Awesome
cmgo
Deriving principle channel metrics from bank and long-profile geometry with the R-package cmgo.
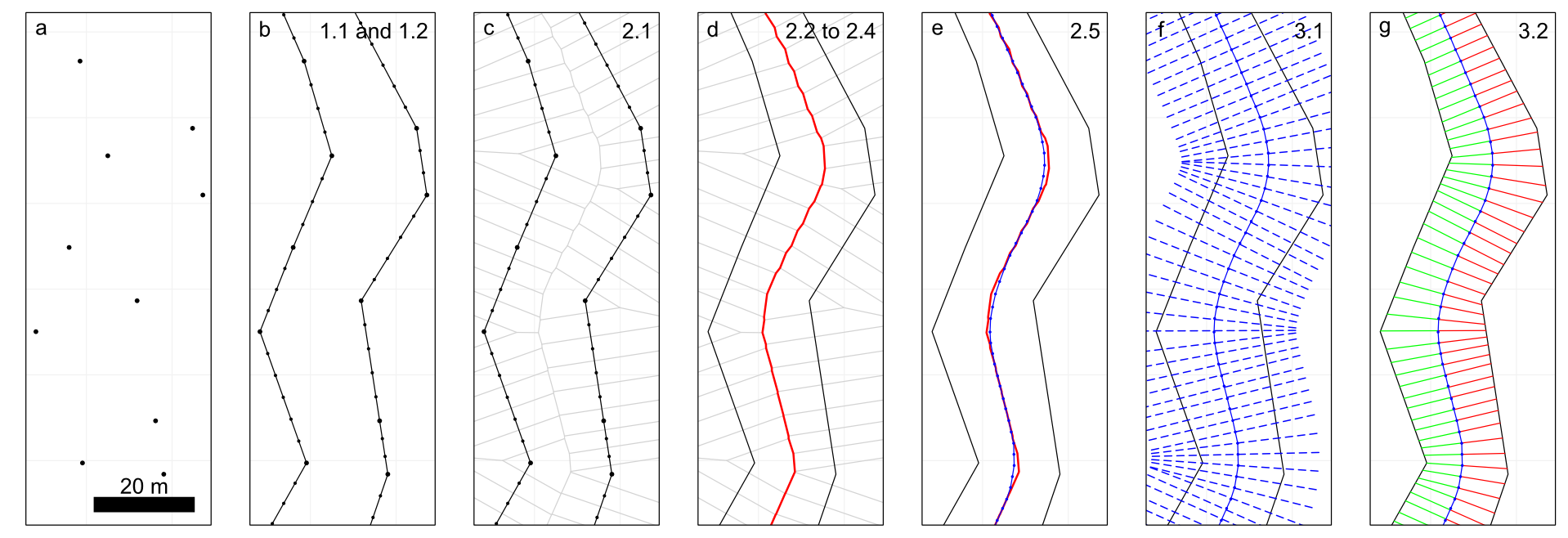 <sup>Figure 1: visualization of the work flow of the package, a) the channel bank points that represent the data input, b) a polygon is generated where bank points are linearly interpolated, c-e) the centerline is calculated via Voronoi polygons, f) transects are calculated, g) the channel width is derived from the transects.</sup>
<sup>Figure 1: visualization of the work flow of the package, a) the channel bank points that represent the data input, b) a polygon is generated where bank points are linearly interpolated, c-e) the centerline is calculated via Voronoi polygons, f) transects are calculated, g) the channel width is derived from the transects.</sup>
What is cmgo?
cmgo performs geometrical calculations on your channel bank points (Fig. 1.a), which represent your basic input. The calculated geometry includes the centerline (Fig. 1.e) of one or multiple given channel shapes, channel length, local and average channel width, local and average slope, local and average bank retreat, or the distances from the centerline to the banks respectively, as well as allows to project additional spatial metrics to the centerline.
Motivation
Computer-aided products for studying rivers have a long tradition and numerous efforts exist to derive principle channel metrics from remote or in-situ measurements of channel banks. In Golly et al. 2017b we compare numerous tools for analyzing river geometry and conclude that cmgo adds a unique value to the available approaches by providing a tool for objectively deriving channel metrics, while being easy and free to use and modify and allowing a high degree of parametrization and fine-tuning.
License / Citation
The program is free to use, modify and redistribute under the terms of the GNU General Public License version 3 as published by the Free Software Foundation. If you make use of the work, please cite the work as follows:
Golly, A. and Turowski, J. M.: Deriving principal channel metrics from bank and long-profile geometry with the R package cmgo, Earth Surf. Dynam., 5, 557-570, https://doi.org/10.5194/esurf-5-557-2017, 2017.
Find the paper at ESURF.
Installation
Get, install and open R and run the following code in the R console:
# install devtools
install.packages("devtools")
# load the devtool package
library(devtools)
# installation (required only once)
install_github("AntoniusGolly/cmgo")
Run cmgo
# include the package (required for every start of an R session)
library(cmgo)
# set your working directory
setwd("d:/your_folder") # in that folder an "input" folder must exist which contains one or more files with point data
# load parameter
par = CM.par()
par$bank.interpolate.max.dist = 4 # set roughly to your expected channel width
# load data assuming your file is lying in directory "input"
cmgo.obj = CM.ini(NULL, par)
# Generate a polygon from input data and plot // Fig. 1b
cmgo.obj = CM.generatePolygon(cmgo.obj)
# Generate the voronoi polygons and calculate the centerlin // Fig. 1c-e
cmgo.obj = CM.calculateCenterline(cmgo.obj)
# Process the centerline (generate width) // Fig. 1f-g
cmgo.obj = CM.processCenterline(cmgo.obj)
Input data
You can find more info on how the data is structured typing $ ?CM.ini which is the function to initialize the main object. It will expect a file ./input/*, relative to your working directory. Note, the filename is not important as all files in that folder will be read in.
The file by default should have this structure, where POINT_X and POINT_Y are ortorectified coordinates. The data can be either collected during field surveys with GPS or total stations or through remote sensing techniques with further digitizing for example in a GIS. The input can be given in any ASCII table format. By default, the program expects tab-delimited columns of a table with one header line with the header names Names (for the side) and POINT_X/_Y/Z (the coordinates of the bank points) where the z component is optional. The expected column names and tab delimiters are set in the parameters (see documentation of CM.par() for details). The order of the points can be either all right bank points first or all left bank points first but not mixed.
Name POINT_X POINT_Y
right 401601.0819 3106437.335
right 401586.5327 3106406.896
right 401568.3238 3106383.586
right 401558.4961 3106364.129
...
left 401621.4337 3106431.134
left 401602.9913 3106405.991
left 401574.6073 3106352.232
left 401582.2671 3106323.134
...
If you seek to change column names, column delimiters or alike, please check the default parameters and adapt them $ ?CM.par
FAQ
For support and common technical fails please see the FAQ
Documentation
# package documentation
?cmgo
# function documentation
?cmgo.run # e.g. for the docu of cmgo.run()