Awesome
PhilEO BENCH: EVALUATING GEO-SPATIAL FOUNDATION MODELS
Table Of Contents
- Introduction
- Evaluation framework
- Downstream Dataset
- Getting Started!
- Model Weights
- Acknowledgements
Introduction <a name="introduction"></a>
This repository introduces the PhilEO Bench, a novel evaluation framework
for EO Foundation Models. In an attempt to address the need to evaluate different Foundation Models on a fair and uniform benchmark, the framework comprises of a
testbed and a novel 400GB Sentinel-2 dataset containing labels for the three downstream tasks of building density estimation,
road segmentation, and land cover classification. We present
experiments using our framework evaluating several different Foundation Models, including Prithvi and SatMAE, at multiple n-shots and convergence rates.
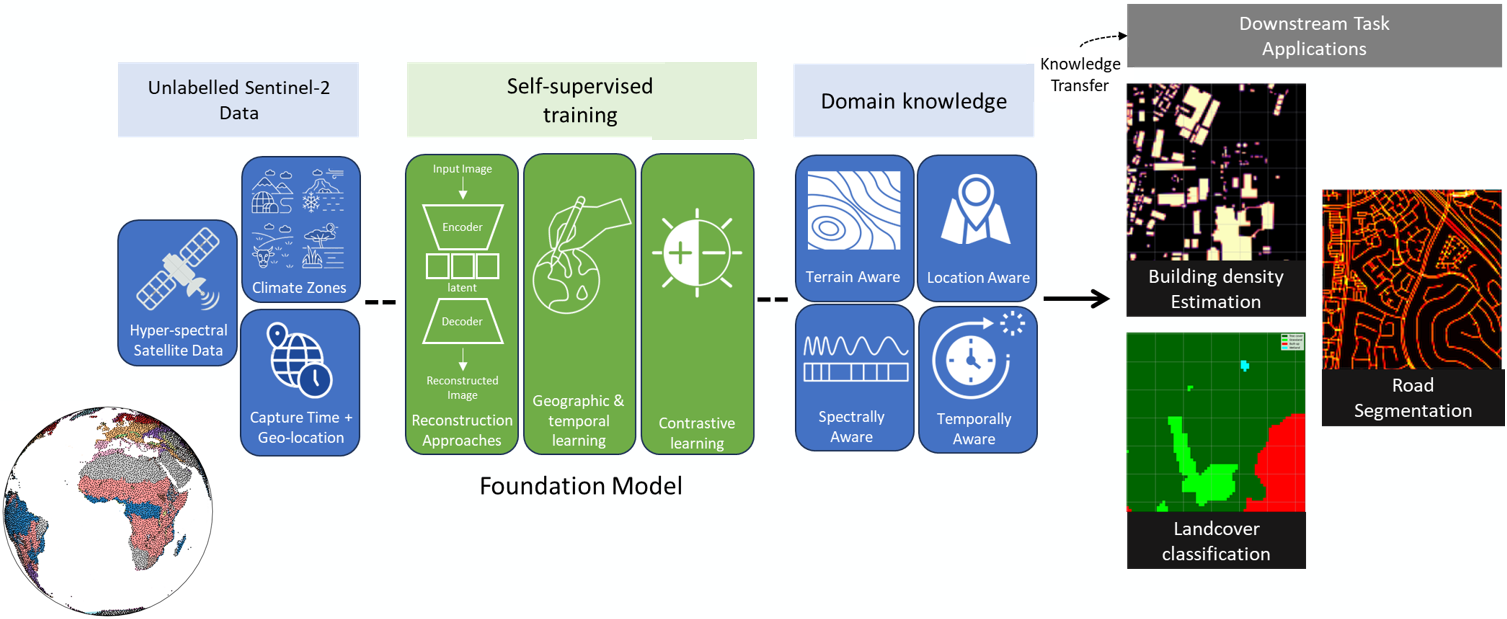
Evaluation framework <a name="framework"></a>
One of the biggest challenges in evaluating FMs is disentangling the performance impact of various factors such as: model architectures, pre-training tasks, and downstream task training data. The effectiveness of a FM can be measured by the quality of its latent representations, and how the key features learnt through the process of pre-training can boost downstream task performance. Hence, to provide a fair comparison between different FMs within our evaluation framework, we minimize the impact of confounding variables by providing: (1) consistent and repeatable training and evaluation datasets, and (2) a common downstream task head for all the pre-trained models.
-
Dataset creation: To minimize the impact of variability in the downstream task datasets, a common hold out Test Set for each downstream task was created providing comparable results across all evaluated models. A data partitioning script is also provided that allows for the creation of smaller subsets (n-shot or percentage split) from the full Phileo, Downstream Task training dataset enabling us to evaluate the impact of training set size on model performance. The indexes of training samples used are automatically saved. Hence, different models can be trained on the identical sub-datasets.
-
One head to rule them all: To minimize the impact of different decoder heads on the downstream task performance, we propose the use of a common decoder head. The latent representations of each of the FMs are fed to a similar decoder. Hence, the comparable performance of a model is a consequence of the effectiveness of the pre-training task and the representational strength of its latent space. For segmentation downstream tasks, we use a multi-convolution decoder based on the U-Net design. For some models, it is required to up-sample or down-sample the features to achieve the desired output image size. For classification downstream tasks, a linear decoder is used. For ViT models, the cls token is used as the input to the linear decoder.
Our framework supports two training configurations: (1) Fine-tuning, which allows for updating of all downstream task model weights including the FM encoder, and (2) Linear probing, where only the decoder head weights are updated, freezing the FM encoder parameters. Phileo, also contains U-Net, Mixer, and ViT architectures. Phileo, supports pre-trained models such as Masked Auto-Encoder (MAE) ViT, and Pre-trained U-Nets, as well as the models Prithvi, SatMAE, and SeCo. In addition, the testbed should be flexible and easy to use. Hence, an Object Oriented Programming approach is used with an emphasis on modularity, allowing for the easy addition of other downstream tasks, architectures, and pre-trained models.
Downstream Dataset <a name="data"></a>
The PhilEO dataset is a 400 GB global dataset of S2 images and has labels for roads, buildings, and land cover, where these are the three downstream tasks. The data is sampled from geographically diverse regions around the globe including: Denmark, East Africa, Egypt, Guinea, Europe, Ghana, Israel, Japan, Nigeria, North America, Senegal, South America, Tanzania, and Uganda. Each region has up to 200 tiles of varying sizes. Some locations have been revisited up to 3 times. The data contain 11 bands at 10m resolution in the following order: 0-SCL, 1-B02, 2-B03, 3-B04, 4-B08, 5-B05, 6-B06, 7-B07, 8-B8A, 9-B11, and 10-B12 where SCL is the Scene Classification Layer. As shown in the figure, each S2 tile in PhilEO has a label for each of the downstream tasks:
- ROADS: The labels are expressed as a number of squared meters of roads in a given pixel. The values are between 0 and 100, and for a resolution of 10m, this reflect the percentage of coverage.
- BUILDINGS: The labels are expressed as squared me- ters of buildings. The values are between 0 and 100. For 10m resolution, this reflect the coverage (in %).
- LANDCOVER: Land cover labels are taken from ESA World Cover3: 11 classes, e.g. tree cover and built-up
PhilEO Dataset Resources
The data preprocessing scripts can be found here.
The dataset can be found here
Getting Started! <a name="getstarted"></a>
Enviorment
conda env create -f environment.yml
Usage
python training_script.py [--experiment_name EXPERIMENT_NAME] --model_name
{baseline_cnn,core_unet_base,core_unet_large,core_unet_huge,mixer_base,mixer_large,mixer_huge,linear_vit_base,linear_vit_larger,linear_vit_huge,autoencoder_vit_base,autoencoder_vit_large,autoencoder_vit_huge}
[--lr LR] [--batch_size BATCH_SIZE] [--epochs EPOCHS] [--early_stop EARLY_STOP] [--lr_scheduler {None,reduce_on_plateau,cosine_annealing}] [--warmup] [--device DEVICE] [--num_workers NUM_WORKERS]
[--vis_val] --downstream_task {roads,building,lc} [--input_channels INPUT_CHANNELS] --input_size INPUT_SIZE --output_channels OUTPUT_CHANNELS
[--regions {None,denmark-1,denmark-2,east-africa,egypt-1,eq-guinea,europe,ghana-1,isreal-1,isreal-2,japan,nigeria,north-america,senegal,south-america,tanzania-1,tanzania-2,tanzania-3,tanzania-4,tanzania-5,uganda-1}]
[--n_shot N_SHOT] [--split_ratio SPLIT_RATIO] [--augmentations][--pretrained_model_path][--freeze_pretrained]
or python training_script.py --read_yaml=default_args.yml
Experiment Script Usage
Trains a series of models (for a specific downstream task) on variouse training dataset sizes and plots the test loss vs number of training samples.
python p_split_experiment.py [--experiment_name EXPERIMENT_NAME] --model_name
{baseline_cnn,core_unet_base,core_unet_large,core_unet_huge,mixer_base,mixer_large,mixer_huge,linear_vit_base,linear_vit_larger,linear_vit_huge,autoencoder_vit_base,autoencoder_vit_large,autoencoder_vit_huge}
[--lr LR] [--batch_size BATCH_SIZE] [--epochs EPOCHS] [--early_stop EARLY_STOP] [--lr_scheduler {None,reduce_on_plateau,cosine_annealing}] [--warmup] [--device DEVICE] [--num_workers NUM_WORKERS]
[--vis_val] --downstream_task {roads,building,lc} [--input_channels INPUT_CHANNELS] --input_size INPUT_SIZE --output_channels OUTPUT_CHANNELS
[--regions {None,denmark-1,denmark-2,east-africa,egypt-1,eq-guinea,europe,ghana-1,isreal-1,isreal-2,japan,nigeria,north-america,senegal,south-america,tanzania-1,tanzania-2,tanzania-3,tanzania-4,tanzania-5,uganda-1}]
[--n_shot N_SHOT] [--split_ratio SPLIT_RATIO] [--augmentations][--pretrained_model_path][--freeze_pretrained]
python n_shot_experiment.py [--experiment_name EXPERIMENT_NAME] --model_name
{baseline_cnn,core_unet_base,core_unet_large,core_unet_huge,mixer_base,mixer_large,mixer_huge,linear_vit_base,linear_vit_larger,linear_vit_huge,autoencoder_vit_base,autoencoder_vit_large,autoencoder_vit_huge}
[--lr LR] [--batch_size BATCH_SIZE] [--epochs EPOCHS] [--early_stop EARLY_STOP] [--lr_scheduler {None,reduce_on_plateau,cosine_annealing}] [--warmup] [--device DEVICE] [--num_workers NUM_WORKERS]
[--vis_val] --downstream_task {roads,building,lc} [--input_channels INPUT_CHANNELS] --input_size INPUT_SIZE --output_channels OUTPUT_CHANNELS
[--regions {None,denmark-1,denmark-2,east-africa,egypt-1,eq-guinea,europe,ghana-1,isreal-1,isreal-2,japan,nigeria,north-america,senegal,south-america,tanzania-1,tanzania-2,tanzania-3,tanzania-4,tanzania-5,uganda-1}]
[--n_shot N_SHOT] [--split_ratio SPLIT_RATIO] [--augmentations][--pretrained_model_path][--freeze_pretrained]
python n_shot_experiment_classifier.py [--experiment_name EXPERIMENT_NAME] --model_name
{baseline_cnn,core_unet_base,core_unet_large,core_unet_huge,mixer_base,mixer_large,mixer_huge,linear_vit_base,linear_vit_larger,linear_vit_huge,autoencoder_vit_base,autoencoder_vit_large,autoencoder_vit_huge}
[--lr LR] [--batch_size BATCH_SIZE] [--epochs EPOCHS] [--early_stop EARLY_STOP] [--lr_scheduler {None,reduce_on_plateau,cosine_annealing}] [--warmup] [--device DEVICE] [--num_workers NUM_WORKERS]
[--vis_val] --downstream_task {roads,building,lc} [--input_channels INPUT_CHANNELS] --input_size INPUT_SIZE --output_channels OUTPUT_CHANNELS
[--regions {None,denmark-1,denmark-2,east-africa,egypt-1,eq-guinea,europe,ghana-1,isreal-1,isreal-2,japan,nigeria,north-america,senegal,south-america,tanzania-1,tanzania-2,tanzania-3,tanzania-4,tanzania-5,uganda-1}]
[--n_shot N_SHOT] [--split_ratio SPLIT_RATIO] [--augmentations][--pretrained_model_path][--freeze_pretrained]
Some of Our Experimental Results


Parameters
-- experiment_name (str): Experiment name
-- downstream_task (str): Select downstream task to test, validate and test on.
Options: ['lc', 'building', 'roads',
'lc_classification', 'building_classification', 'roads_classification']
-- model_name (str): Select model.
Options: CNN_LIST = ['baseline_cnn', 'core_unet_nano','core_unet_tiny','core_unet_base', 'core_unet_large', 'core_unet_huge',
'core_vae_nano', 'resnet_imagenet', 'resnet', 'core_encoder_nano', 'resnet_imagenet', 'resnet',]
VIT_CNN_LIST = ['vit_cnn_base', 'vit_cnn_base_wSkip']
MIXER_LIST = ['mixer_nano', 'mixer_tiny', 'mixer_base', 'mixer_large', 'mixer_huge']
VIT_LIST = ['linear_vit_base', 'linear_vit_larger', 'linear_vit_huge','autoencoder_vit_base',
'autoencoder_vit_large', 'autoencoder_vit_huge']
CNN_PRETRAINED_LIST = ['GeoAware_core_nano', 'GeoAware_core_tiny', 'GeoAware_mixer_nano', 'GeoAware_mixer_tiny',
'GeoAware_contrastive_core_nano', 'GeoAware_mh_pred_core_nano', 'GeoAware_combined_core_nano',
'GeoAware_core_autoencoder_nano', 'seasonal_contrast']
VIT_CNN_PRETRAINED_LIST = ['prithvi', 'SatMAE', 'vit_cnn', 'vit_cnn_gc']
N.B. Some models have classification variants e.g. 'resnet_imagenet_classifier'
-- augmentations (bool, optional): Toggle on/off basic data augmentations (Rotation, Mirror, Noise). Defaults to False.
-- batch_size (int, optional): Define training batch size. Defaults to 16.
-- model_device (_type_, optional): Select model device. Defaults to torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu').
-- generator_device (_type_, optional): Select dataloader device. Defaults to torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu').
-- num_workers (int, optional): Select number of workers for dataloader. Defaults to 4.
-- early_stop (int, optional): Define early stoping patience. Defaults to 25.
-- epochs (int, optional): Define number of training epochs. Defaults to 250.
-- input_channels (int, optional): Define number of data input channels. Defaults to 10.
-- output_channels (int, optional): Define number of model output channels. Defaults to 1.
-- input_size (int, optional): Define data input size. Defaults to 128.
-- lr (float, optional): Define optimizer learning rate. Defaults to 0.001.
-- lr_scheduler (str, optional): Define learning rate scheduler. Options: [None, 'reduce_on_plateau', 'cosine_annealing']. Defaults to None.
-- n_shot (int, optional): Define dataset protocol - n samples per region. Defaults to None.
-- split_ratio (float, optional): Define dataset protocol - percentage of full dataset. Defaults to 0.1.
-- regions (list, optional): Select regions to include in training and test sets. If no regions are defined (None) all avalible regions will be included
Options: [None, 'denmark-1', 'denmark-2', 'east-africa', 'egypt-1', 'eq-guinea', 'europe', 'ghana-1',
'isreal-1', 'isreal-2', 'japan', 'nigeria', 'north-america', 'senegal', 'south-america',
'tanzania-1', 'tanzania-2', 'tanzania-3', 'tanzania-4', 'tanzania-5', 'uganda-1'] Defaults to None.
-- vis_val (bool, optional): If set to True data visulisations will be generated at each validation step. Defaults to True.
-- warmup (bool, optional): If set to True a linear optimizer warmup phase will occour. Defaults to False.
-- warmp_steps (int, optional): Define number of steps for linear warmup phase. Defaults to 5.
-- warmup_gamma (int, optional): Define learning rate increase per step in linear warmup phase - new_lr = lr*gamma. Defaults to 10.
N.B. initial lr is calulated as follows init_lr = lr/(gamma**warmup_steps)
-- pretrained_model_path (str, optional): For pretrained models define the model weights path. Defaults to None.
-- freeze_pretrained (bool, optional): If True pretrained encoder weights will be frozen during training. Defaults to None.
-- data_path_128_10m (str, optional): Define data path for 128x128 10m resolution dataset. Defaults to None.
-- data_path_224_10m (str, optional): Define data path for 224x224 10m resolution dataset. Defaults to None.
-- data_path_224_30m (str, optional): Define data path for 224x224 30m resolution dataset. Defaults to None.
-- output_path (str, optional): Define folder to save artifacts in. Defaults to None.
-- data_parallel (bool, optional): If set to True Model training will be parallized on multiple gpus. Defaults to False.
-- device_ids (list, optional): Define GPU IDs to use for parallization. Defaults to None.
Main files
The main file in this GitHub repository is "training_script.py". - The Jupyter Notebook is "demo.ipynb".
Project webpage
The main project webpage is PhilEO-Bench.
The paper is in arXiv-PhilEO.
Model Weights <a name="model_weights"></a>
:bell: ALL models are available for non-commercial research purposes only.
| Model | Architecture | Link |
|---|---|---|
| Prithvi | Masked-AutoEncoder ViT | Prithvi_100M |
| SatMAE | Masked-AutoEncoder ViT | pretrain-vit-large-e199 |
| SeCo | Resnet-50 | SeCo-1M |
| Phileo-ViT | Masked-AutoEncoder ViT | MaskedAutoencoderViT |
| Phileo-ViT-Grouped-Channels | Masked-AutoEncoder ViT | MaskedAutoencoderGroupChannelViT |
| Phileo-GeoAware-MvMF | UNET-Encoder | GeoAware-MvMF |
| Phileo-GeoAware-PseudoContrastive | UNET-Encoder | GeoAware-PseudoContr |
| Phileo-GeoAware-MultiheadPred | UNET-Encoder | GeoAware-MH |
Acknowledgements <a name="acknowledgements"></a>
Some code from this repository is inspired by:
If you use our code, please cite:
Casper Fibaek, Luke Camilleri, Andreas Luyts, Nikolaos Dionelis, and Bertrand Le Saux, “PhilEO Bench: Evaluating Geo-Spatial Foundation Models,” arXiv:2401.04464, 2024.
@misc{fibaek2024PhilEO,
title = "PhilEO Bench: Evaluating Geo-Spatial Foundation Models",
author = "Casper Fibaek and Luke Camilleri and Andreas Luyts and Nikolaos Dionelis and Bertrand Le Saux",
eprint = {arXiv:2401.04464},
year = 2024
}