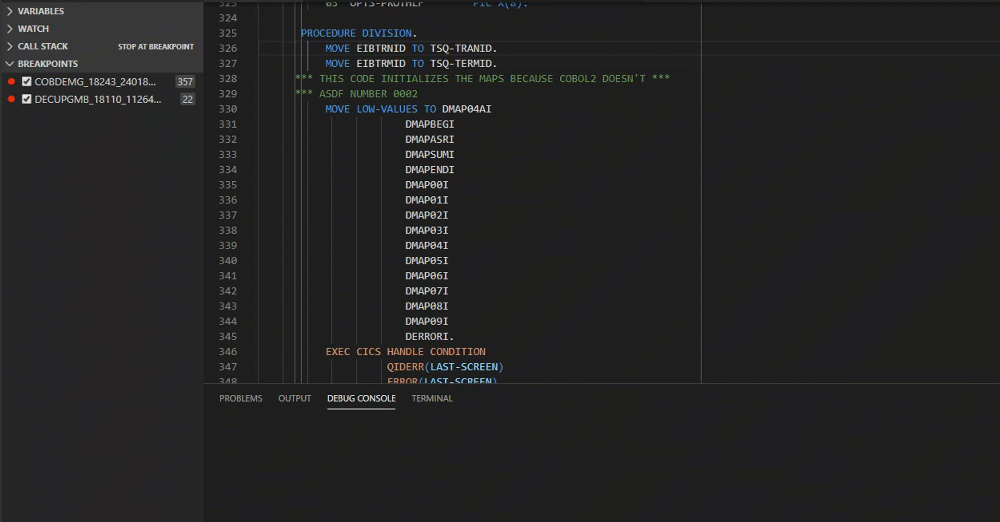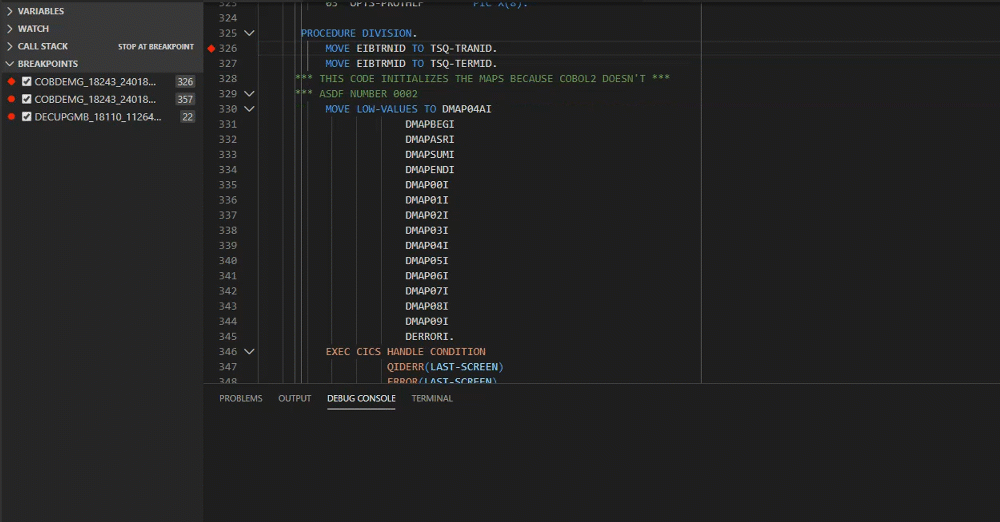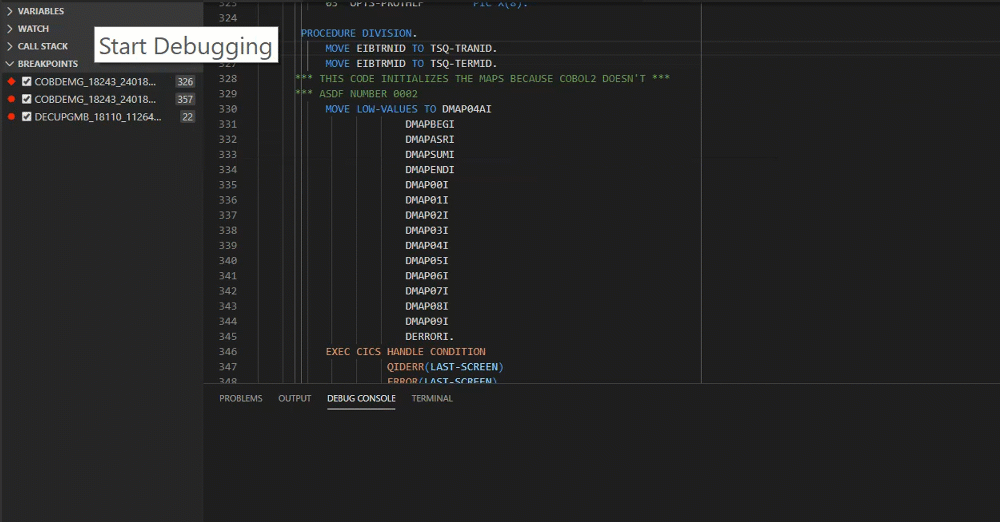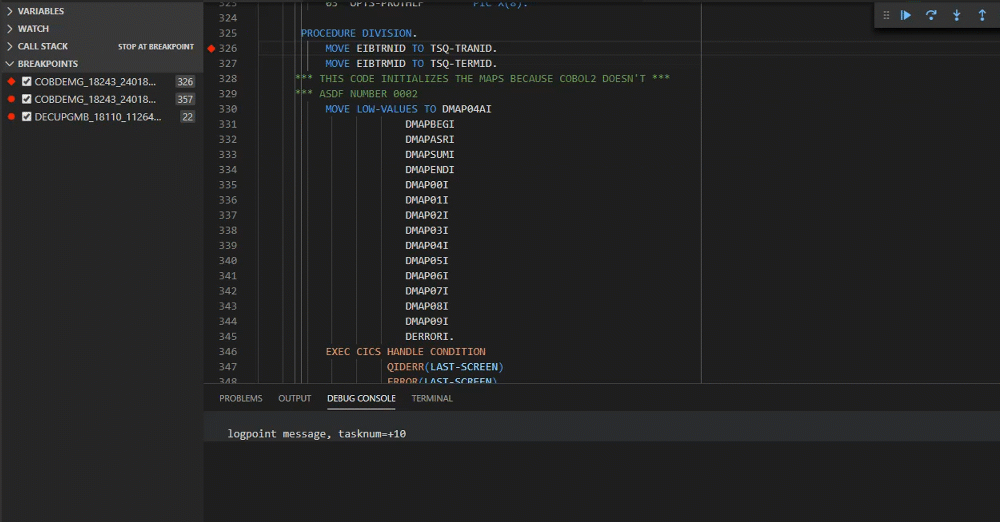
Logpoints mark a particular part of the code, however unlike breakpoints, they do not break or stop the program. Logpoints can highlight an issue within a program while it is running, without causing the program to terminate.
Logpoints can contain text and variables from the code. Enclose the variables in curly brackets without any spaces, as follows:
‘text {variableName} text’
Important: Ensure that the variableName is a single block of text with no spaces and is contained within curly brackets.
The text in the logpoint can be used for detailed observations about the behaviour of the code. The message output from the logpoints is displayed in the debug console.
Logpoints are especially useful as:
- They allow analysis of how the program behaves after this point, and whether the identified issue affects the program and how.
- They allow live analysis while users continue to use functionaility, minimizing costly downtime.
- Logpoints can be added on an ad-hoc basis, with no need to pre-plan, so debugging can be done flexibly according to resource availability.
- Logpoint notes are separate from source code, and require minimal clean-up after debugging is completed.
Execution Counts
Debugger for Mainframe includes an execution count feature which states how many times each line of code is run between each breakpoint or abend in your debugging session. The execution count feature is only supported for Batch programs.
The execution count feature is disabled by default. It can be enabled in launch.json before you begin your debug session. For more information, see Add Configuration.
To enable or disable the execution count feature during your debug session, use the debug console commands /counts on and /counts off. After you submit the /counts on command, perform an action which progresses the debugging session to display the execution count.
The execution count variable is stored on the mainframe and is only reset when you perform an action which progresses the debugging session. It is not reset by the /counts off command or by closing Visual Studio Code.
Set up Secure Connection
You can use Debugger for Mainframe over a secure connection if your Testing Tools Server instance is configured for a secure connection.
To use Debugger for Mainframe over a secure connection, obtain the server certificate for your Testing Tools Server instance and import it to the trust store of the JRE under which the Debugger for Mainframe DA client is running on your local machine. You can use command line or a UI tool.
Import Server Certificate Using Command Line
Enter the following command: sudo keytool -import -alias hostname -file hostname.cer -storetype JKS -keystore cacerts
Import Server Certificate on a Linux Subsystem
- Verify that Java is installed by running the command
java -version. - Locate your subsystem's java installation.
- Go to /lib/security to find cacerts.
- Run the following command to import the certificate:
sudo keytool -import -alias hostname -file hostname.cer -storetype JKS -keystore cacerts
Import Server Certificate using a UI
- In your preferred UI, locate and open cacerts.
- Import the certificate to cacerts.
- Name the certificate with an appropriate alias to ensure it is easily identified.
- Save your changes.
After you have imported your certificate, run a test debug session with "interTestSecure": true in your launch.json file. If the session fails, ensure that you imported the correct certificate to the correct JRE trust store and try again.
You have configured Debugger for Mainframe to use a secure connection to InterTest.
Troubleshooting
Known Limitations
- Conditional breakpoints validator does not work on VS Code version 1.74.
- We currently only support one user on an active debugging session at one time. If multiple users join the same session from the Batch Link Queue, it might affect performance and cause other unwanted issues.
- COBOL table variables defined with the OCCURS X TIMES keyword can only be updated from the variables view, not from the editor.
Enable Troubleshooting Log
To generate a troubleshooting log, add the following parameters to your launch.json file:
- "logLevel":
- Specifies the amount of information reported to the log. Specify one of the following values:
- "SEVERE"
- "WARNING"
- "INFO"
- "CONFIG"
- "FINE"
- "FINER"
- "FINEST"
These values are ordered from returning the least information ("SEVERE"; errors only) to the most information ("FINEST"; all details).
- Specifies the amount of information reported to the log. Specify one of the following values:
- "logOutput":
- Specifies where the log is displayed. Specify one of the following values:
- "console"
- Displays the troubleshooting log on the IDE console.
- "file"
- Stores the troubleshooting log in a file in the
/.c4zfolder in your workspace.
- Stores the troubleshooting log in a file in the
- "console"
- Specifies where the log is displayed. Specify one of the following values:
Technical Assistance and Support for Debugger for Mainframe
The Debugger for Mainframe extension is made available to customers on the Visual Studio Code Marketplace in accordance with the terms and conditions contained in the provided End-User License Agreement (EULA).
If you are on active support for InterTest, you get technical assistance and support in accordance with the terms, guidelines, details, and parameters that are located within the Broadcom Working with Support guide.
This support generally includes:
- Telephone and online access to technical support
- Ability to submit new incidents 24x7x365
- 24x7x365 continuous support for Severity 1 incidents
- 24x7x365 access to Broadcom Support
- Interactive remote diagnostic support
- Technical support cases must be submitted to Broadcom in accordance with guidance provided in “Working with Support”.
Note: To receive technical assistance and support, you must remain compliant with “Working with Support”, be current on all applicable licensing and maintenance requirements, and maintain an environment in which all computer hardware, operating systems, and third party software associated with the affected Broadcom software are on the releases and version levels from the manufacturer that Broadcom designates as compatible with the software. Changes you elect to make to your operating environment could detrimentally affect the performance of Broadcom software and Broadcom shall not be responsible for these effects or any resulting degradation in performance of the Broadcom software. Severity 1 cases must be opened via telephone and elevations of lower severity incidents to Severity 1 status must be requested via telephone.

